Notice
Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum - Paris 2012 : SHIfTing evidence in heart failure management.
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
Title : Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum - Paris 2012 : SHIfTing evidence in heart failure management.
Speaker: Jeffrey BORER, New York, USA
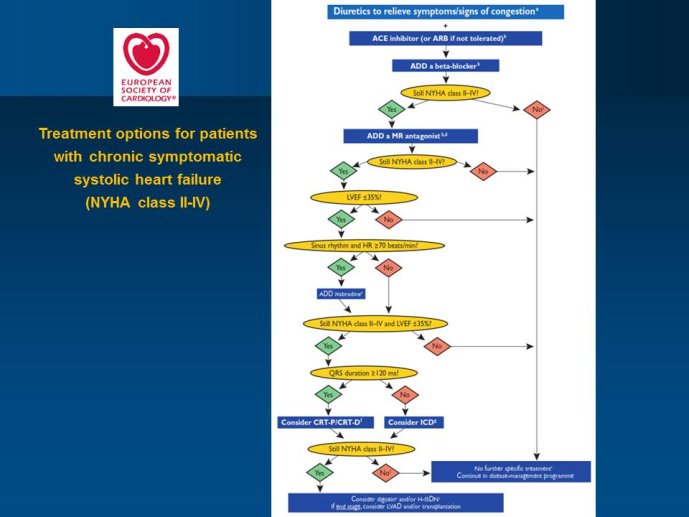
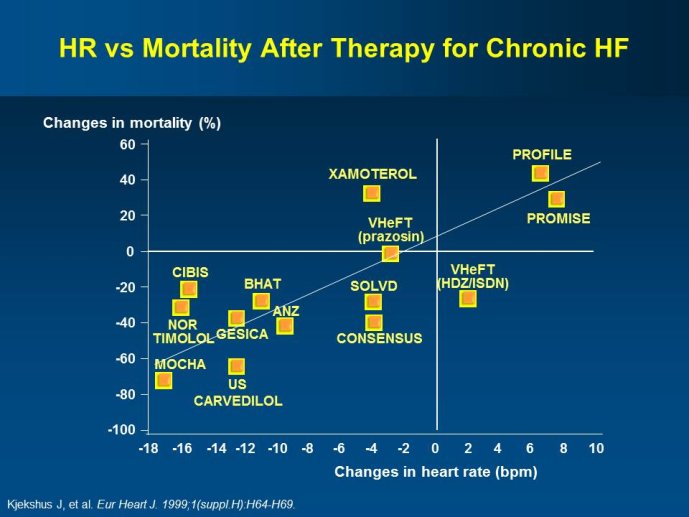
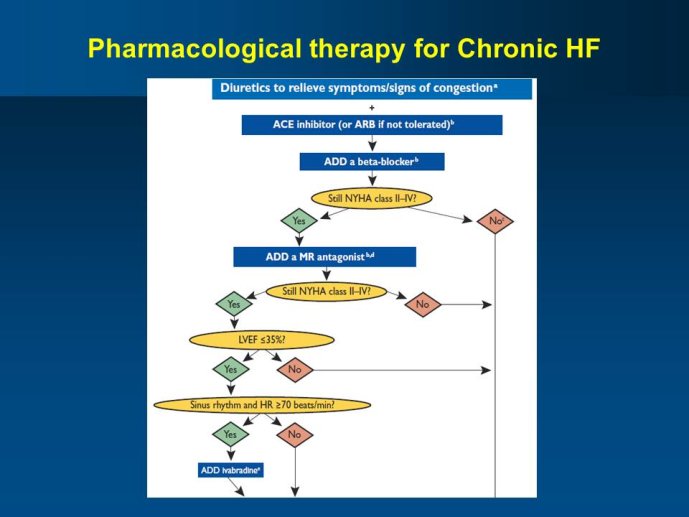
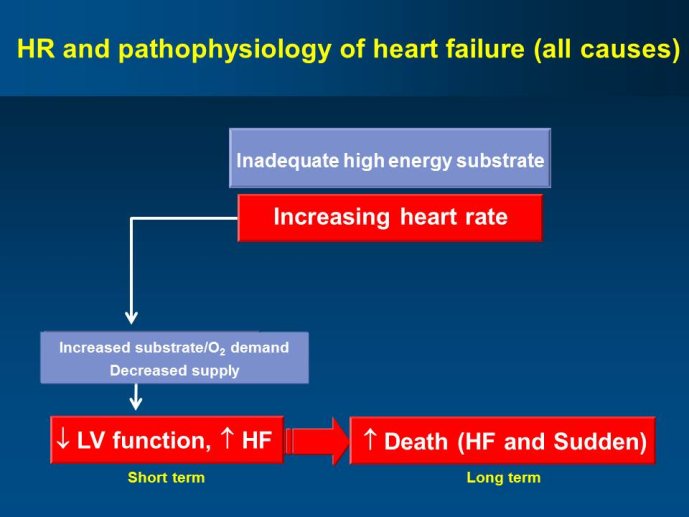
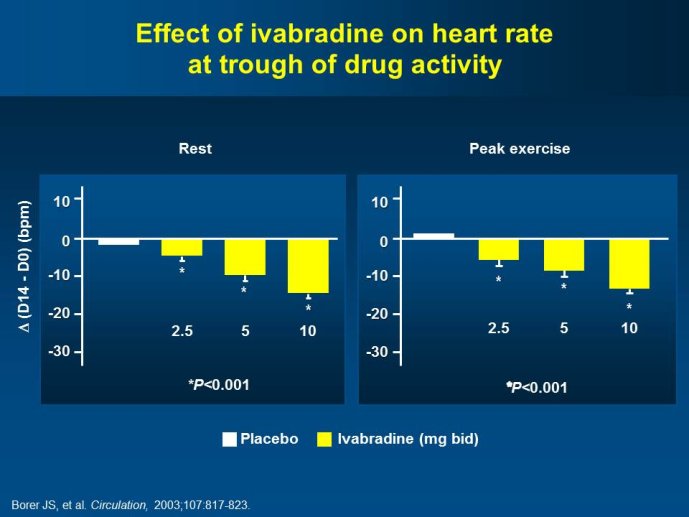
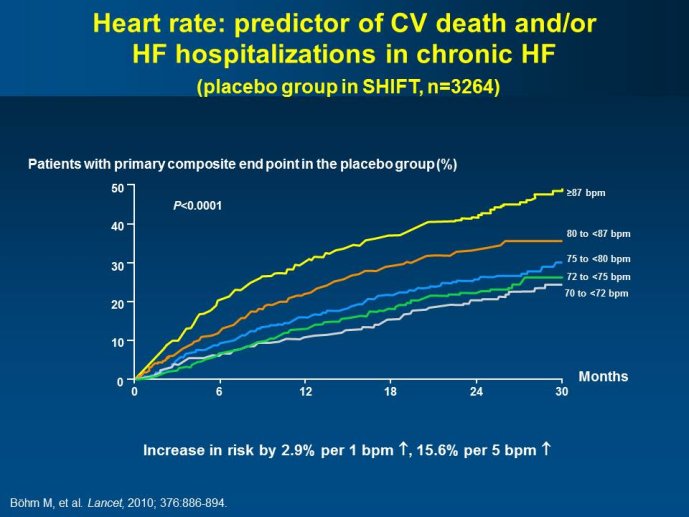
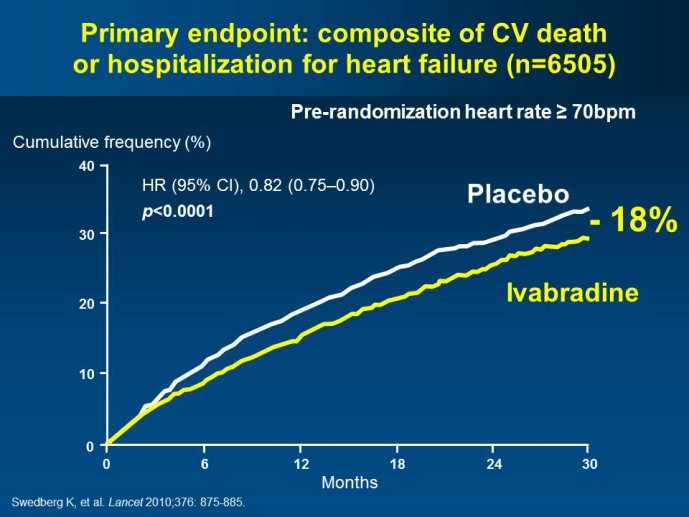
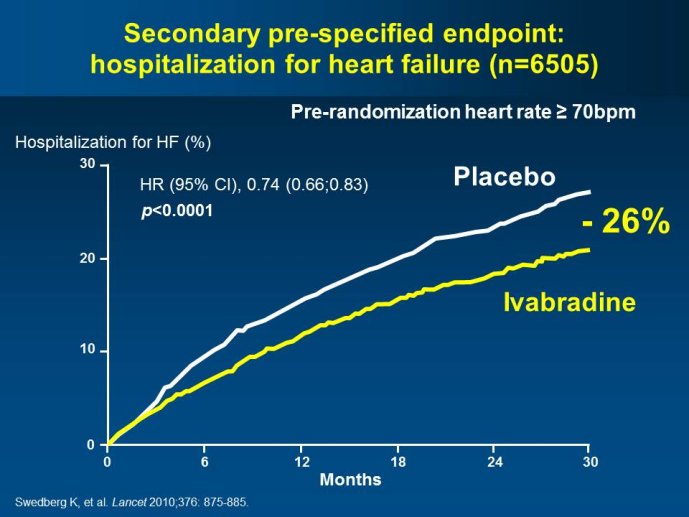
