Notice
4.4. Object level Perception functions (SLAM + DATMO)
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
This video is dedicated tothe object level perception functions: Simultaneous Localization Mapping (SLAM) and Detection and Tracking surrounding Mobile Objects (DATMO).
Thème
Documentation
Liens
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
4.5. Detection and Tracking of Mobile Objects – Problem and Approaches
LaugierChristianThis video adresses the Detection and Tracking of Mobile Objects (DATMO) problem.
-
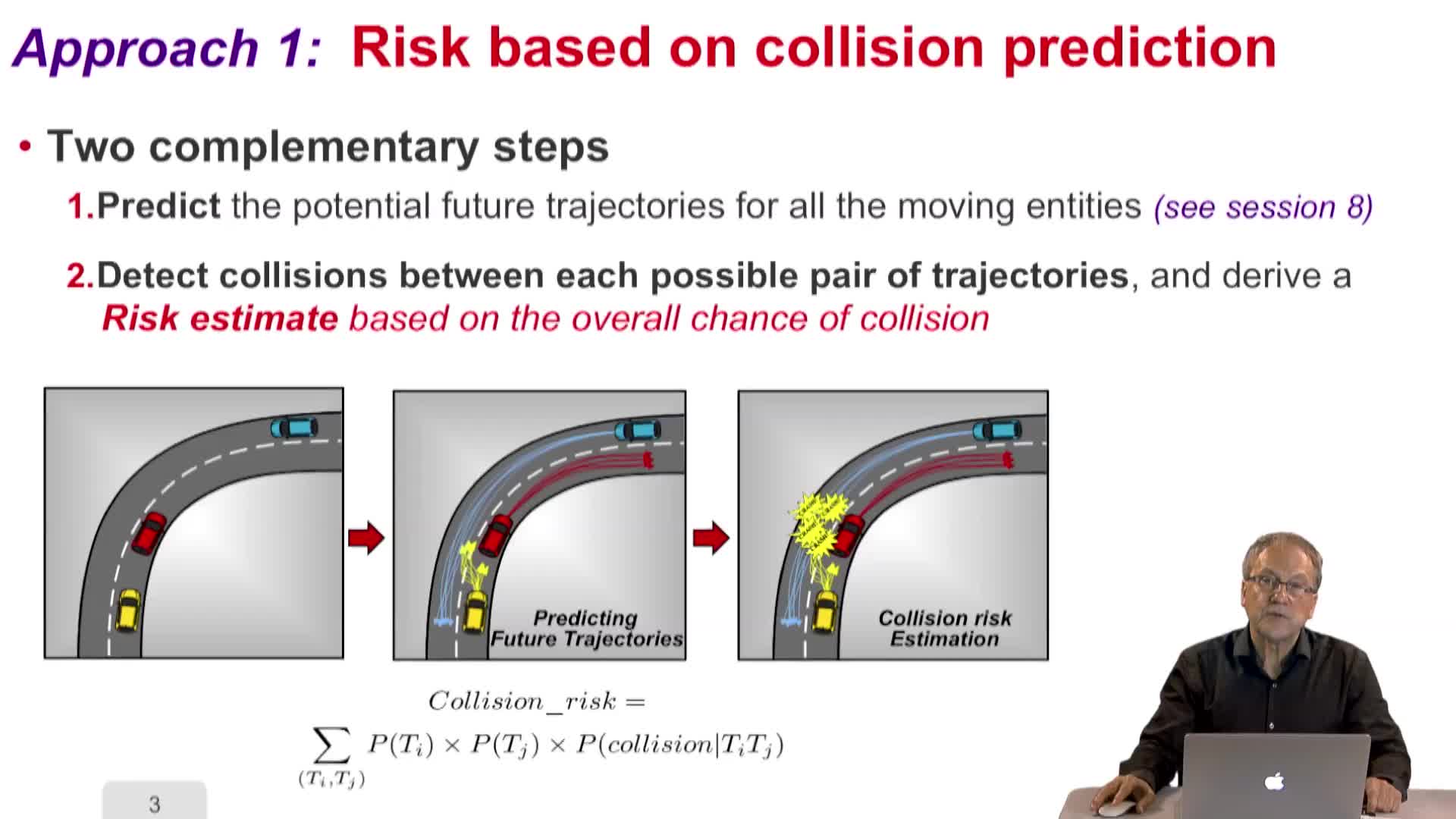
4.9. Situation Awareness – Collision Risk Assessment and Decision (Object level)
LaugierChristianThis video addresses the problem of collision risk assessment and decision.
-
4.3. Dynamic Probabilistic Grids – Implementation approaches
LaugierChristianThis video addresses the problem of the practical implementation for the dynamic probabilistic grid.
-
4.6. Detection and Tracking of Mobile Objects – Model and Grid based approaches
LaugierChristianThis video addresses the question of model-based and grid-based approaches.
-
4.8. Situation Awareness – Problem statement and Motion / Prediction Models
LaugierChristianThis videos addresses the problem of situation awareness and motion prediction models.
