Notice
Using High Performance Computing to decipher the impact of ageing process on collagens
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
Plant cells have to face environmental stress, and in this context, being able to decipher the organization of the plant plasma membrane is a key point to better understand this adaptability of plasma membranes in immune signaling, host-pathogen interactions or plant-microorganism interactions for instance.
Experimental procedures allow to study the composition and some properties of plant plasma membranes. Biophysical characterization of plasma membrane leaflets has already been carried out [1] [2]. Besides, in combination with this experimental data, molecular dynamics simulations are a very interesting way to investigate the dynamical behavior of lipids in membranes. Atomistic simulations are widely used but for increased system sizes, an approach called coarse-grained simulations, consisting of considering several atoms as one bead, is very useful and allows to reach larger scales. By this way, a model of animal plasma membrane has already been published [3]. However, the plasma membrane of plants is very poorly studied in modeling and simulation, which is particularly due to the lack of plant-specific lipids in databases. The use of high-performance computing can help to simulate larger systems in longer time duration.
The aim of our work is to be able to study the behavior of lipids in a plant plasma membrane. After preparing structures and topologies of the required lipids, membrane models of different compositions are simulated, therefore we run numerous molecular dynamics simulations on one node with CPU Intel Skylake and GPU NVIDIA P100. This work involves researchers from several different labs. This collaboration allows to get competences in experimental biophysics as well as modeling in this transdisciplinary project. Together with the use of data generated by experiments, notably lipid composition and biophysical properties of both plasma membrane leaflets, we combine atomistic and coarse-grained approaches to get insights into the characteristics and behavior of a model of plant plasma membrane. Indeed, we are able to get global membrane properties such as area per lipid, lipid tail order or bilayer thickness. Moreover, we investigate the dynamics and interactions of lipids of the two leaflets. Indeed, thanks to high-performance computing, this work allows to provide knowledge about leaflet communication, lipid-lipid interactions and lipid behavior in a plant plasma membrane.
Funding
This work has been funded by the ANR PLAYMOBIL.
References
[1] K. Grosjean et al., ‘Interactions between lipids and proteins are critical for organization of plasma membrane-ordered domains in tobacco BY-2 cells', Journal of Experimental Botany, vol. 69, no. 15, pp. 3545–3557, Jun. 2018, doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery152.
[2] A. Mamode Cassim et al., ‘Biophysical analysis of the plant-specific GIPC sphingolipids reveals multiple modes of membrane regulation', Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 296, p. 100602, Jan. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100602.
[3] H. I. Ingólfsson et al., ‘Lipid Organization of the Plasma Membrane', J. Am. Chem. Soc., vol. 136, no. 41, pp. 14554–14559, Oct. 2014, doi: 10.1021/ja507832e.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Thème
Documentation
Dans la même collection
-
Table ronde et discussions : infrastructures de calcul et ateliers de la donnée de recherche Data G…
CastexStéphanieRenardArnaudAlbaretLucieRenonNicolasDufayardJean-FrançoisPARTIE 5 : Des interactions croisées, à propos des compétences
-
Table ronde et discussions : infrastructures de calcul et ateliers de la donnée de recherche Data G…
CastexStéphanieRenardArnaudAlbaretLucieRenonNicolasDufayardJean-FrançoisPARTIE 2 : Les ateliers de la données
-
Table ronde et discussions : infrastructures de calcul et ateliers de la donnée de recherche Data G…
CastexStéphanieRenardArnaudAlbaretLucieRenonNicolasDufayardJean-FrançoisPARTIE 7 : Conclusion
-
Table ronde et discussions : infrastructures de calcul et ateliers de la donnée de recherche Data G…
CastexStéphanieRenardArnaudAlbaretLucieRenonNicolasDufayardJean-FrançoisPARTIE 4 : Des interactions croisées, liens entre le calcul et les données.
