Notice
5.2. The tree, an abstract object
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
When we speak of trees, of species,of phylogenetic trees, of course, it's a metaphoric view of a real tree. Our trees are abstract objects. Here is a tree and the different components of this tree. Here is what we call an edge or a branch. We have nodes, a particular nodeis the root and other nodes are the leaves here terminal nodesand we see that when we draw a tree as an abstract object, we put the root upside and the leaves downside so it's the reverse of a classical natural tree. We need an expression to describe a tree and we will use this kind of expression, how does it work? It uses parenthesis and you see that this means that part of the tree, this that part of thetree and then it's easy to see that, that part of the expression refers to this and the final expression refers to the whole tree. OK. A tree expression, we willuse this kind of expression when describing the execution of our phylogenetic tree or reconstruction algorithm. Of course it doesn't matter howthe tree is drawn, it could be like that with the same leaves and it is the same topology and so it is the same tree expression.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Thème
Documentation
Dans la même collection
-
5.7. The application domains in microbiology
RechenmannFrançoisBioinformatics relies on many domains of mathematics and computer science. Of course, algorithms themselves on character strings are important in bioinformatics, we have seen them. Algorithms and
-
5.1. The tree of life
RechenmannFrançoisWelcome to this fifth and last week of our course on genomes and algorithms that is the computer analysis of genetic information. During this week, we will firstsee what phylogenetic trees are and how
-
5.5. Differences are not always what they look like
RechenmannFrançoisThe algorithm we have presented works on an array of distance between sequences. These distances are evaluated on the basis of differences between the sequences. The problem is that behind the
-
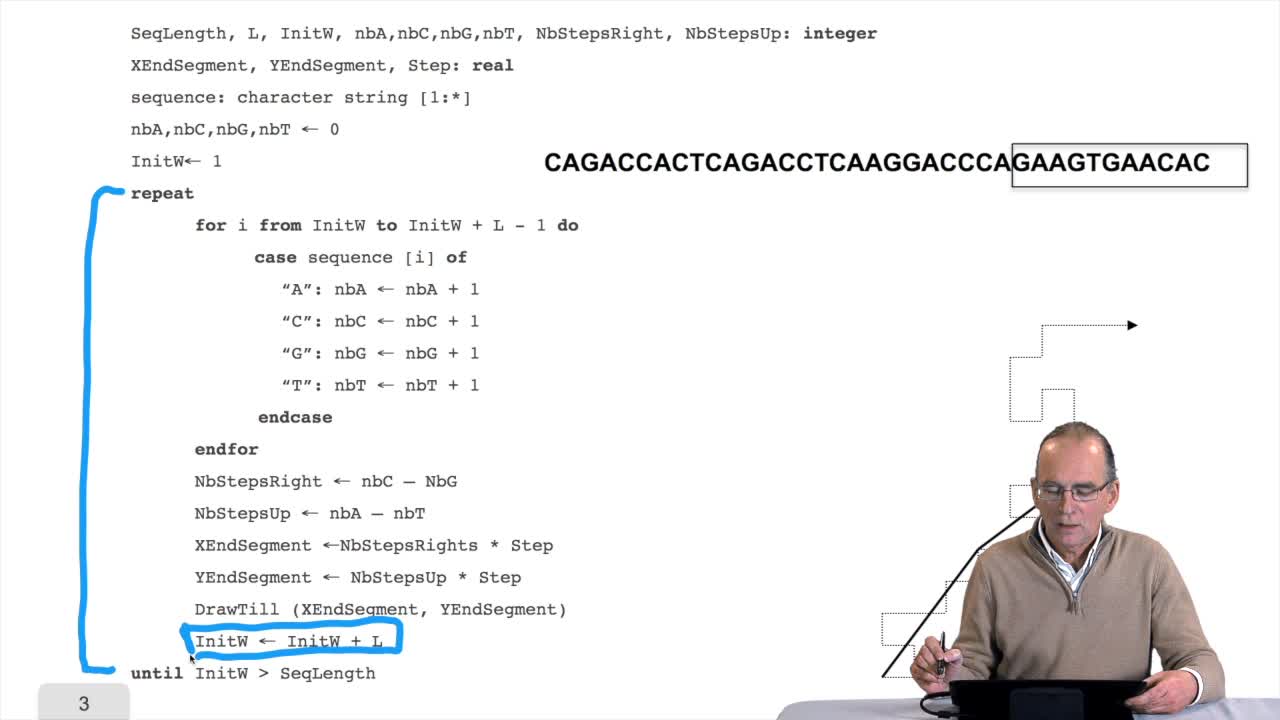
5.3. Building an array of distances
RechenmannFrançoisSo using the sequences of homologous gene between several species, our aim is to reconstruct phylogenetic tree of the corresponding species. For this, we have to comparesequences and compute distances
-
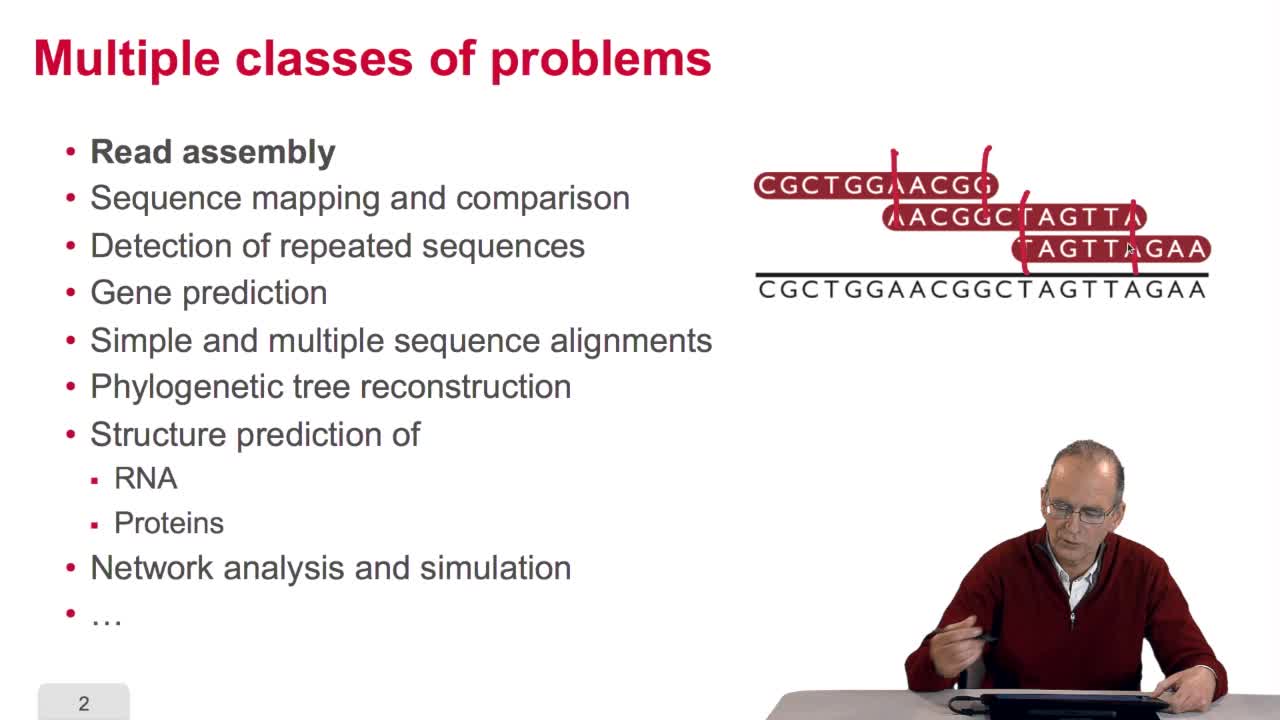
5.6. The diversity of bioinformatics algorithms
RechenmannFrançoisIn this course, we have seen a very little set of bioinformatic algorithms. There exist numerous various algorithms in bioinformatics which deal with a large span of classes of problems. For example,
-
5.4. The UPGMA algorithm
RechenmannFrançoisWe know how to fill an array with the values of the distances between sequences, pairs of sequences which are available in the file. This array of distances will be the input of our algorithm for
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
1.1. The cell, atom of the living world
