Inria - Institut national de recherche en sciences et technologies du numérique

Nos dernières publications
Formally Verified (Post-Quantum) Cryptography, by Gilles Barthe (MPI-SP)
The NIST Post-Quantum Standardization program (2016-ongoing) aims to standardize a new generation of cryptographic algorithms resistant against quantum attackers.The talk will report and reflect on
Le projet SPARS : analyser pour comprendre la chirurgie
Pierre Jannin, directeur de recherche Inserm, nous parle du projet SPARS, un projet dont l'objectif est de développer des méthodes d'analyse de données pour mieux comprendre la chirurgie.
Webinaire « Retour d’expérience » de scientifiques « chiche » d’aller dans les classes – RDV du 25 …
Webinaire « Retour d’expérience » de scientifiques « chiche » d’aller dans les classes – RDV du 25 novembre 2025.
Une minute avec Mélanie Prague
De l’envie d’être juge pour enfants aux statistiques pour l’immunologie et la médecine translationnelle, Mélanie Prague, responsable de l’équipe-projet SISTM du Centre Inria de l’université de
Une minute avec Pierrick Legrand
De Nantes à Bordeaux en passant par le Mexique, Pierrick Legrand nous partage son parcours guidé par la passion des mathématiques et le plaisir d’apprendre chaque jour.
Désassemblons le numérique #E15 - Demain, des avions aussi silencieux que des oiseaux ?
Dans ce nouvel épisode de Désassemblons le numérique, nous vous invitons à prendre... un peu d'altitude ! Fermez les yeux et imaginez : un avion qui décolle sans fracas, qui traverse le ciel sans
Une minute avec Alessia Del Grosso
Rencontre avec Alessia Del Grosso, chercheuse ISFP (Inria Starting Faculty Position) au sein de l’équipe-projet Memphis du Centre Inria de l’université de Bordeaux.
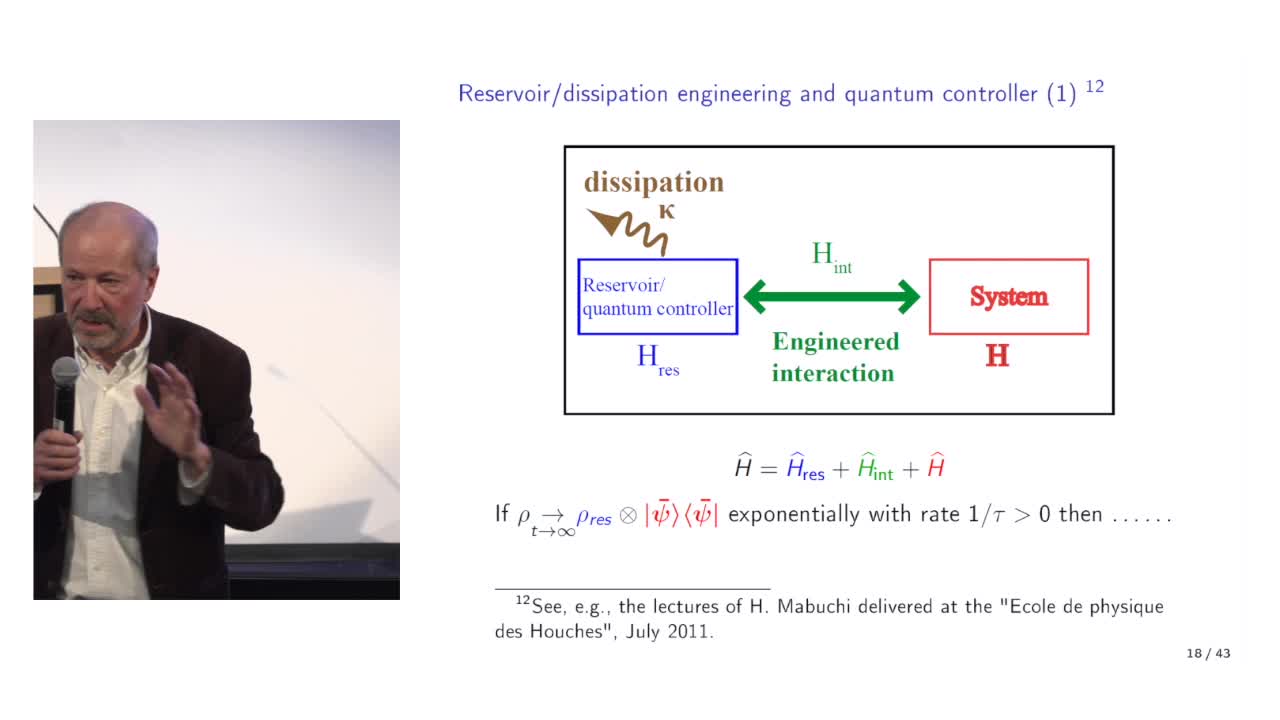
Quantum feedback engineering, bosonic codes and quantum error correction, by Pierre Rouchon (Mines …
Quantum error correction relies on a feedback loop. This feedback generally corresponds to a classical controller. Quantum error correction can also exploit the dissipation associated with the
Désassemblons le numérique - #Episode14 : Et si demain, l'IA lisait dans nos pensées ?
