Gandon, Fabien (1975-....)
Titulaire d'un doctorat en sciences (Informatique, Nice, 2002)
Fabien GANDON est directeur de Recherche à Inria et responsable de l'équipe Wimmics (Inria, I3S, CNRS, UNS) qui étudie des modèles et algorithmes pour concilier le Web social et le Web sémantique. Il est aussi représentant d'Inria au consortium international de standardisation pour le Web (W3C).
Vidéos
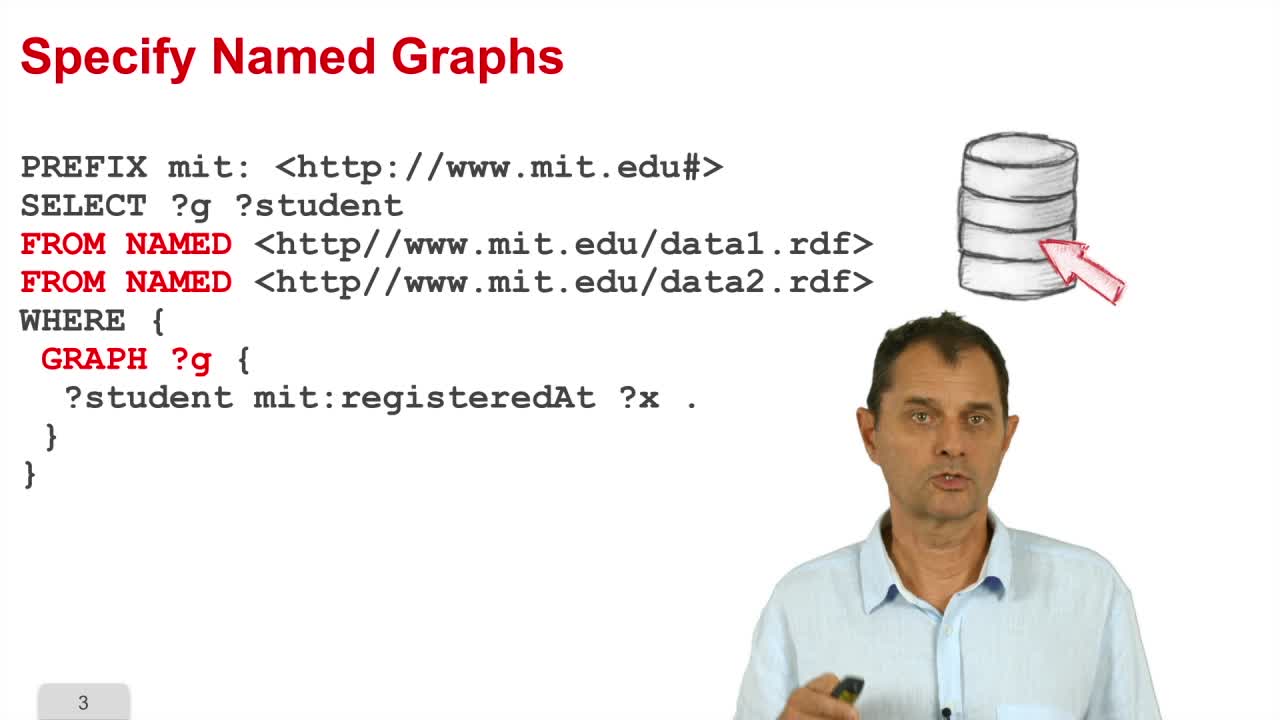
5. Several Query Forms
In the fifth part, we will see several query forms. Until now, we have seen the select where SPARQL query form but there are
