Notice
La Dynamique du lapin
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
Série Dynamique Holomorphe.
Les différents domaines mathématiques ne se prêtent que rarement à l'expression audiovisuelle, souvent en raison de la difficulté ou de la non-pertinence de visualiser. La dynamique holomorphe est l'une des exceptions, et peut offrir des images remarquables, à la fois supports et objets même d'étude. Plus encore, il y a des phénomènes pour lesquels le mathématicien a une vision très directe qu'il est difficile, voire pratiquement impossible de communiquer par les moyens classiques. Encore faut-il produire effectivement les images, et élaborer le contexte de leur présentation.
Thème
Documentation
Distinctions
Grand prix Investigation au 2ème Festival du film de chercheur de Nancy 1997.
Vinci d'excellence du prix LVMH Sciences pour l'art 1997.
Sur le même thème
-
« Traitement et analyse des données au sein d'une chaîne éditoriale » (mars 2022)
PorteGuillaumeHeidenSergePrésentées conjointement, ces deux briques de la chaîne sont en effet intimement liées. Via la présentation de certains outils, nous verrons comment l’enrichissement d’un document numérique à l’aide
-
Initiation à l’analyse de réseaux
Ruiz FaboPabloLes réseaux constituent une structure pratique pour représenter des données relationnelles de façon à donner un aperçu de groupes et interactions.
-
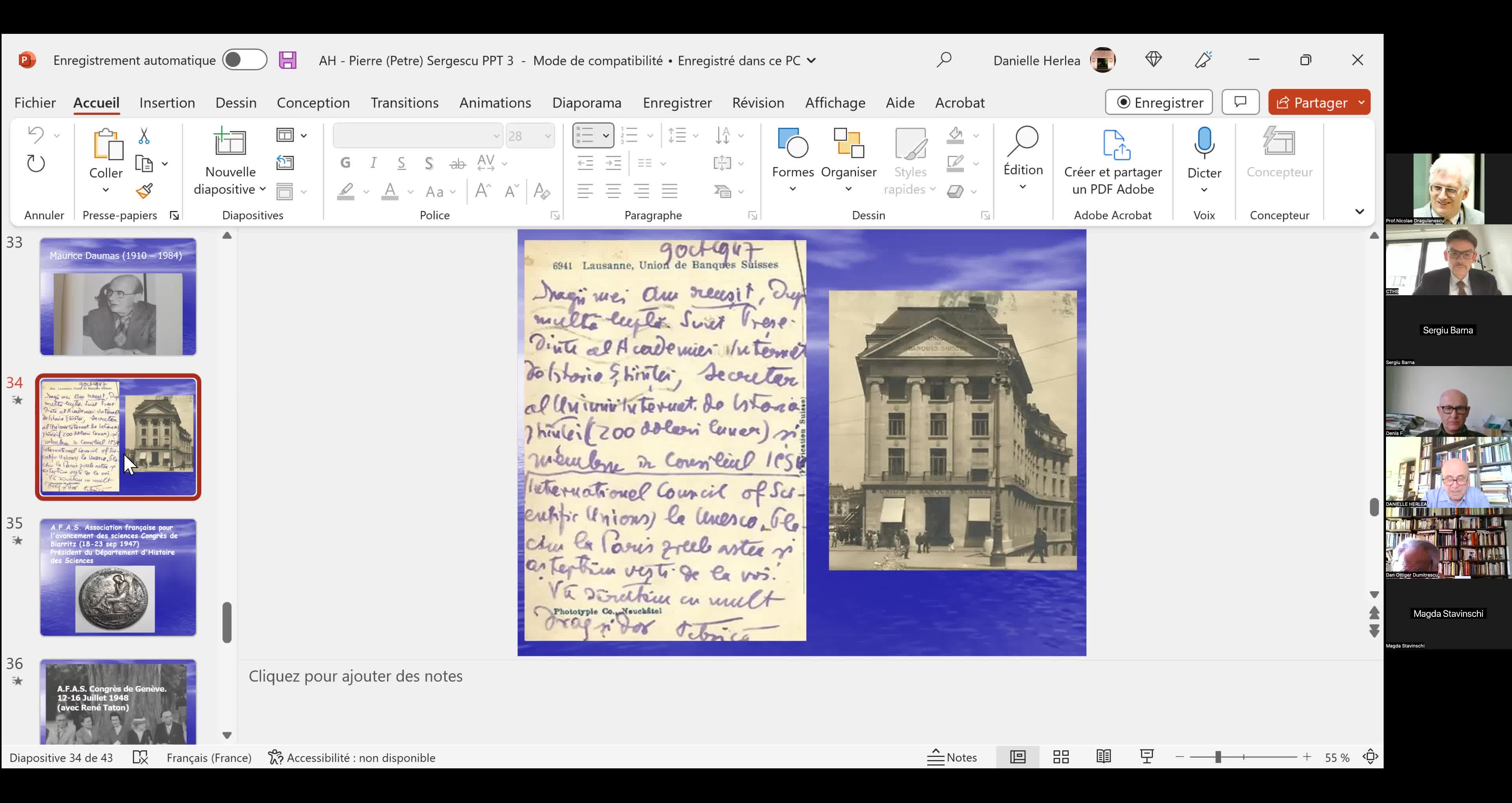
"Le mathématicien Petre (Pierre) Sergescu, historien des sciences, personnalité du XXe siècle"