-
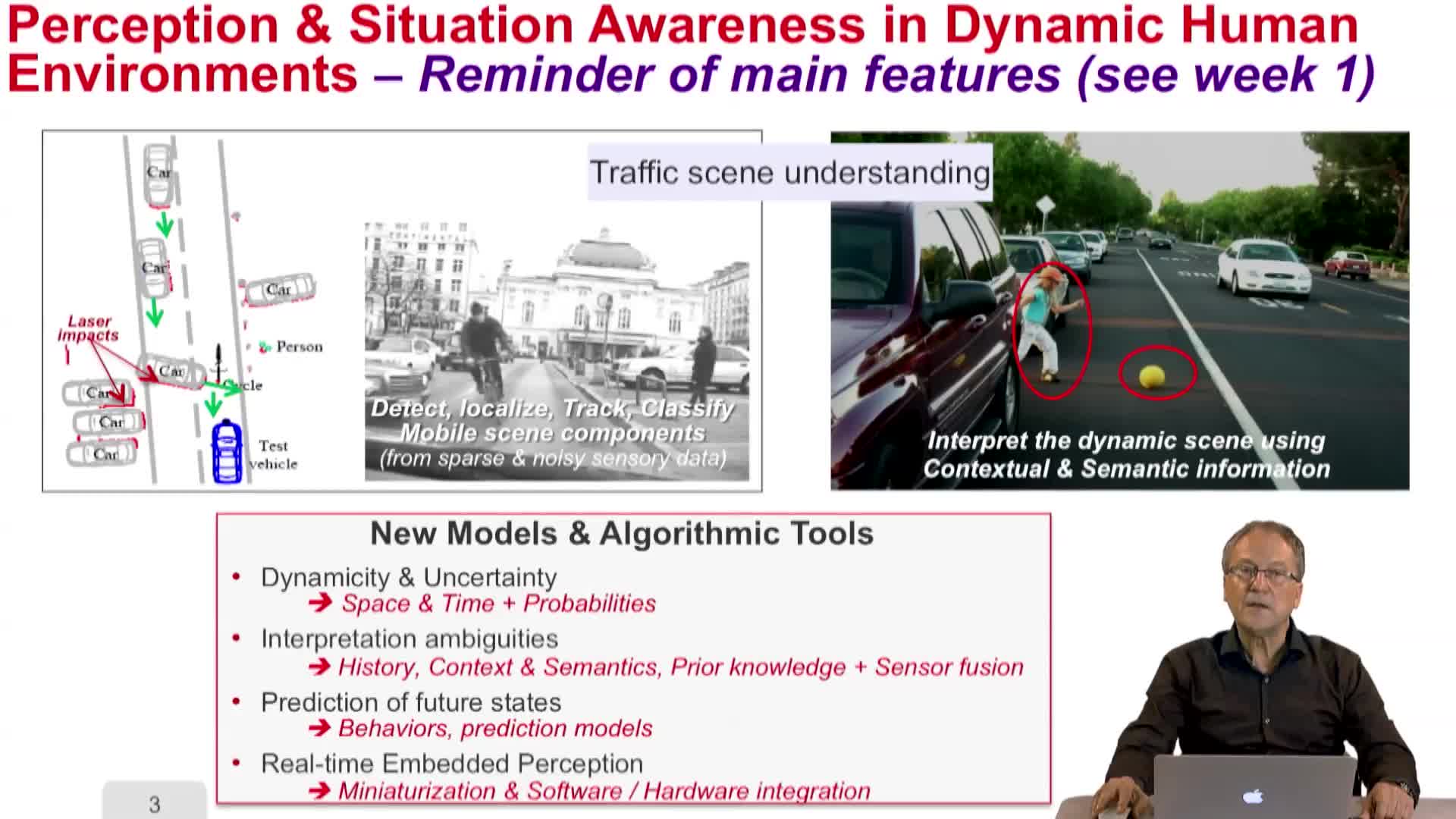
4.1. Robot Perception for Dynamic environments: Outline and DP-Grids concept
LaugierChristianThe fourth part of the course addresses perception, situation awareness and decision making. In this first video, we're giving an outline of the problem and introducing the new concept of dynamic
-
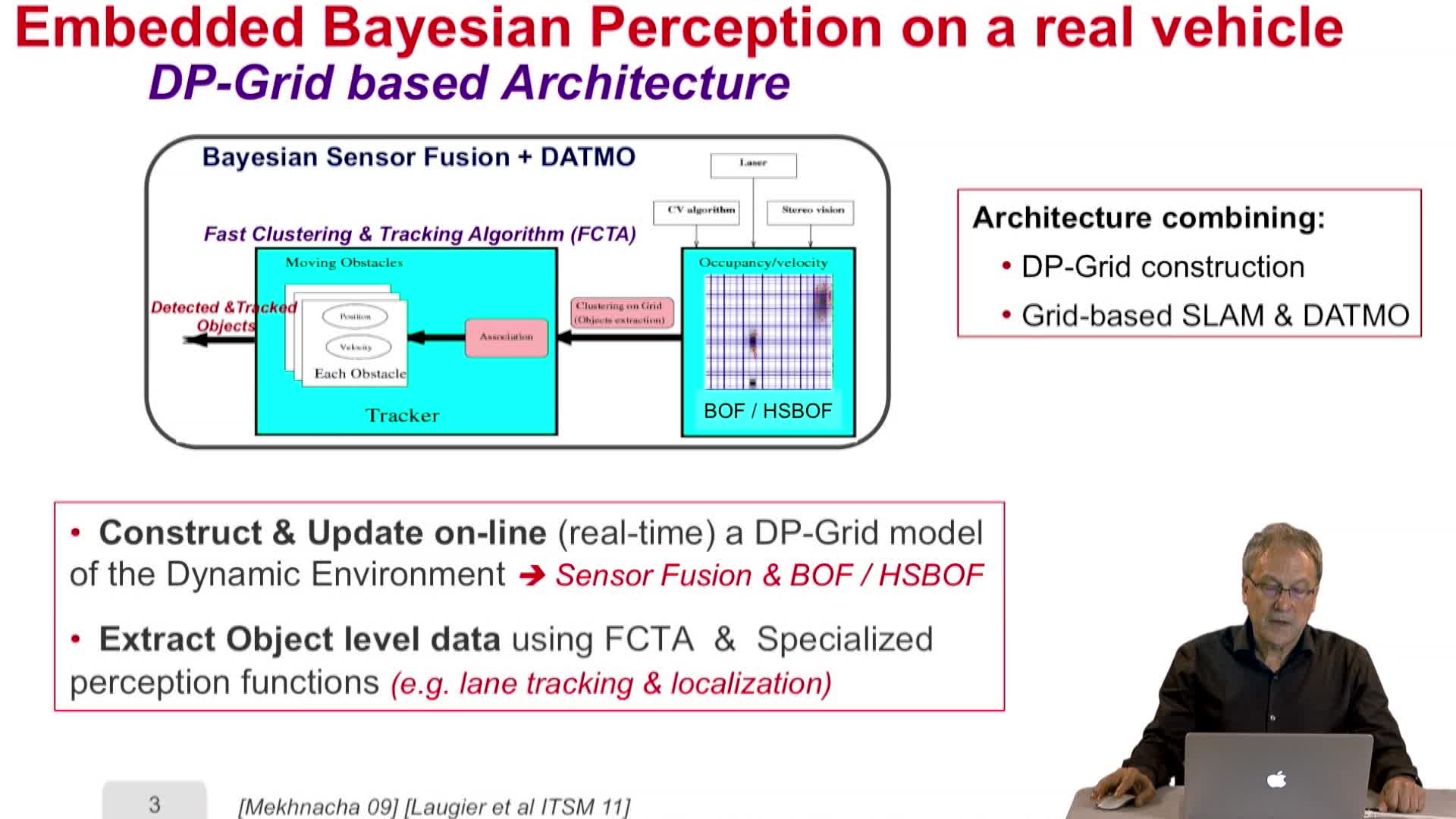
4.7. Embedded Bayesian Perception and Short-term collision risk (DP-Grid level)
LaugierChristianThis video deals with embedded Bayesian perception and short-term collision risk.