3. From pages to resources
In this third part, we will see another evolution of the Web, or more precisely, an evolution of the way we use the Web. We will
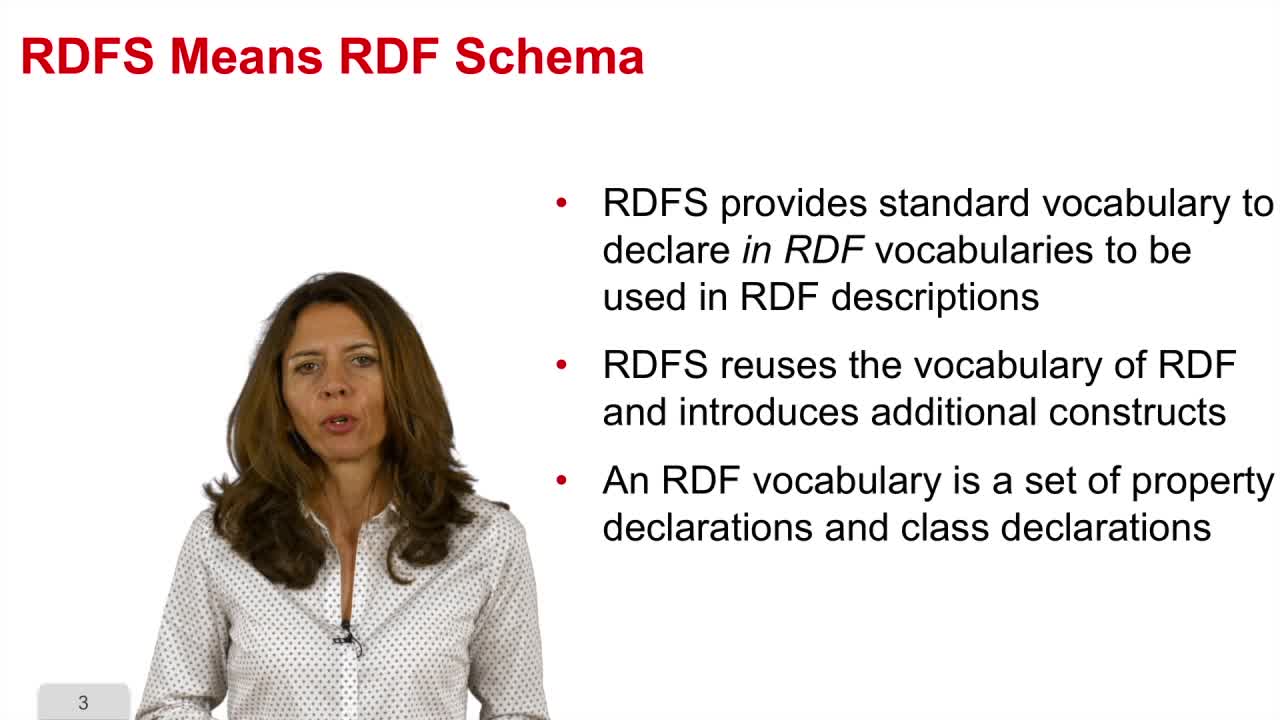
7. RDF Schema
This sequence will introduce you to the RDF Schema, the standard to represent vocabularies to be used in RDF descriptions. In the
3. JSON-LD: JSON syntax for RDF
JSON-LD is a JSON syntax for RDF. JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation. It is a hierarchical structure of name-value pairs. It is