Dans ce nouvel épisode de Désassemblons le numérique, nous vous proposons un petit détour par… votre cerveau ! Enfin, plus précisément, par la façon dont les machines pourraient un jour le comprendre.
Une minute avec Michel Bergmann
Rencontre avec Michel Bergmann, directeur de recherche au sein de l’équipe Memphis, du Centre Inria de l'université de Bordeaux.
Risk and Return in Scientific Research
Intervention de Pierre Azoulay, lors des premières Rencontres du Programme Inria Quadrant qui ont eu lieu le 18 juin 2025, au Grand Amphithéâtre de l'Université Paris Cité.
High Risk High Reward Research Funding: Can We Learn from the US System?
Intervention de Martin Vetterli, lors des premières Rencontres du Programme Inria Quadrant qui ont eu lieu le 18 juin 2025, au Grand Amphithéatre de l'Université Paris Cité.
Intervenants et intervenantes
Docteur en informatique (Paris 11, 1985)
Directeur de recherches à l'Inria et à l'ENS Paris, membre du collège de l'Arcep (en 2022)
Professeur au Collège de France (2011-2012) du cours "Sciences des données : de la logique du premier ordre à la Toile" dans le cadre de la chaire annuelle "Informatique et sciences numériques"
Doctorat de mécanique ; directeur de thèse en Automatique et productique à Grenoble Alpes en 2015
enseignant chercheur au Département d'Informatique de l'Université de Reykjavik en 2011
Titulaire d'un doctorat en Informatique (Oxford Brookes University, 2010)
Rapporteur et membre du jury d'une thèse en Informatique à Université Côte d'Azur en 2024
Chargé de recherche au sein de l'équipe "Thoth project" de l'Inria Grenoble - Rhône-Alpes
Rapporteur lors d'une thèse soutenue à l'INSA Lyon en 2024
Ph. D. (Université de Cambridge, 1977)
Mathématicien. En poste au Department of statistics, University of California, Berkeley, California, USA (en 1985)
Informaticien. Chargé de recherche HDR INRIA, équipe Compilation et analyse, logiciel et matériel (CASH), Laboratoire de l'informatique du parallélisme (LIP, UMR5668 / URA1398), École normale supérieure, Lyon (2025)
Titulaire d'un doctorat de Mathématiques et Informatique, spécialité : Informatique, Bordeaux 1 (en 2007). - Maître de conférences, Université de Lorraine, LORIA (en 2018). - Professeur en informatique, Université de Lorraine (en 2024)
Professeur à la faculté EECS (Electrical Engineering and Computer Science) de l'Université de Berkeley (2019)
Chercheur en Informatique
Auteur d'une thèse en Sciences de l'ingénieur à Nice en 1991
Habilitation à diriger des recherches, université de Nice-Sophia Antipolis (2003)
Directeur de recherche au CNRS, laboratoire I3S, université de Nice-Sophia Antipolis (en 2016). Directeur de recherche CNRS, membre du Laboratoire d'Informatique Signaux et Systèmes de Sophia Antipolis (I3S), Université Côte d'Azur (en 2023)
Membre du jury lors d'une thèse soutenue à l'INSA Lyon en 2023
Directeur de thèse, université de Nice-Sophia Antipolis