-
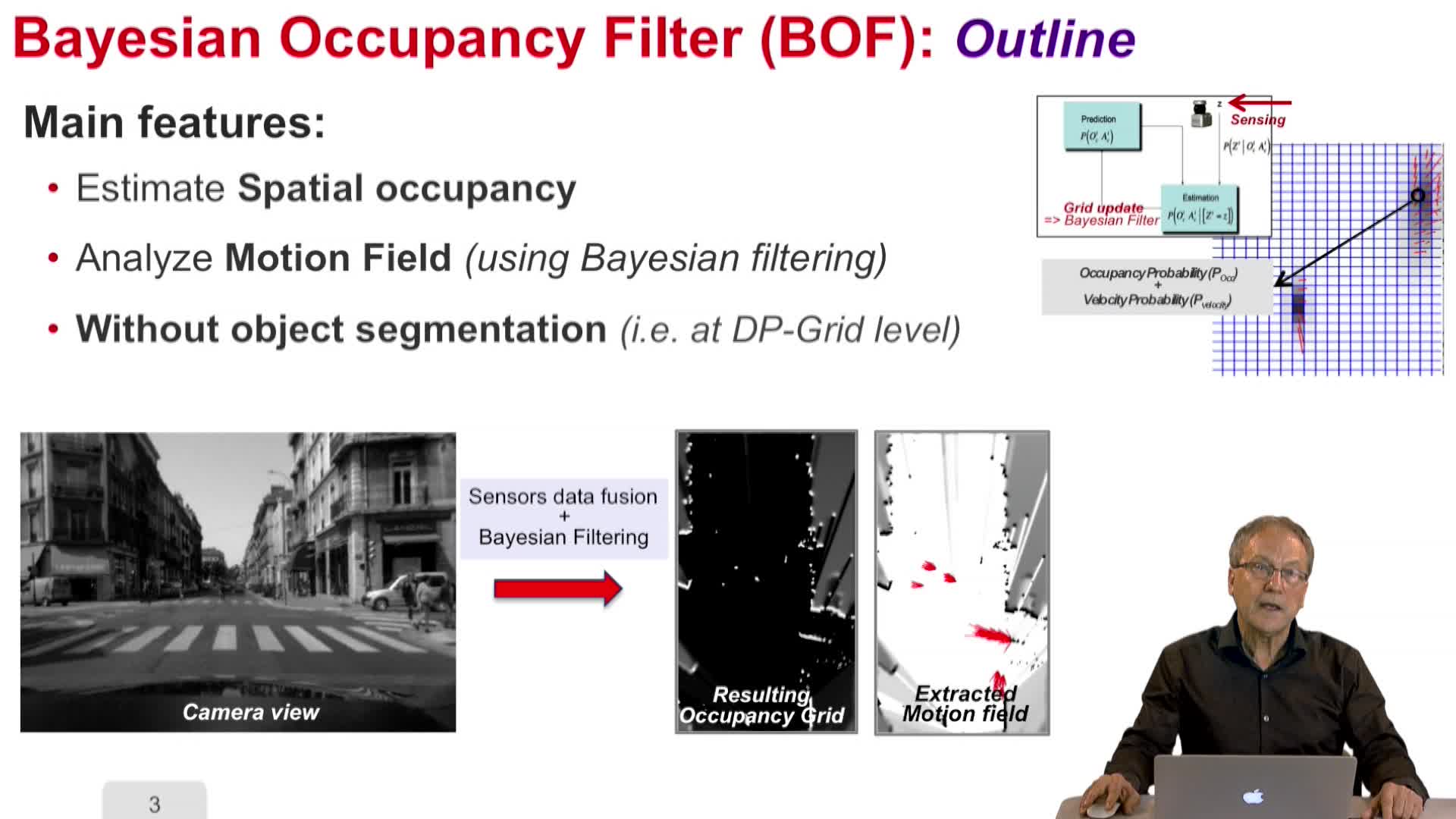
4.2. Dynamic Probabilistic Grids – Bayesian Occupancy Filter concept
LaugierChristianThis video will show how to describe Bayesian occupancy filter concept.
-
1.5. Sensing technologies: Object Detection
LaugierChristianThis video addresses sensing technologies. Sensing technologies is one of the key functions for autonomous robots. Sensing is performed using various internal and external sensors.
-
1.8. Intelligent Vehicles: Context and State of the Art
LaugierChristianThis video introduces intelligent vehicles and presents more specifically the context and a state of the art.