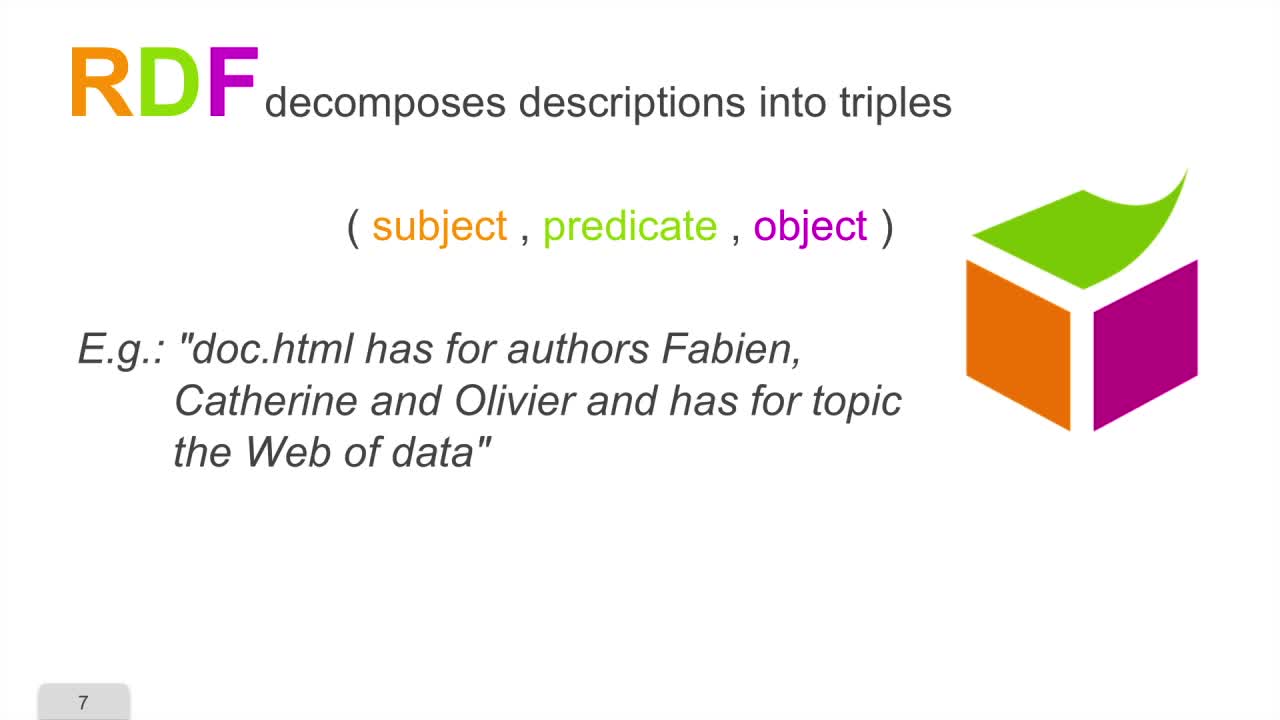
2. A Triple Model and a Graph Model
This sequence will introduce the principles of the RDF model. We will see that it is a triple model and a graph model. RDF stands for
4. Pre and Post Processing
In the fourth part, we will see the pre and post processing of a SPARQL query. An RDF dataset is composed of a default graph
6. LDP : a REST API to linked data
This part is about the Linked Data Platform standard which provides the REST API to link data. This is a set of standardized HTTP and RDF