-
Table ronde et discussions : infrastructures de calcul et ateliers de la donnée de recherche Data G…
CastexStéphanieRenardArnaudAlbaretLucieRenonNicolasDufayardJean-FrançoisPARTIE 1 : Introduction et présentation des intervenants
-
Table ronde et discussions : infrastructures de calcul et ateliers de la donnée de recherche Data G…
CastexStéphanieRenardArnaudAlbaretLucieRenonNicolasDufayardJean-FrançoisPARTIE 6 : L'accompagnement autour de la gestion des données
-
Table ronde et discussions : infrastructures de calcul et ateliers de la donnée de recherche Data G…
CastexStéphanieRenardArnaudAlbaretLucieRenonNicolasDufayardJean-FrançoisPARTIE 3 : les liens entre les structures
-
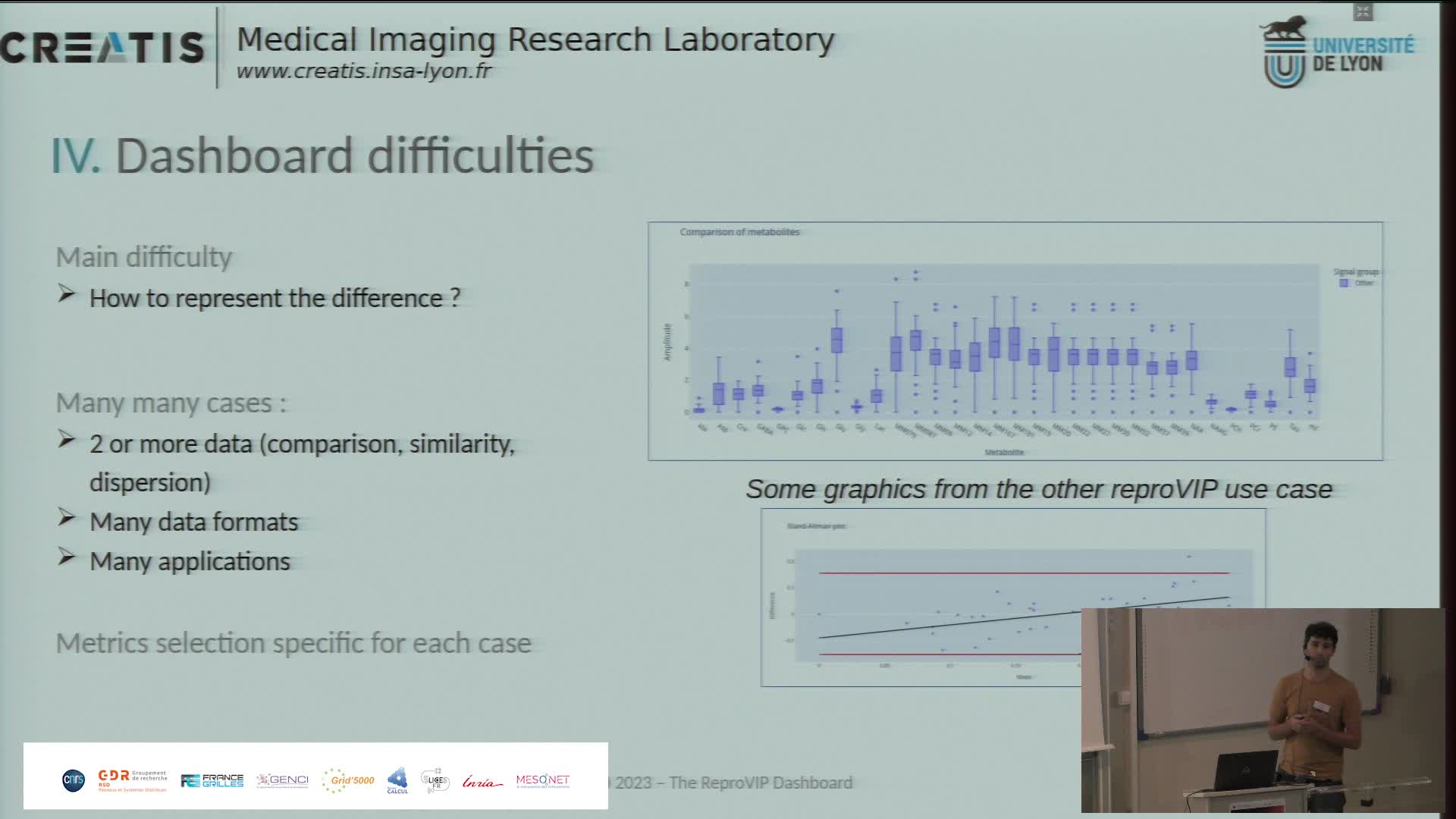
Présentation du dashboard ReproVIP pour visualiser la reproductibilité dans l'imagerie médicale
BonnetAxelLa plateforme d'imagerie virtuelle VIP [1] (https://vip.creatis.insa-lyon.fr) est un portail web de simulation et d'analyse d'images médicales. Elle existe depuis plus de 10 ans et a évolué pour
-
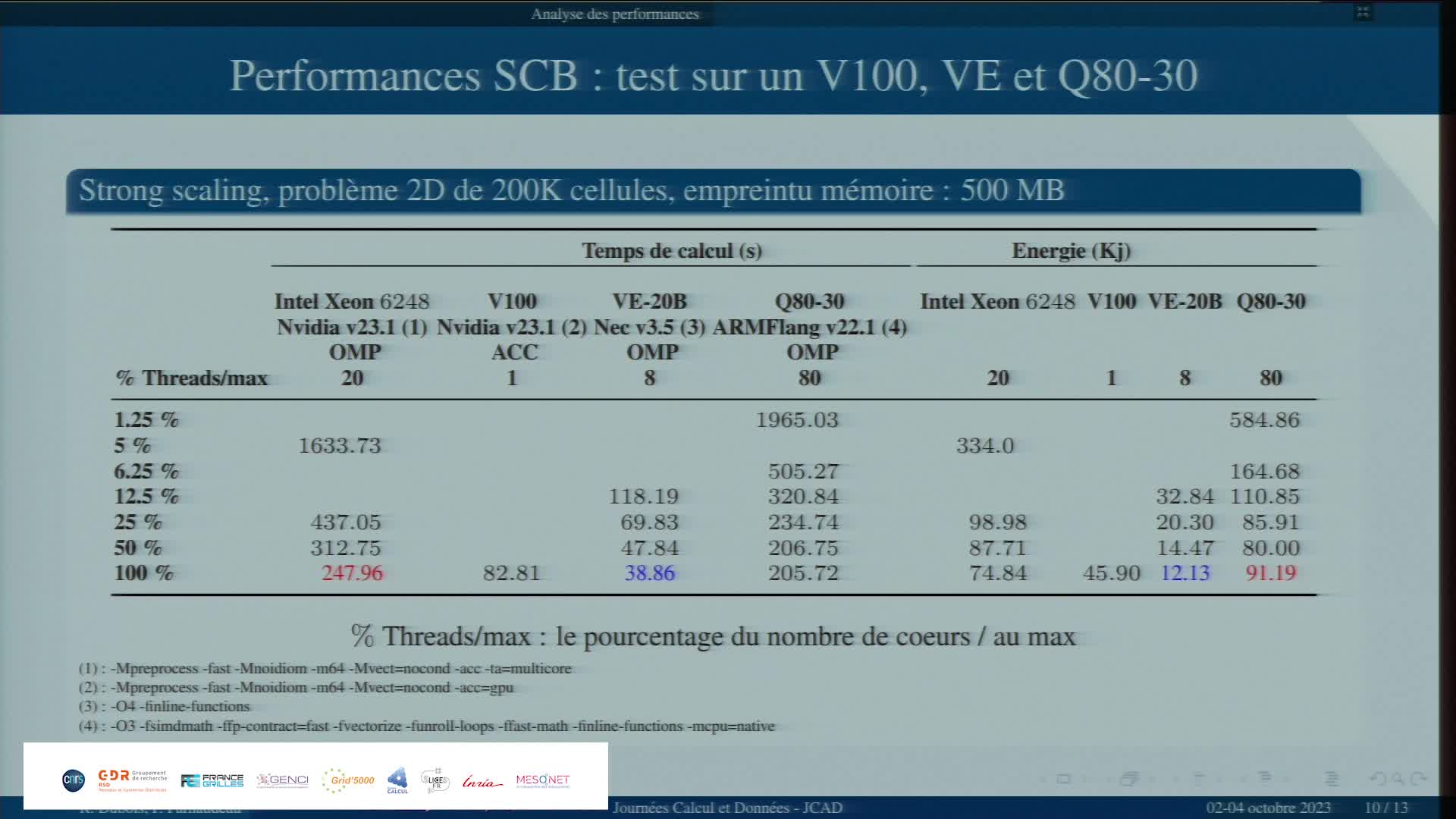
Etude comparative de 3 architectures spécialisées avec un code applicatif
ParnaudeauPhilippeÉtude comparative de 3 architectures spécialisées avec un code applicatif.