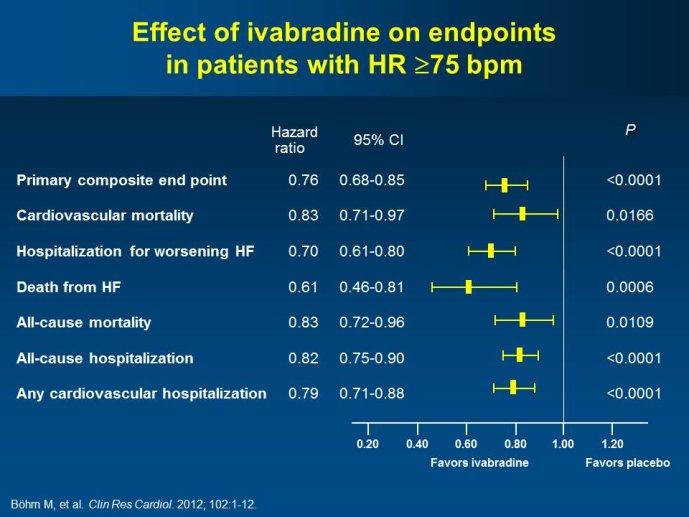
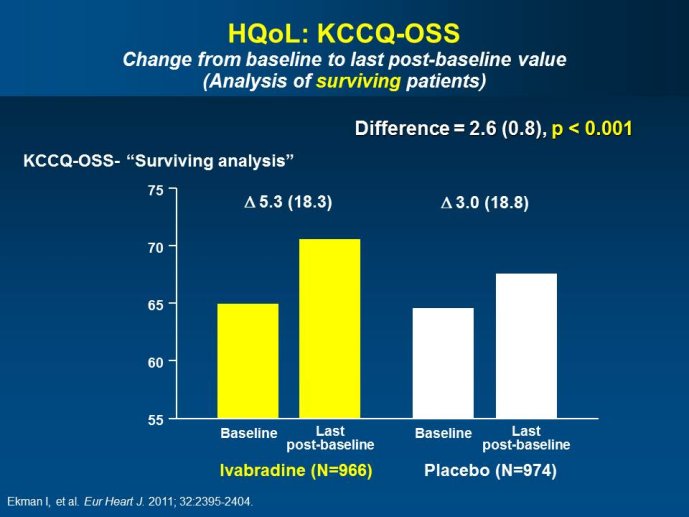
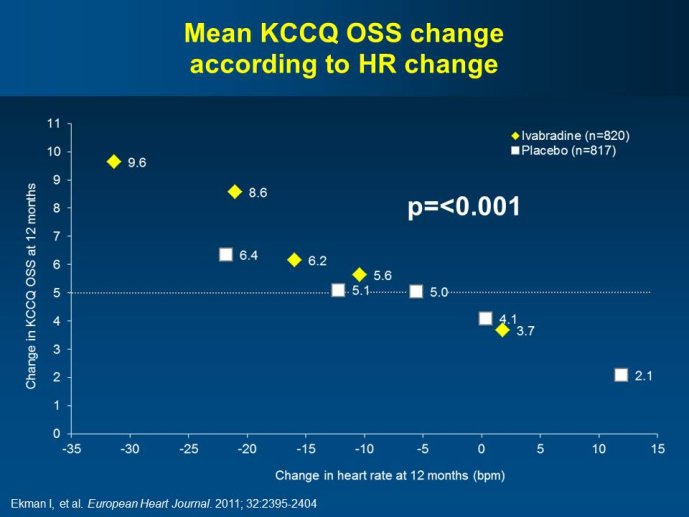
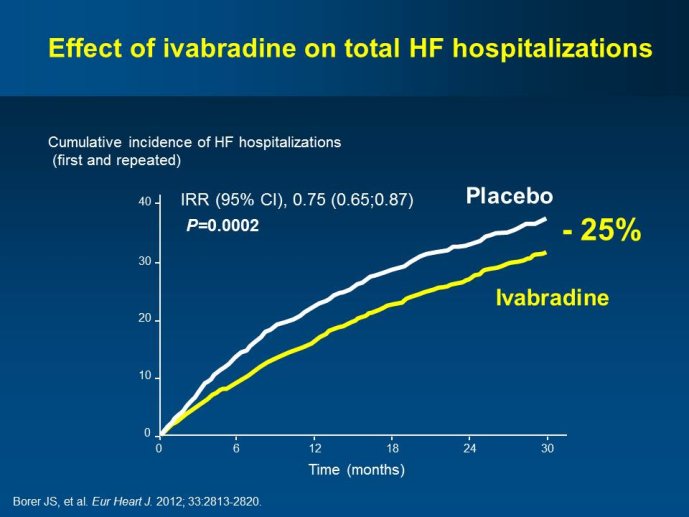
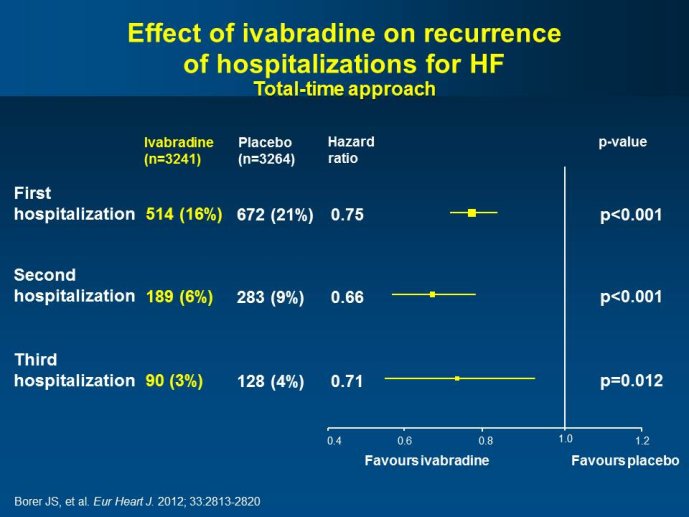
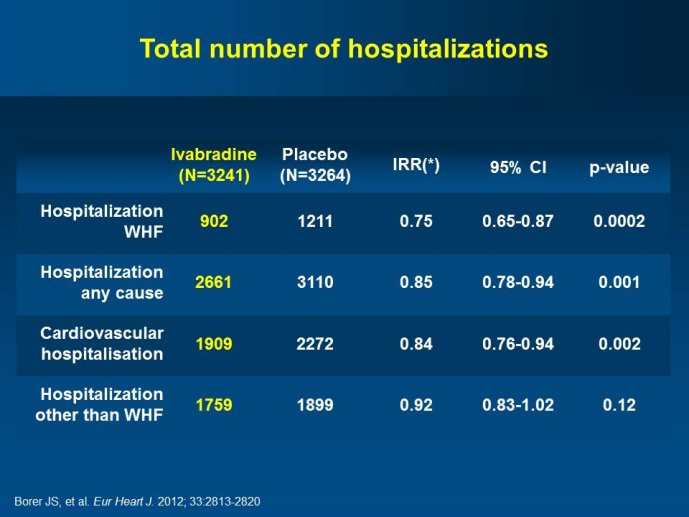
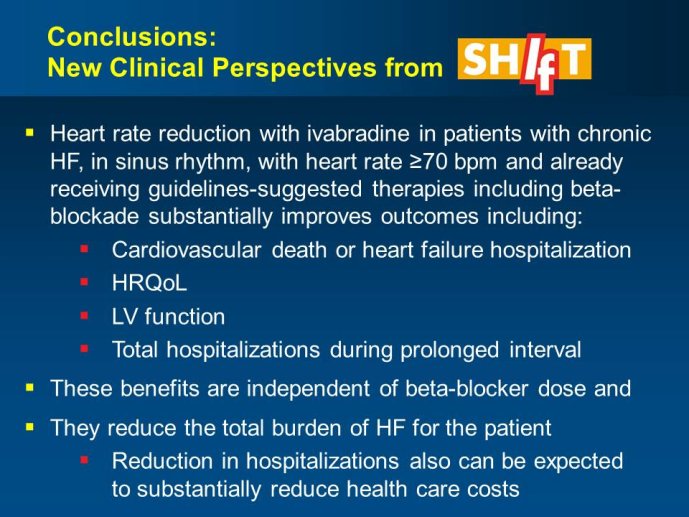
Abstract : SHIFT (Systolic Heart failure treatment with the If inhibitor ivabradine Trial) involved 6505 patients with moderate to severe heart failure (HF), heart rate ?70bpm in sinus rhythm, at least one HF hospitalization during the year prior to study, and LVEF ?35% who were receiving guidelinesbased HF therapy including maximized beta blockade, who were randomized to add either