RechenmannFrançoisWelcome to this introduction to bioinformatics. We will speak of genomes and algorithms. More specifically, we will see how genetic information can be analysed by algorithms. In these five weeks to
-
1.9. Predicting the origin of DNA replication?
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen a nice algorithm to draw, let's say, a DNA sequence. We will see that first, we have to correct a little bit this algorithm. And then we will see how such as imple algorithm can provide
-
2.8. DNA sequencing
RechenmannFrançoisDuring the last session, I explained several times how it was important to increase the efficiency of sequences processing algorithm because sequences arevery long and there are large volumes of
-
3.5. Making the predictions more reliable
RechenmannFrançoisWe have got a bacterial gene predictor but the way this predictor works is rather crude and if we want to have more reliable results, we have to inject into this algorithmmore biological knowledge. We
-
4.6. A path is optimal if all its sub-paths are optimal
RechenmannFrançoisA sequence alignment between two sequences is a path in a grid. So that, an optimal sequence alignmentis an optimal path in the same grid. We'll see now that a property of this optimal path provides
-
5.1. The tree of life
RechenmannFrançoisWelcome to this fifth and last week of our course on genomes and algorithms that is the computer analysis of genetic information. During this week, we will firstsee what phylogenetic trees are and how
-
1.4. What is an algorithm?
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen that a genomic textcan be indeed a very long sequence of characters. And to interpret this sequence of characters, we will need to use computers. Using computers means writing program.
-
2.2. Genes: from Mendel to molecular biology
RechenmannFrançoisThe notion of gene emerged withthe works of Gregor Mendel. Mendel studied the inheritance on some traits like the shape of pea plant seeds,through generations. He stated the famous laws of inheritance
-
2.10. How to find genes?
RechenmannFrançoisGetting the sequence of the genome is only the beginning, as I explained, once you have the sequence what you want to do is to locate the gene, to predict the function of the gene and maybe study the
-
3.8. Probabilistic methods
RechenmannFrançoisUp to now, to predict our gene,we only rely on the process of searching certain strings or patterns. In order to further improve our gene predictor, the idea is to use, to rely onprobabilistic methods
-
4.3. Measuring sequence similarity
RechenmannFrançoisSo we understand why gene orprotein sequences may be similar. It's because they evolve togetherwith the species and they evolve in time, there aremodifications in the sequence and that the sequence
-
5.4. The UPGMA algorithm
RechenmannFrançoisWe know how to fill an array with the values of the distances between sequences, pairs of sequences which are available in the file. This array of distances will be the input of our algorithm for