Notice
On the modified Palm version (workshop ERC Nemo Processus ponctuels et graphes aléatoires unimodulaires)
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
The Palm version of a stationary random measure is an important tool in probability. It is however not well known that there are in fact two Palm versions, with related but different interpretations. For lack of better terms, call the well known version standard and the less known version modified. In this talk we shall focus on the modified Palm version and its interpretation. The concepts of shift-coupling and mass-stationarity will play a key role
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Thème
Documentation
Documents pédagogiques
Dans la même collection
-
Absence of percolation for Poisson outdegree-one graphs (workshop ERC Nemo Processus ponctuels et g…
CoupierDavidA Poisson outdegree-one graph is a directed graph based on a marked Poisson point process such that each vertex has only one outgoing edge. We state the absence of percolation for such graphs
-
Point processes, cost and the growth of rank for locally compact groups (workshop ERC Nemo Processu…
AbertMiklósThe cost of a vertex transitive graph is the infimum of the expected degree of an invariant random wiring of the graph. Similarly, one can define the cost of a point process on a homogeneous
-
On the notion of dimension of unimodular discrete spaces (workshop ERC Nemo Processus ponctuels et …
KhezeliAliIn this talk we will define notions of dimension for unimodular random graphs and point-stationary point processes. These notions are in spirit similar to the Minkowski dimension and the
-
A notion of entropy for limits of sparse marked graphs (workshop ERC Nemo Processus ponctuels et gr…
AnantharamVenkatBordenave and Caputo (2014) defined a notion of entropy for probability distributions on rooted graphs with finite expected degree at the root. When such a probability distribution \rho has finite BC
-
Stein-Malliavin method for discrete alpha stable point processes (workshop ERC Nemo Processus ponct…
DecreusefondLaurentThe notion of discrete alpha-stable point processes generalizes to point processes the notion of stable distribution. It has been introduced and studied by Davydov, Molchanov and Zuyev a few
-
Strict monotonicity of percolation thresholds under covering maps (workshop ERC Nemo Processus ponc…
MartineauSébastienPercolation is a model for propagation in porous media that as introduced in 1957 by Broadbent and Hammersley. An infinite graph G models the geometry of the situation and a parameter p
-
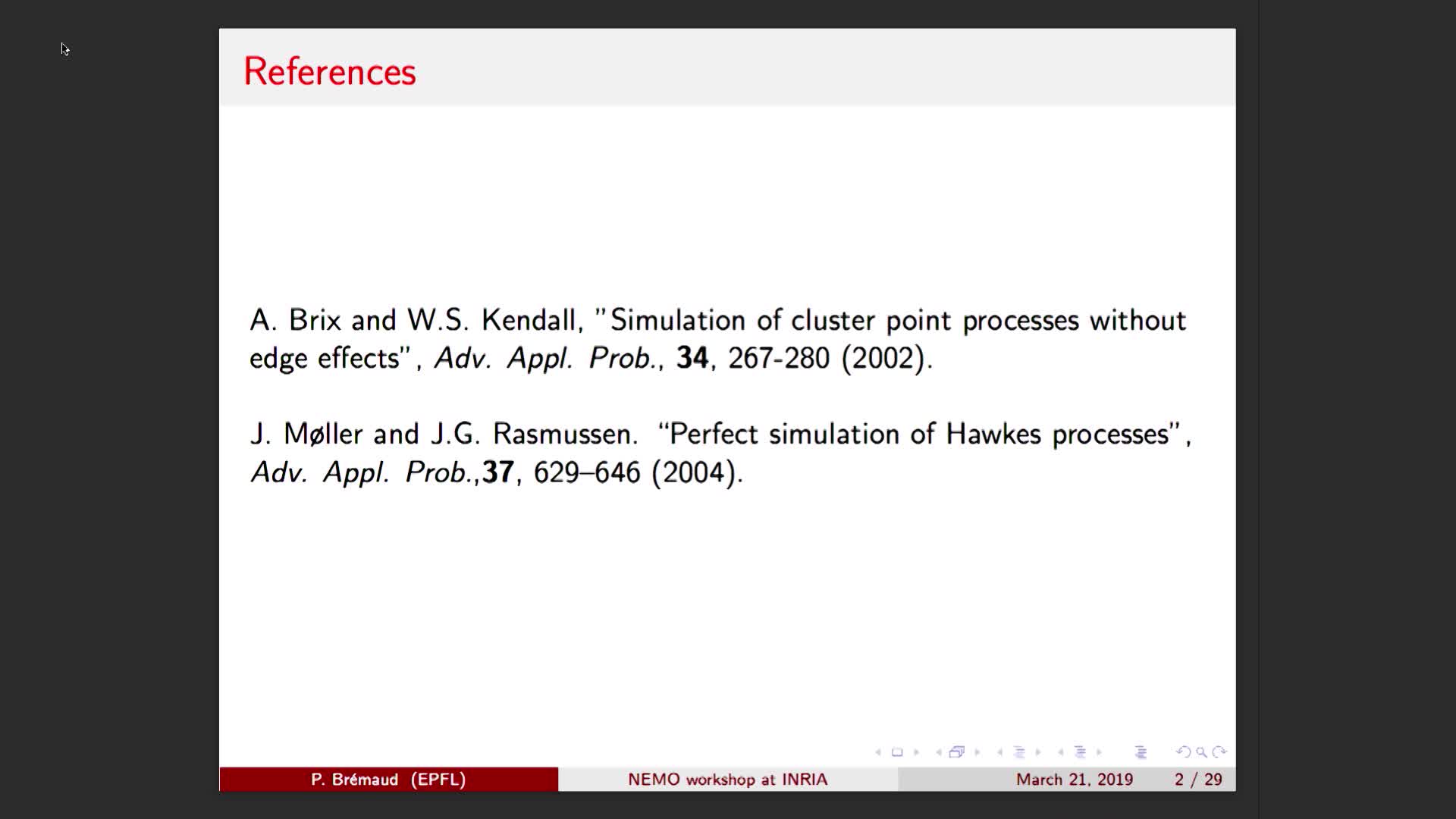
Sampling cluster point processes: a review (workshop ERC Nemo Processus ponctuels et graphes aléato…
BrémaudPierreThe theme of this talk is the sampling of cluster and iterated cluster point processes. It is partially a review, mainly of the Brix–Kendall exact sampling method for cluster point processes and
-
Eternal family trees and dynamics on unimodular random graphs (workshop ERC Nemo Processus ponctuel…
Haji MirsadeghiMir OmidThis talk is centered on covariant dynamics on unimodular random graphs and random networks (marked graphs), namely maps from the set of vertices to itself which are preserved by graph or
-
-
Subdiffusivity of random walks on random planar maps, via stationarity (workshop ERC Nemo Processus…
CurienNicolasRandom planar maps have been the subject of numerous studies over the last years. They are instance of stationary and reversible random planar maps exhibiting a non-conventional geometry at
-
Spectral embedding for graph classification (workshop ERC Nemo Processus ponctuels et graphes aléat…
LelargeMarcLearning on graphs requires a graph feature representation able to discriminate among different graphs while being amenable to fast computation. The graph isomorphism problem tells us that no
-
A stable marriage between order and disorder (workshop ERC Nemo Processus ponctuels et graphes aléa…
LastGünterStable matchings were introduced in a seminal paper by Gale and Shapley (1962) and play an important role in economics. Following closely Holroyd, Pemantle, Peres and Schramm (2009), we shall
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
Forward and backward limits
ThorissonHermannWe start by considering irreducible aperiodic positive recurrent Markov chains, and the proof of the main limit theorem...