placebo or ivabradine (pure HR slowing drug) during a median 22.9 months follow-up. The results of SHIFT unambiguously demonstrated the benefits of HR slowing (placebo-subtracted ivabradinemediated HR reduction averaged approximately 10 bpm at 1 month and 1 year of therapy) in mitigating adversities of HF: 18% reduction in the primary composite SHIFT endpoint of cardiovascular death or HF hospitalization, 26% reduction in HF hospitalization (importantly reducing health care costs) and 26% reduction in HF death, significant and clinically meaningful >5 unit increase in quality of life (HQoL) by Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire and, among patients admitted to study with HR ?75bpm, significant reduction in mortality alone. The combination of improvement in natural history (survival, reduction in hospitalization) and improvement in HQoL is unusual with HF therapies and, specifically, is not a feature of beta blockade. Importantly, despite proven benefits of beta blockade,
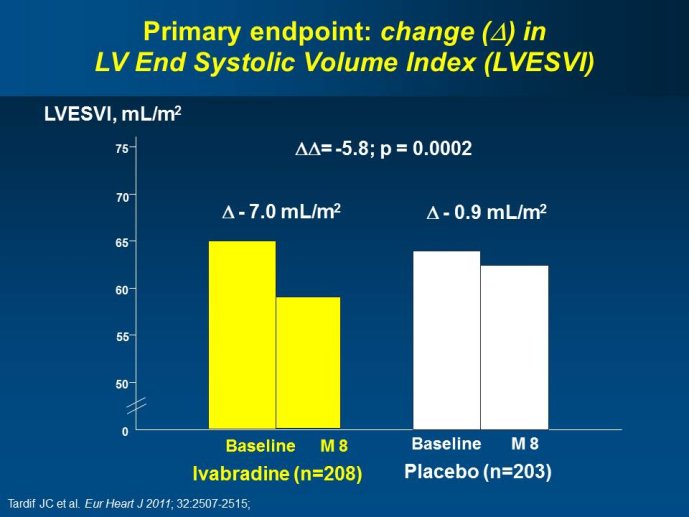
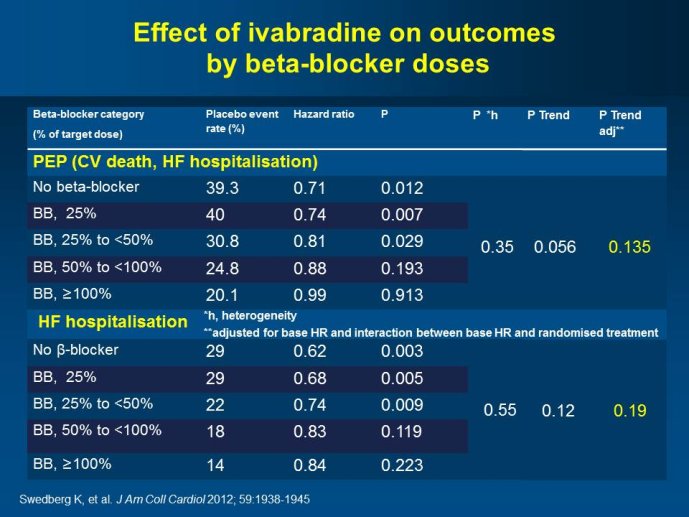
ivabradine-mediated HF benefits were independent of beta blocker dose and were solely attributable to HR slowing; in addition, ivabradine is devoid of many adverse effects of beta blockers unrelated to HR slowing. The plausibility of SHIFT results was supported