HerléaAlexandreAlexandre HERLEA est membre de la section « Sciences, histoire des sciences et des techniques et archéologie industrielle » du CTHS. Professeur émérite des universités, membre effectif de l'Académie
-
Webinaire sur la rédaction des PGD
LouvetViolaineRédaction des Plans de Gestion de Données (PGD) sous l’angle des besoins de la communauté mathématique.
-
Aurel PAGE - Cohomology of arithmetic groups and number theory: geometric, asymptotic and computati…
PageAurel regisIn this lecture series, the first part will be dedicated to cohomology of arithmetic groups of lower ranks (e.g., Bianchi groups), their associated geometric models (mainly from hyperbolic geometry)
-
Phong NGUYEN - Recent progress on lattices's computations 2
NguyenPhong Q.This is an introduction to the mysterious world of lattice algorithms, which have found many applications in computer science, notably in cryptography. We will explain how lattices are represented by
-
Zachary Himes - On not the rational dualizing module for $\text{Aut}(F_n)$
Bestvina--Feighn proved that $\text{Aut}(F_n)$ is a rational duality group, i.e. there is a $\mathbb{Q}[\text{Aut}(F_n)]$-module, called the rational dualizing module, and a form of Poincar\'e duality
-
Tobias Moede - Coclass theory for nilpotent associative algebras
The coclass of a finite p-group of order p^n and class c is defined as n-c. Using coclass as the primary invariant in the investigation of finite p-groups turned out to be a very fruitful approach.