-
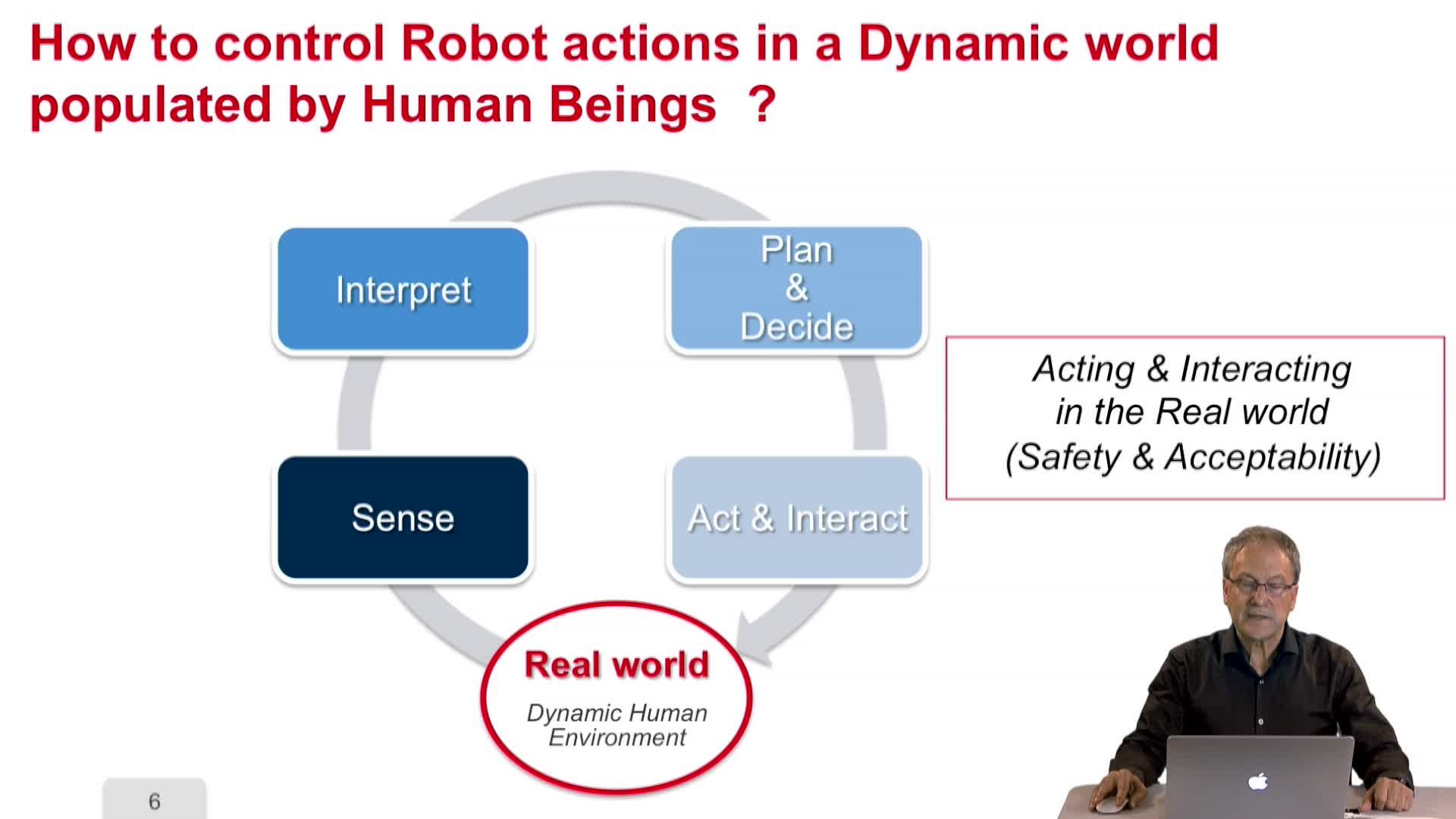
1.4. Decisional and Control Architecture for Autonomous Mobile Robots and IV
LaugierChristianThis video is presenting the decision and control architecture for autonomous mobile robots and intelligent vehicles. The question is how to control robot action in a dynamic world populated by
-
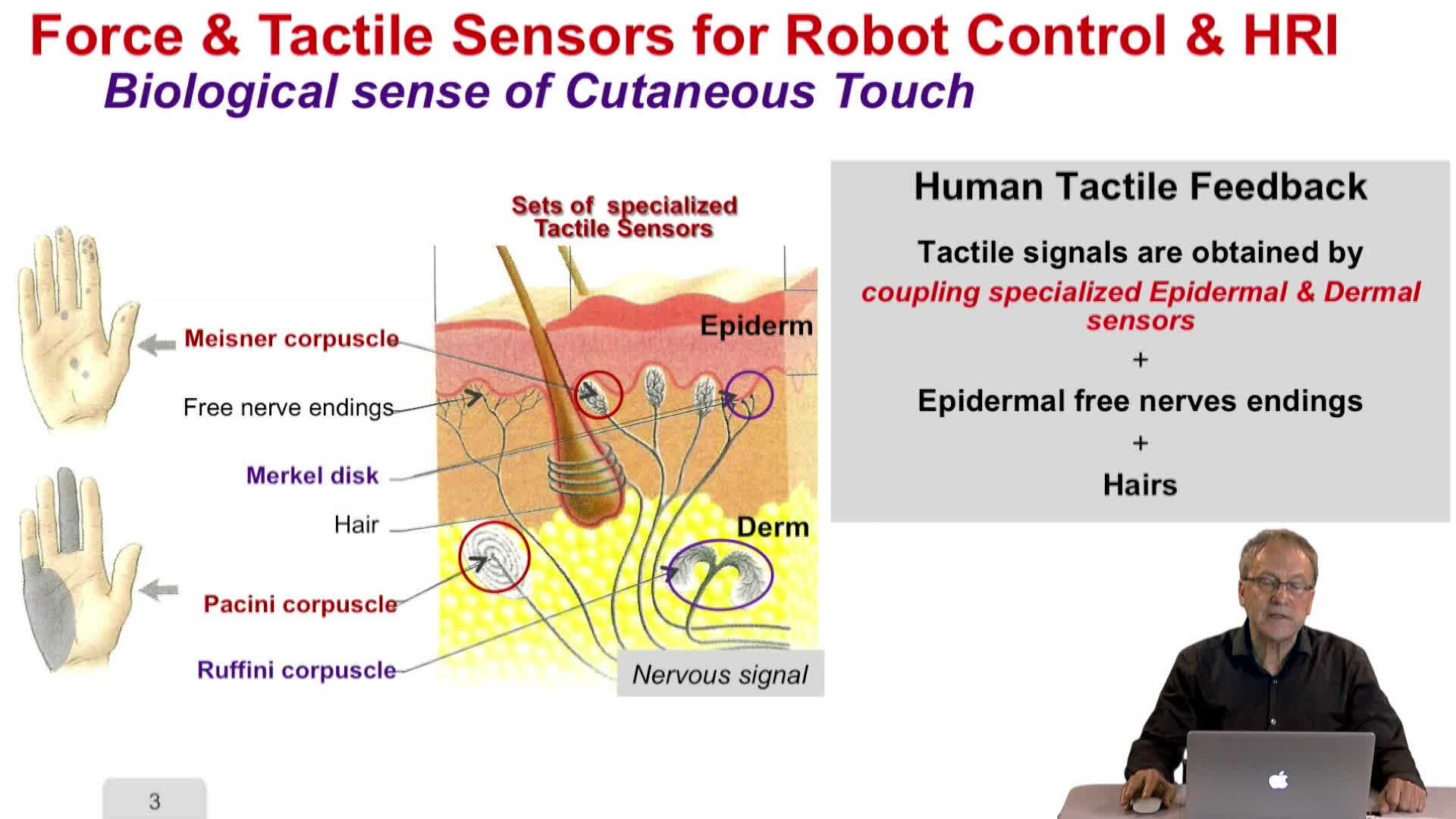
1.6. Sensing technologies: Robot Control and HRI
LaugierChristianThis video addresses sensing technology, and focuses on robot control and human-robot interaction applications.
Sur le même thème
-
Et si l’intelligence artificielle déferlait sur les océans ?