by improved LV function and reduced LV volumes with ivabradine (vs placebo) in an echocardiographic substudy of SHIFT. The results of SHIFT
support a new clinical perspective for management of HF, i.e., pure HR slowing, currently possible pharmacologically only with ivabradine, provides profound natural history and QoL benefits for patients with moderate and severe systolic HF when undertaken on a background of standard HF therapy including beta blockade.
L’auteur n’a pas transmis de conflit d’intérêt concernant les données diffusées dans cette vidéo ou publiées dans la référence citée.
Conférence enregistrée : 9th Global Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists Forum • Paris 2012
Satellite symposium : new evidence, new guidelines and future developments with Ivabradine
-The new set of guidelines of the ESC Heart Failure Association and of other major international societies has recently been published. They have integrated the newest evidence with the main pharmacological innovation Ivabradine.
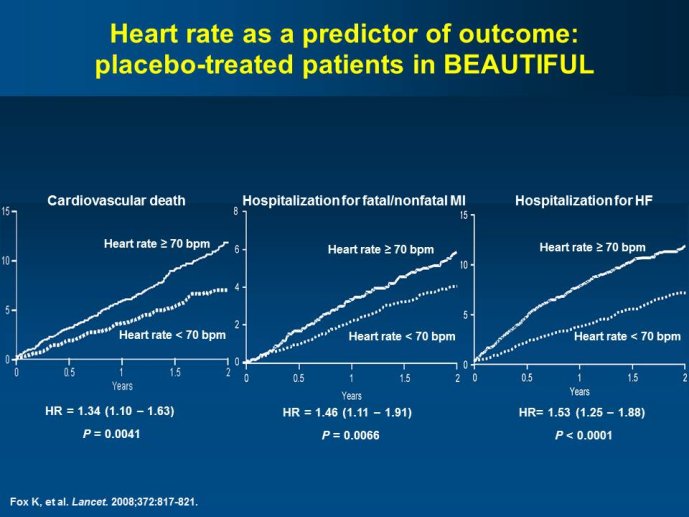
- Beyond the main results of the BEAUTIfUL and SHIfT trials, a number of pre-specified analyses have yielded results that will help optimizing the implementation of the use of this new agent in ischemic heart diseases as well as in heart failure with LV systolic dysfunction.