Demos about The RDF Data Model
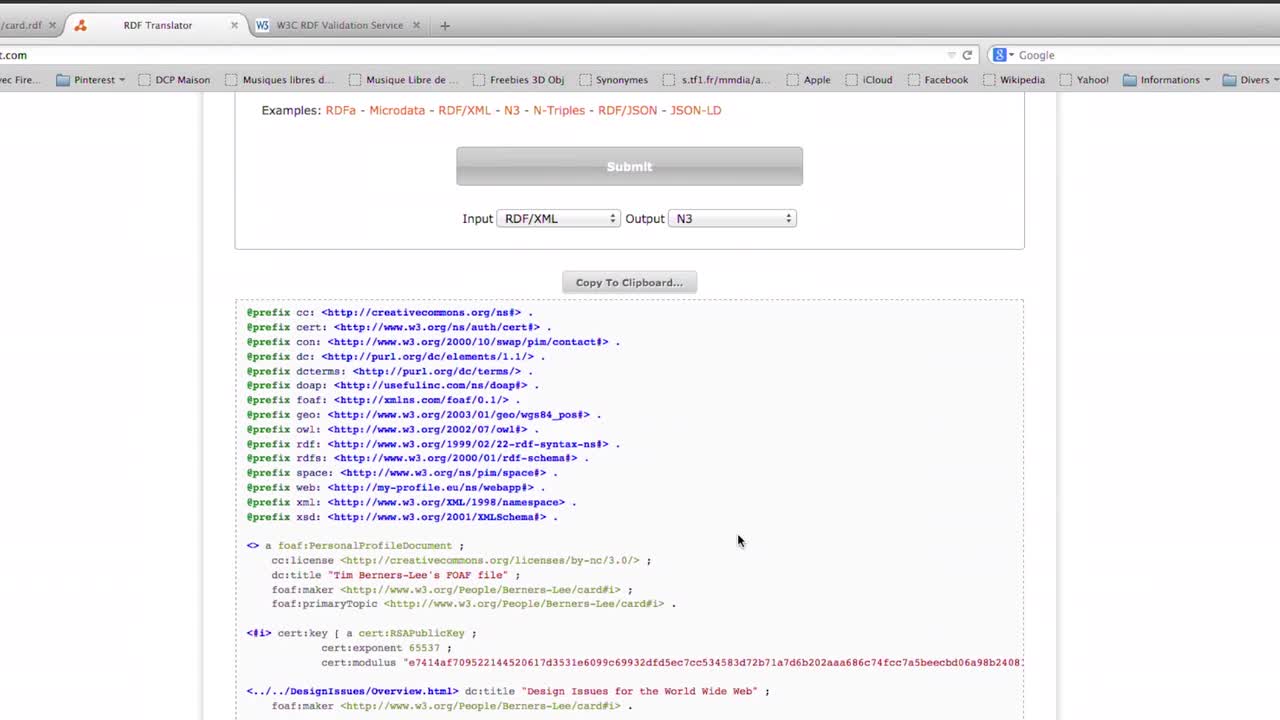
Validating and translating RDF data The W3C RDF validation service checks the validity of RDF statements in the RDF/XML syntax and, in the case where these statements are valid, it displays
1. Historical Introduction to the Web Architecture
Going back in history, back in 1945, Vannevar Bush wrote an article entitled "As we may think". In this article, he
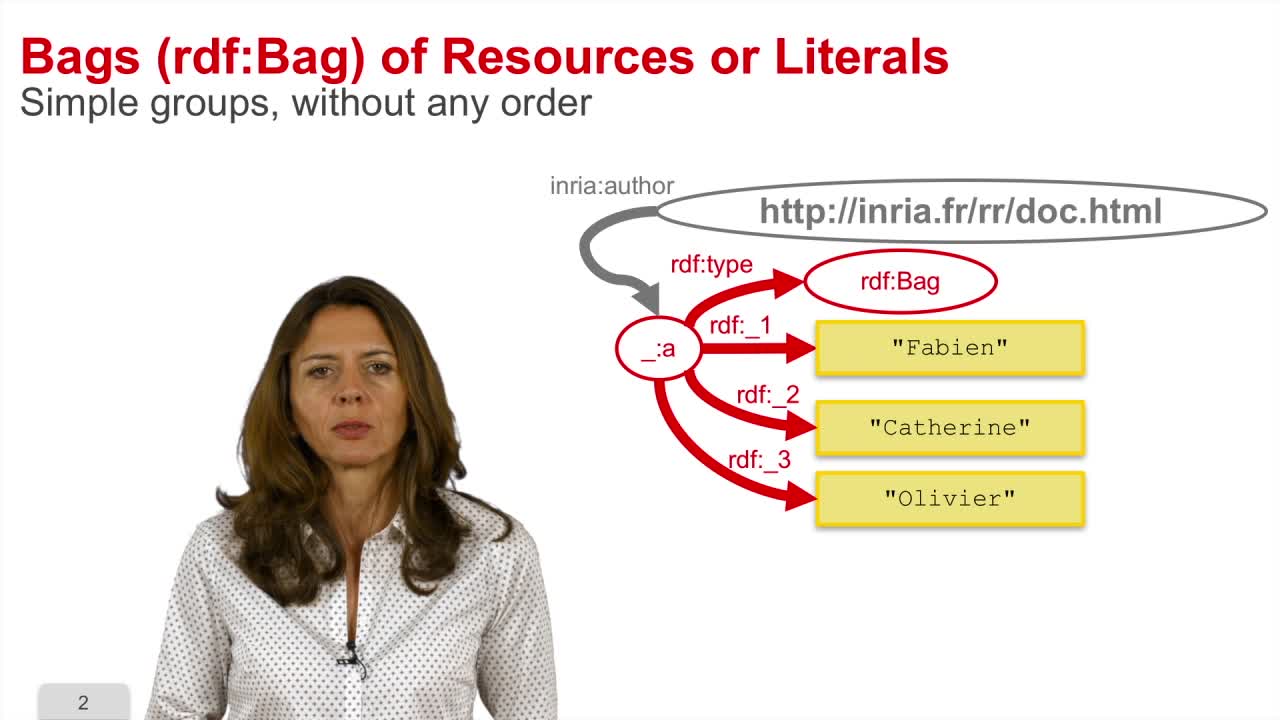
5. Representing groups