L’évolution des technologies d’observation et de modélisation a joué un rôle central dans l’accroissement des connaissances sur le fonctionnement des océans ou dans le développement des activités
-
La vidéo sous-marine au service de la recherche halieutique
Accessible à de nombreuses applications, tant en biologie ou qu'en technologie des pêches, la vidéo sous-marine est de plus en plus utilisée dans le domaine de la recherche halieutique. Les progrès
-
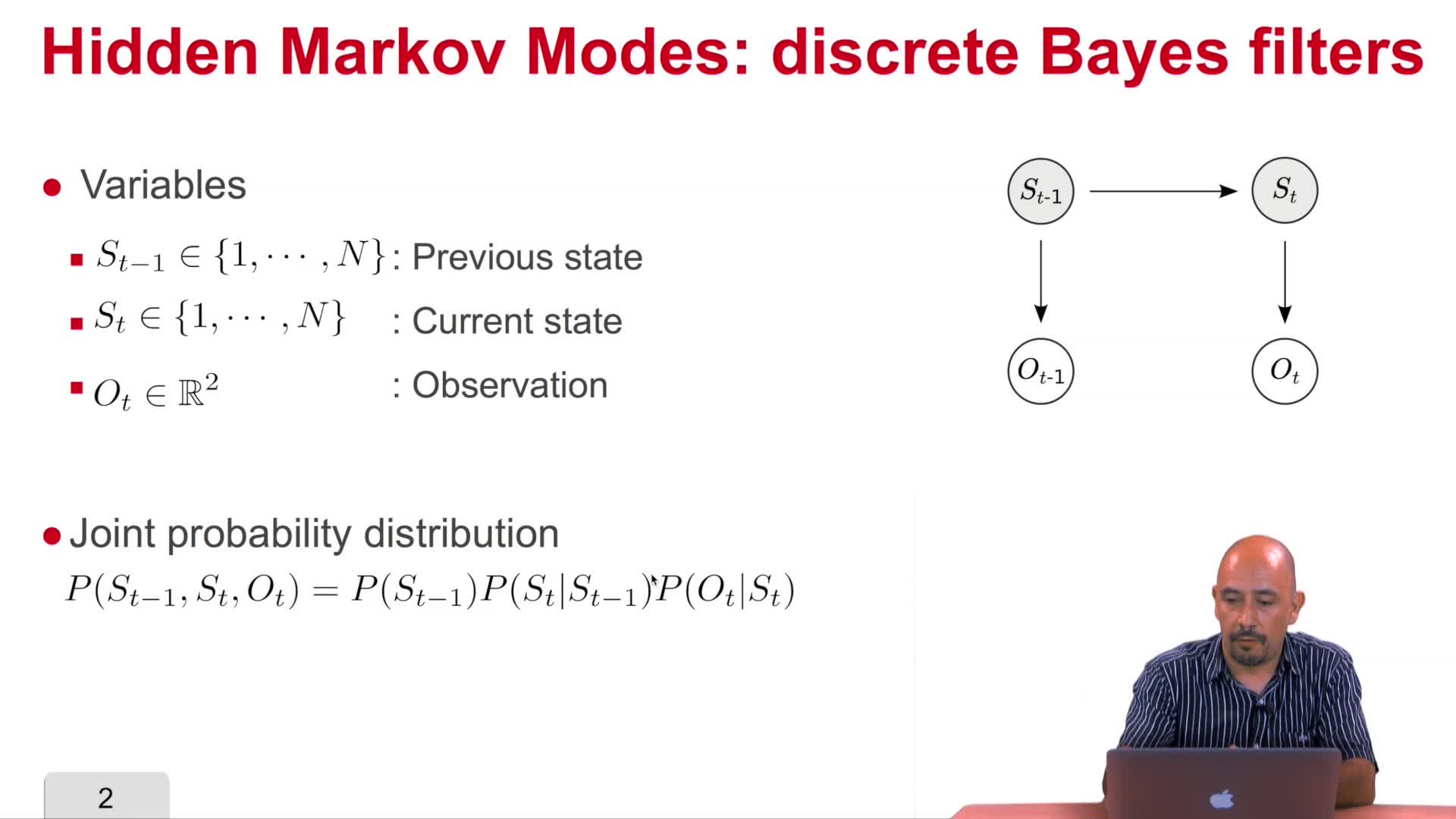
5.4. Bayesian filter inference
Vasquez GoveaAlejandro DizanIn this video we will review the base filter and we will study a particular instance of the Bayesian filter called Hidden Markov models which is a discrete version of a Bayesian filter.