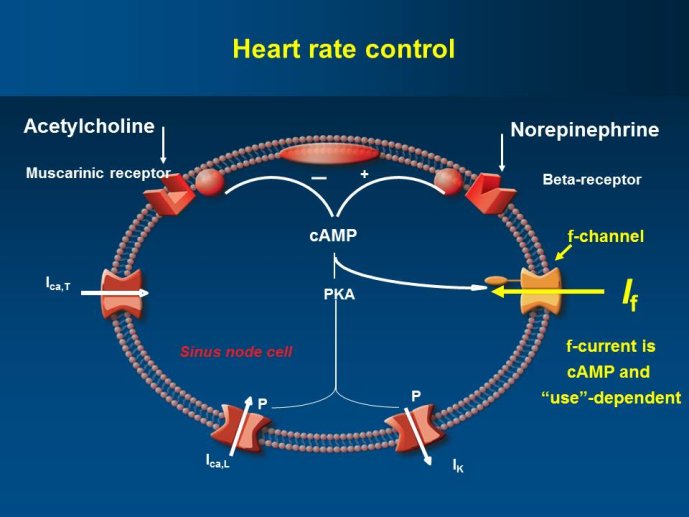
- Ivabradine is a specific inhibitor of the If current in the sinoatrial node providing a pure HR reduction without modification of other cardiovascular parameters. Treatment with ivabradine therefore provides an opportunity to assess the effects of lowering HR without directly altering other aspects of cardiac function. Beta-blockers and digoxin are other heart rate slowing agents, but with additional pharmacological effects, some of which are beneficial and others are deleterious, thus limiting the safety and adherence to these agents.
- It is likely that the newest heart failure guidelines will extend the recommendation of using mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) to Class I, level of evidence A. While, ivabradine benefits were observed in SHIfT on top of betablockers, of digoxin and also of MRAs, the question of the right timing of initiating ivabradine, relative to the optimization of beta-blocker and digoxin therapy and the timing of initiating an MRA is to be debated.
- BEAUTIfUL and SHIfT have also led to a series of stimulating hypotheses that constitute the rationale for the currently
SIGNIfY trial, which is enrolling patients with coronary artery disease and normal left ventricular systolic function with a resting HR of ?70 bpm. The primary endpoint will take into consideration only coronary artery disease outcomes.
- Is heart failure with preserved ejection fraction the next frontier?