This sequence is about the specificities of the RDF model for representing groups. The type Bag is predefined in the RDF model to represent
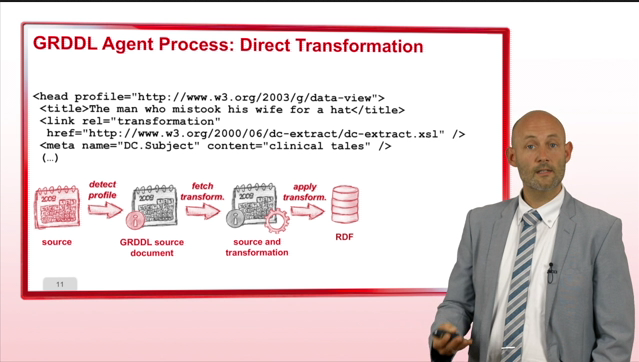
2. GRDDL: extract RDF from X(HT)ML
GRDDL is a mechanism to extract RDF from XML and HTML.
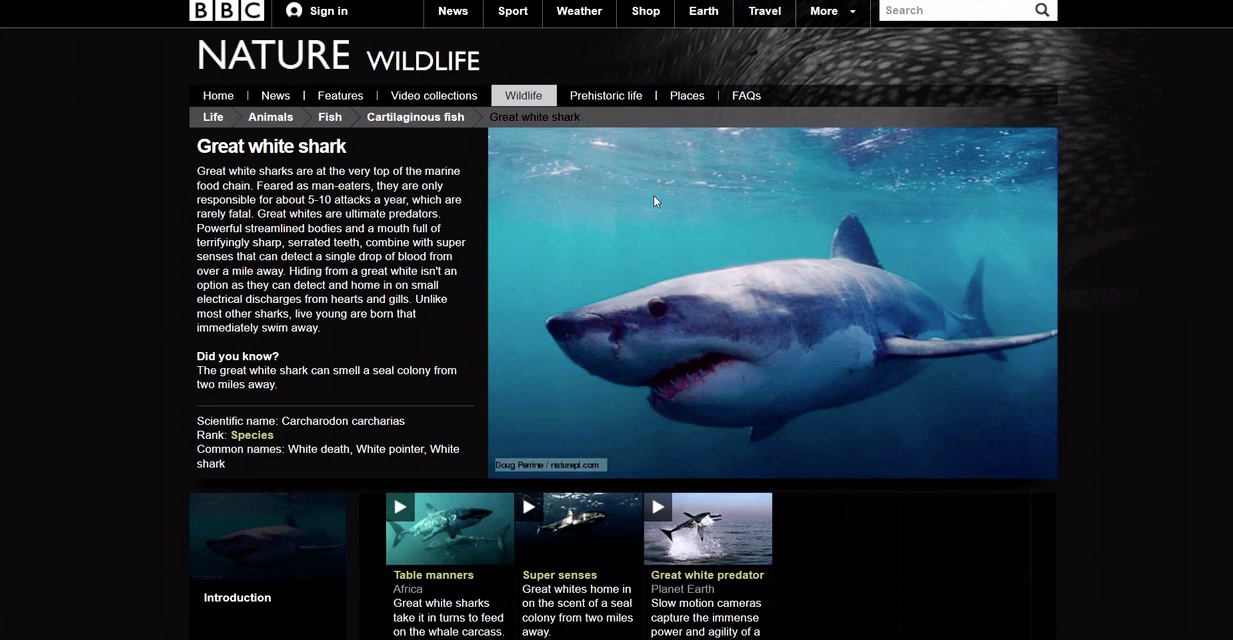
Demos about a Web of Linked data
The BBC Web site uses linked (open) data The Wildlife documentary catalog on the Web site of BBC The Web site of BBC is structured and augmented with both internal and public linked data. In