-
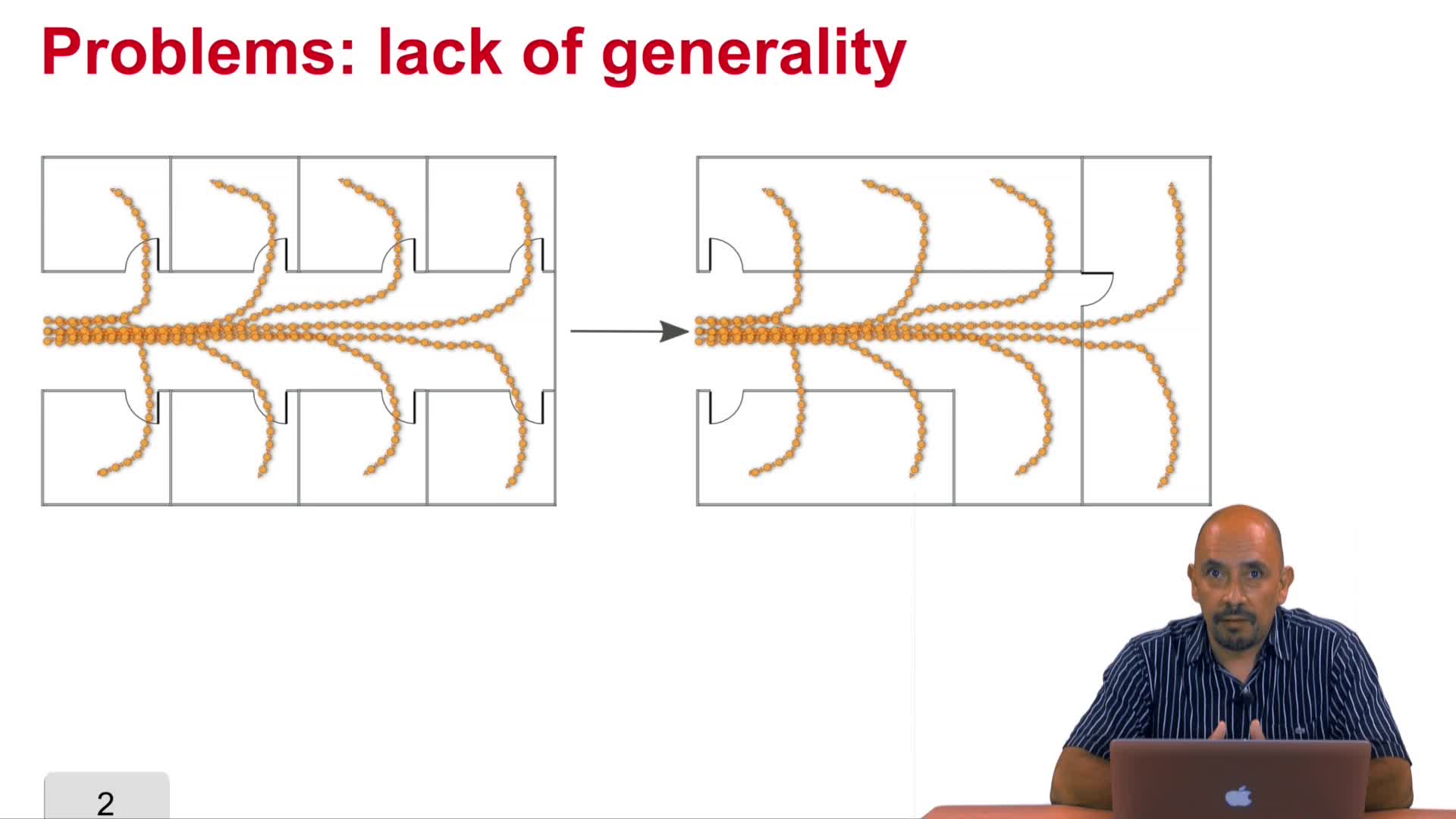
5.7. Typical Trajectories: drawbacks
Vasquez GoveaAlejandro DizanIn previous videos we have discussed how to implement the typical trajectories and motion patterns approach. In this video we are going to discuss what are the drawbacks of such an approach,
-
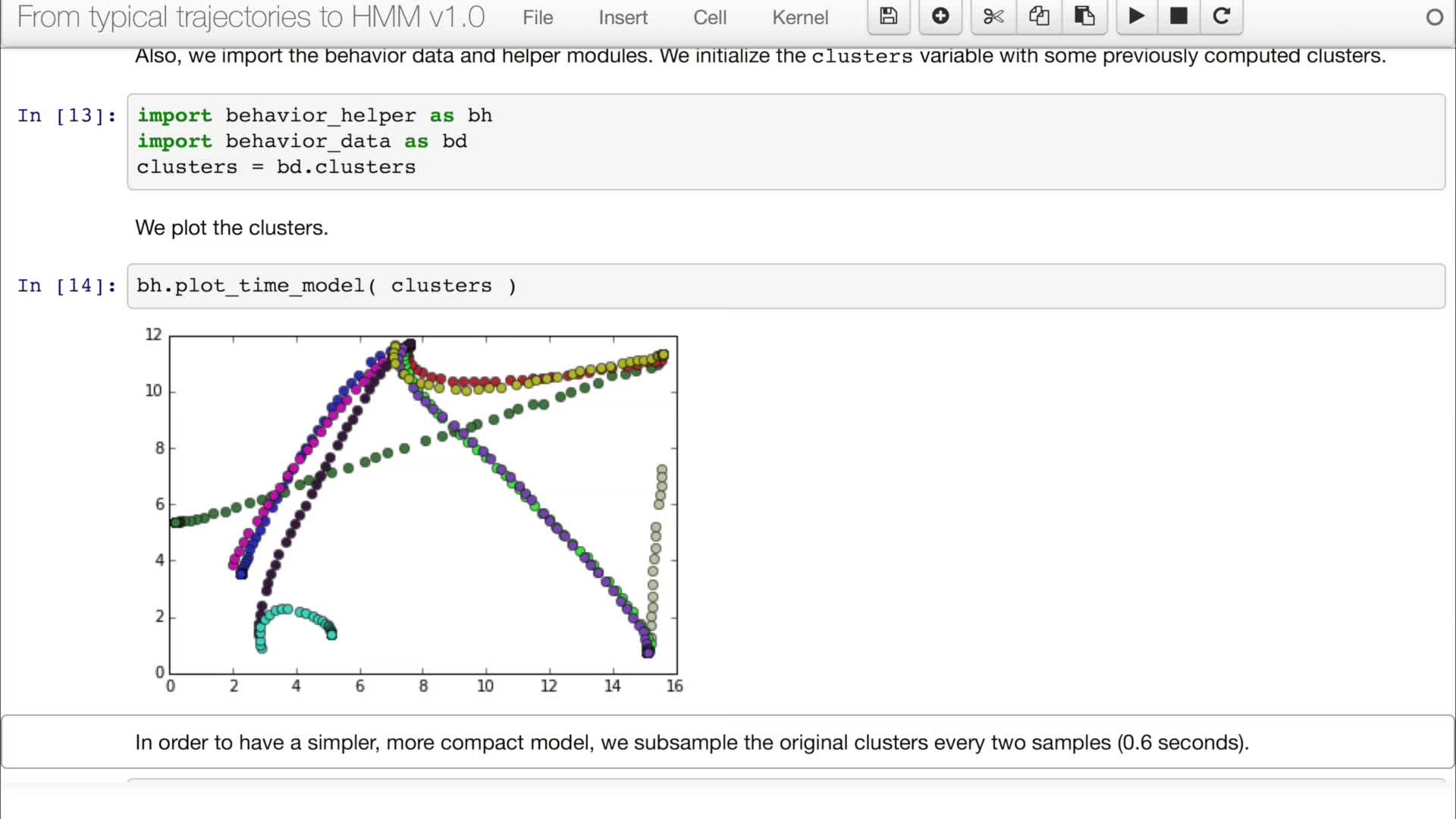
5.5. From trajectories to discrete time-state models
Vasquez GoveaAlejandro DizanIn this video we are going to apply the concepts we have reviewed in the video 5.4 into real trajectories.
-
5.8. Other approaches: Social Forces
Vasquez GoveaAlejandro DizanIn this video we will review one of the alternatives we are proposing to the use of Hidden Markov models and typical trajectories: the Social Force model.