Chairpersons: Jean-Claude TARDIF, Montréal, CAN - Faiez ZANNAD, Nancy, FRA
Réalisation, production : Canal U/3S et CERIMES
Keyword : Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists, Paris, 2012, Cardiovascular prevention, Baro-stimulation, ivabradine
Dans la même collection
-
Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum – Paris 2012 - Workshop 1 : New indications: Is hear…
DeliargyrisEfthymiosMODIGLIANI Workshop 1 - Friday November 30, 2012 : THE THROMBOSIS TRIALISTS WORKSHOP DOSE AND TARGET PATIENT POPULATIONS ISSUES Chairpersons: Peter CLEMMENSEN, Copenhagen, DEN - George-Andrei DAN,
-
Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum – Paris 2012 - Lunch Session 1 : Industry perspectiv…
WoehrleHolgerMODIGLIANI Lunch Debate Session 1 - Friday November 30, 2012 THE DEVICE THERAPY TRIALISTS WORKSHOP Chairpersons: Gaetano DE FERRARI, Pavia, ITA - Ileana PIÑA, New York, USA Webcast: Tariq AHMAD,
-
Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum – Paris 2012 - Workshop 1 : New indications: Is hear…
PrasadKrishnaMODIGLIANI Workshop 1 - Friday November 30, 2012 : THE THROMBOSIS TRIALISTS WORKSHOP DOSE AND TARGET PATIENT POPULATIONS ISSUES Chairpersons: Peter CLEMMENSEN, Copenhagen, DEN - George-Andrei DAN,
-
Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum – Paris 2012 - Workshop 1 : Different doses, differe…
VerheugtFreekMODIGLIANI Workshop 1 - Friday November 30, 2012 : THE THROMBOSIS TRIALISTS WORKSHOP DOSE AND TARGET PATIENT POPULATIONS ISSUES Chairpersons: Peter CLEMMENSEN, Copenhagen, DEN - George-Andrei DAN,
-
Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum – Paris 2012 - Lunch Session 1 : Non randomized and/…
PocockStuart J.MODIGLIANI Lunch Debate Session 1 - Friday November 30, 2012 THE DEVICE THERAPY TRIALISTS WORKSHOP Chairpersons: Gaetano DE FERRARI, Pavia, ITA - Ileana PIÑA, New York, USA Webcast: Tariq AHMAD,
-
Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum – Paris 2012 - Workshop 1 : New indications: Is hear…
ZannadFaiezMODIGLIANI Workshop 1 - Friday November 30, 2012 : THE THROMBOSIS TRIALISTS WORKSHOP DOSE AND TARGET PATIENT POPULATIONS ISSUES Chairpersons: Peter CLEMMENSEN, Copenhagen, DEN - George-Andrei DAN,
-
Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum – Paris 2012 - Workshop 1 : How to secure the optima…
GibsonMichaelMODIGLIANI Workshop 1 - Friday November 30, 2012 : THE THROMBOSIS TRIALISTS WORKSHOP DOSE AND TARGET PATIENT POPULATIONS ISSUES Chairpersons: Peter CLEMMENSEN, Copenhagen, DEN - George-Andrei DAN,
-
Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum – Paris 2012 - Workshop 1 : Industry viewpoint (Joer…
KoeckJean-LouisMODIGLIANI Workshop 1 - Friday November 30, 2012 : THE THROMBOSIS TRIALISTS WORKSHOP DOSE AND TARGET PATIENT POPULATIONS ISSUES Chairpersons: Peter CLEMMENSEN, Copenhagen, DEN - George-Andrei DAN,
-
Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum – Paris 2012 - Workshop 2 : Well Established Methods…
KoenigWolfgangMODIGLIANI Workshop 2 - Friday November 30, 2012 : ATHEROSCLEROSIS IMAGING IN CLINICAL TRIALS Facilitating the discovery of effective therapies Chairpersons: Jagat NARULA, New York, USA - Ahmed
-
Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum – Paris 2012 - Lunch Session 1 : Options of and alte…
AbrahamWilliam T.MODIGLIANI Lunch Debate Session 1 - Friday November 30, 2012 THE DEVICE THERAPY TRIALISTS WORKSHOP Chairpersons: Gaetano DE FERRARI, Pavia, ITA - Ileana PIÑA, New York, USA Webcast: Tariq AHMAD,
-
Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum – Paris 2012 - Workshop 1 : How to secure the optima…
GellerNancy L.MODIGLIANI Workshop 1 - Friday November 30, 2012 : THE THROMBOSIS TRIALISTS WORKSHOP DOSE AND TARGET PATIENT POPULATIONS ISSUES Chairpersons: Peter CLEMMENSEN, Copenhagen, DEN - George-Andrei DAN,
-
Cardiovascular Clinical Trialists (CVCT) Forum – Paris 2012 - Debate Session 5 : Ultrafiltration fo…
RossiGian PaoloMODIGLIANI Debate Session 5 - Saturday December 1st, 2012 NOVEL DIURETIC STRATEGIES IN HEART FAILURE Chairpersons: Keld KJELDSEN, Copenhagen, DEN - Gian Paolo ROSSI, Padua, ITA Webcast: Patrick