-
Oussama Hamza - Hilbert series and mild groups
Let $p$ be an odd prime number and $G$ a finitely generated pro-$p$ group. Define $I(G)$ the augmentation ideal of the group algebra of $G$ over $F_p$ and define the Hilbert series of $G$ by: $G(t):
-
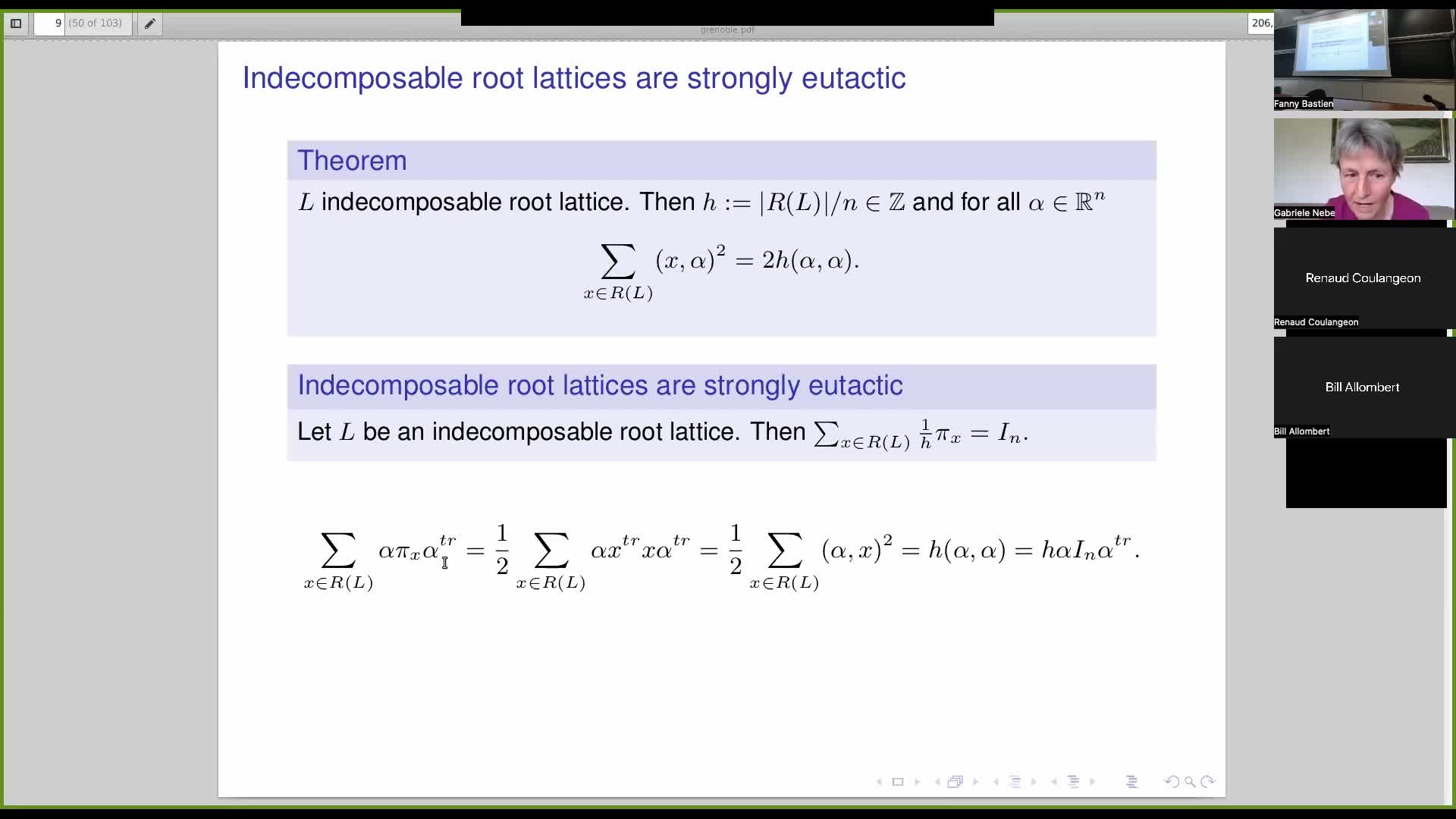
Gabriele NEBE - Lattices, Perfects lattices, Voronoi reduction theory, modular forms, computations …
NebeGabrieleThe talks of Coulangeon will introduce the notion of perfect, eutactic and extreme lattices and the Voronoi's algorithm to enumerate perfect lattices (both Eulcidean and Hermitian). The talk of Nebe
-
Alexander HULPKE - Computational group theory, cohomology of groups and topological methods 4
The lecture series will give an introduction to the computer algebra system GAP, focussing on calculations involving cohomology. We will describe the mathematics underlying the algorithms, and how to
-
Alexander HULPKE - Computational group theory, cohomology of groups and topological methods 5
The lecture series will give an introduction to the computer algebra system GAP, focussing on calculations involving cohomology. We will describe the mathematics underlying the algorithms, and how to