-
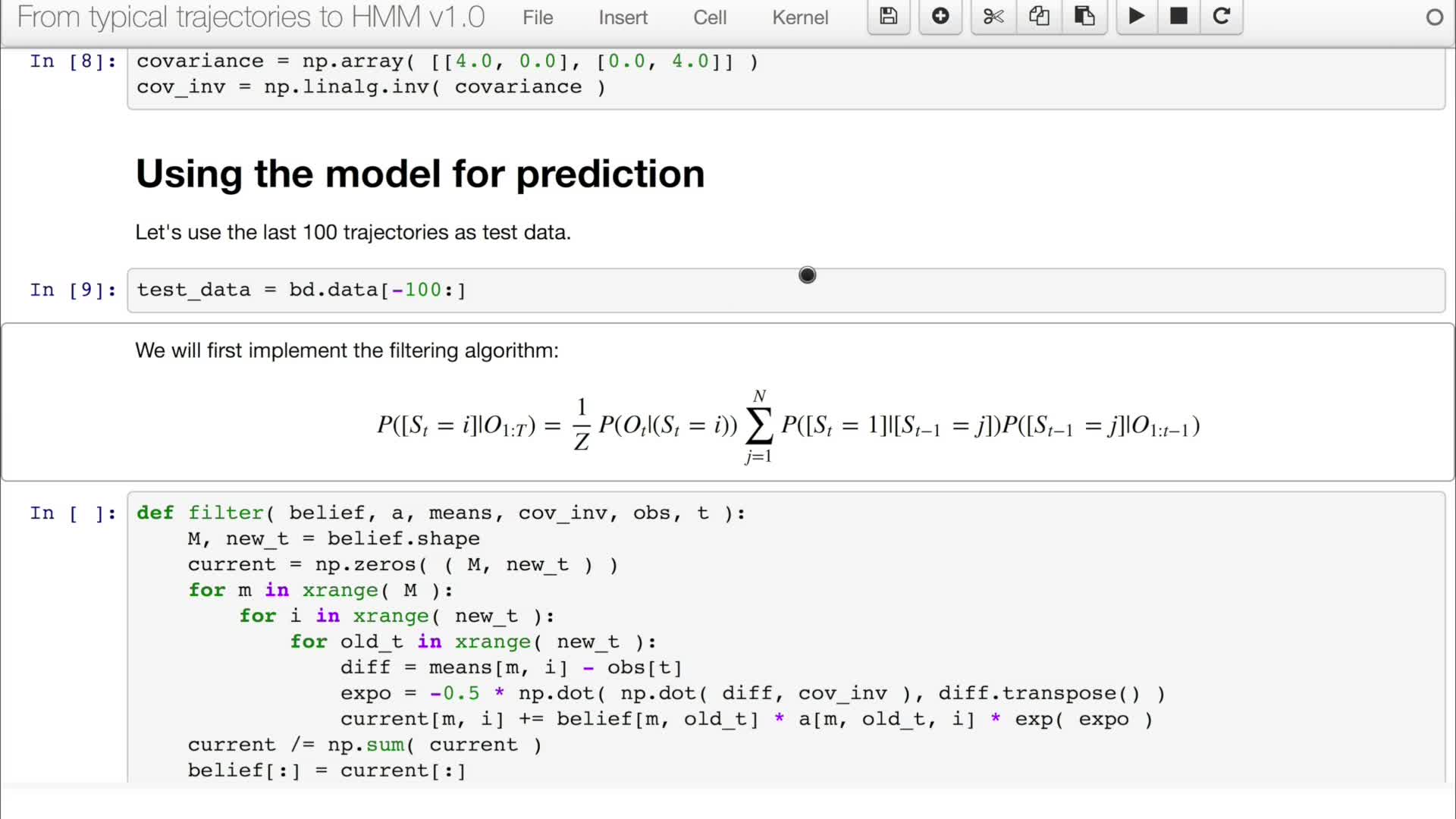
5.6. Predicting Human Motion
Vasquez GoveaAlejandro DizanIn video 5.5 we have defined an HMM in Python. In this video we are going to learn how to use it to estimate and predict motion.
-
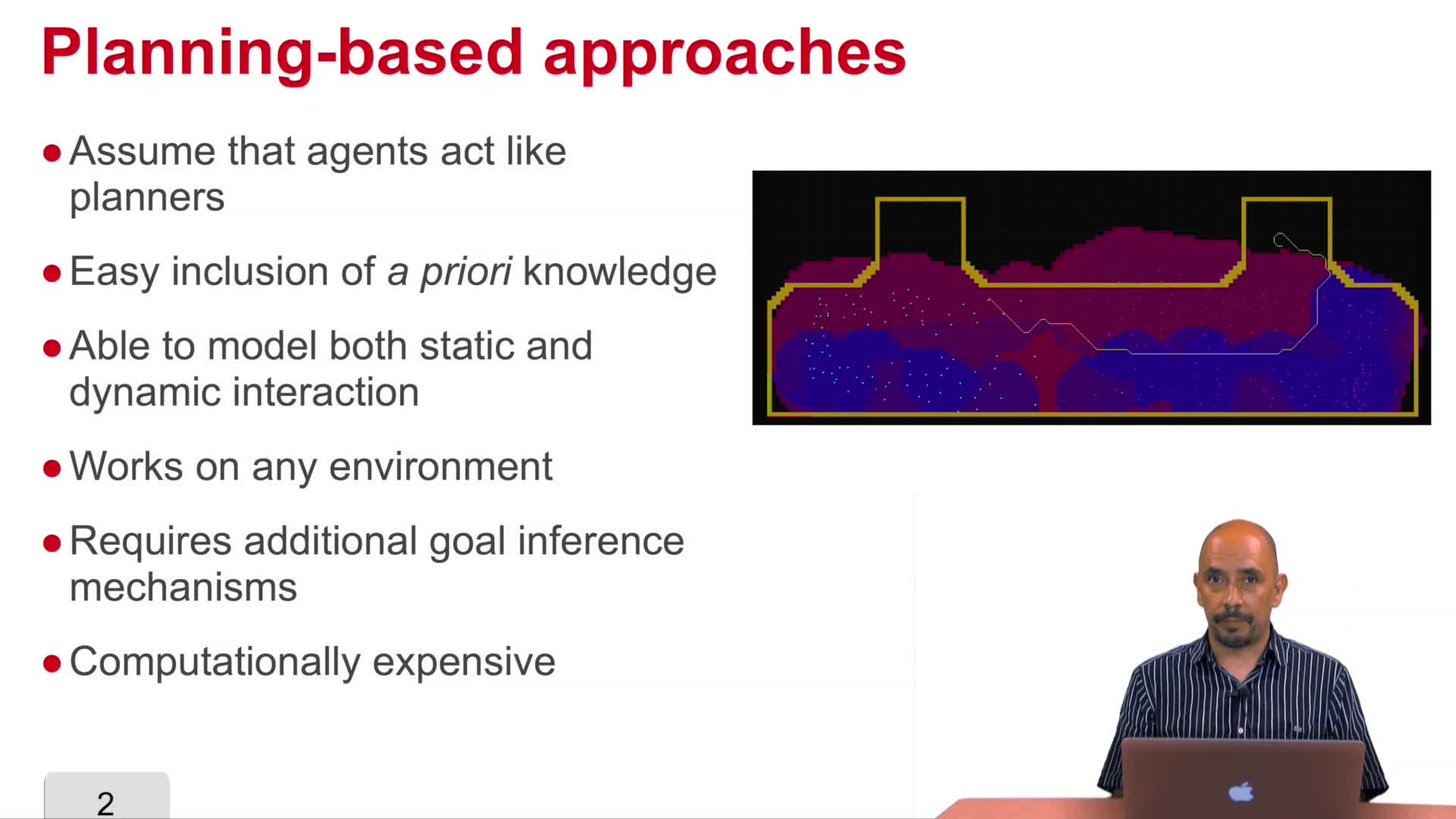
5.9. Other approaches: Planning-based approaches
Vasquez GoveaAlejandro DizanIn this video we are going to study a second, and probably the most promising alternative for motion prediction: planning-based algorithms.
-
4.6. Detection and Tracking of Mobile Objects – Model and Grid based approaches
LaugierChristianThis video addresses the question of model-based and grid-based approaches.
-
4.8. Situation Awareness – Problem statement and Motion / Prediction Models
LaugierChristianThis videos addresses the problem of situation awareness and motion prediction models.
-
4.1. Robot Perception for Dynamic environments: Outline and DP-Grids concept
LaugierChristianThe fourth part of the course addresses perception, situation awareness and decision making. In this first video, we're giving an outline of the problem and introducing the new concept of dynamic
-
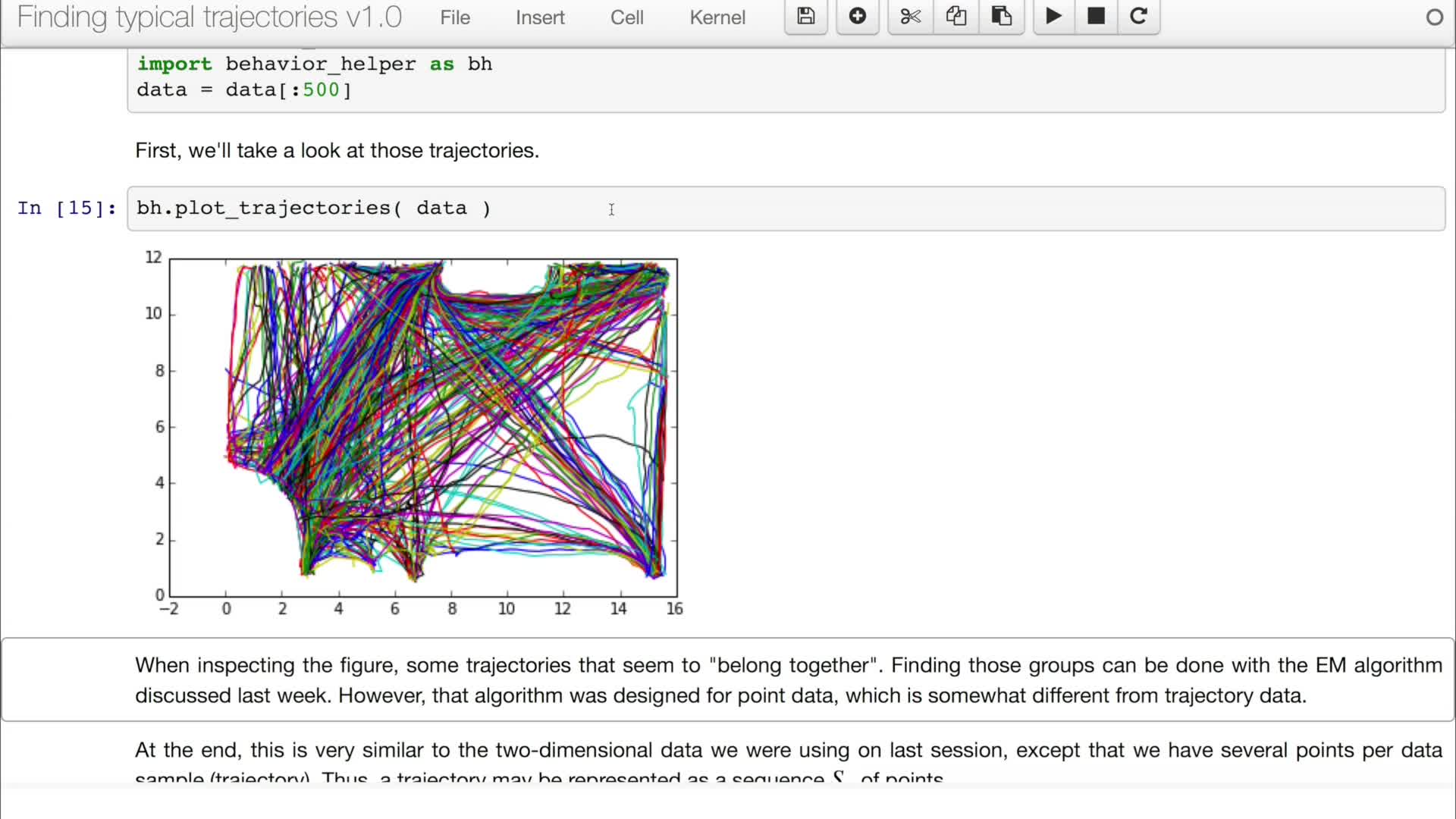
5.3a. Learning typical trajectories 1/2
Vasquez GoveaAlejandro DizanIn video 5.2 we showed how to apply the expectation maximization clustering algorithm to two-dimensional data. In this video we will learn how to apply it to trajectory data. And then we will be