-
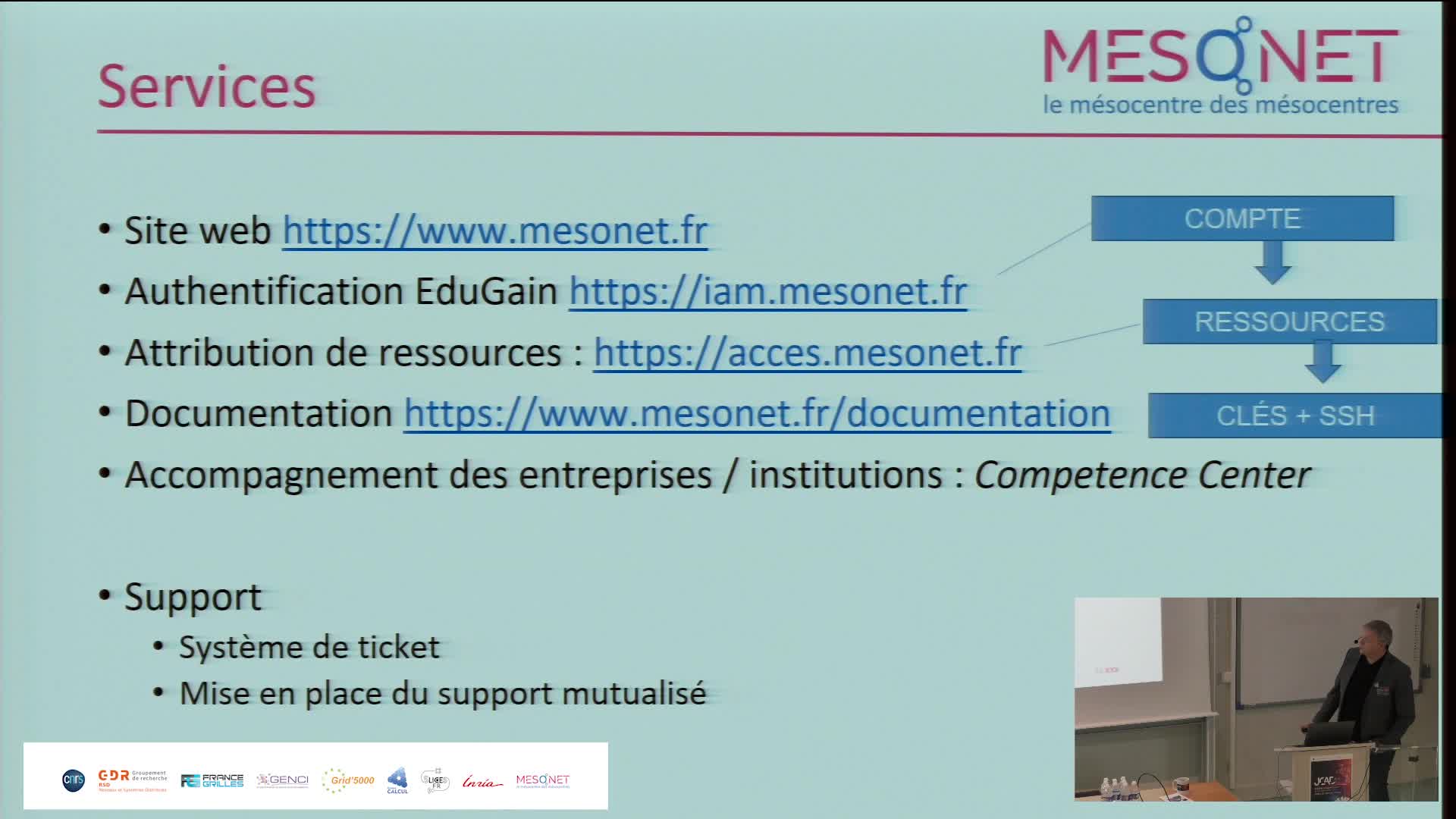
MesoNET : Structuration nationale des mésocentres de Calcul et de Données
RenardArnaudMesoNET répond aux besoins régionaux de calcul pour la recherche académiques, la formation et les entreprises en proposant des équipements structurants.
-
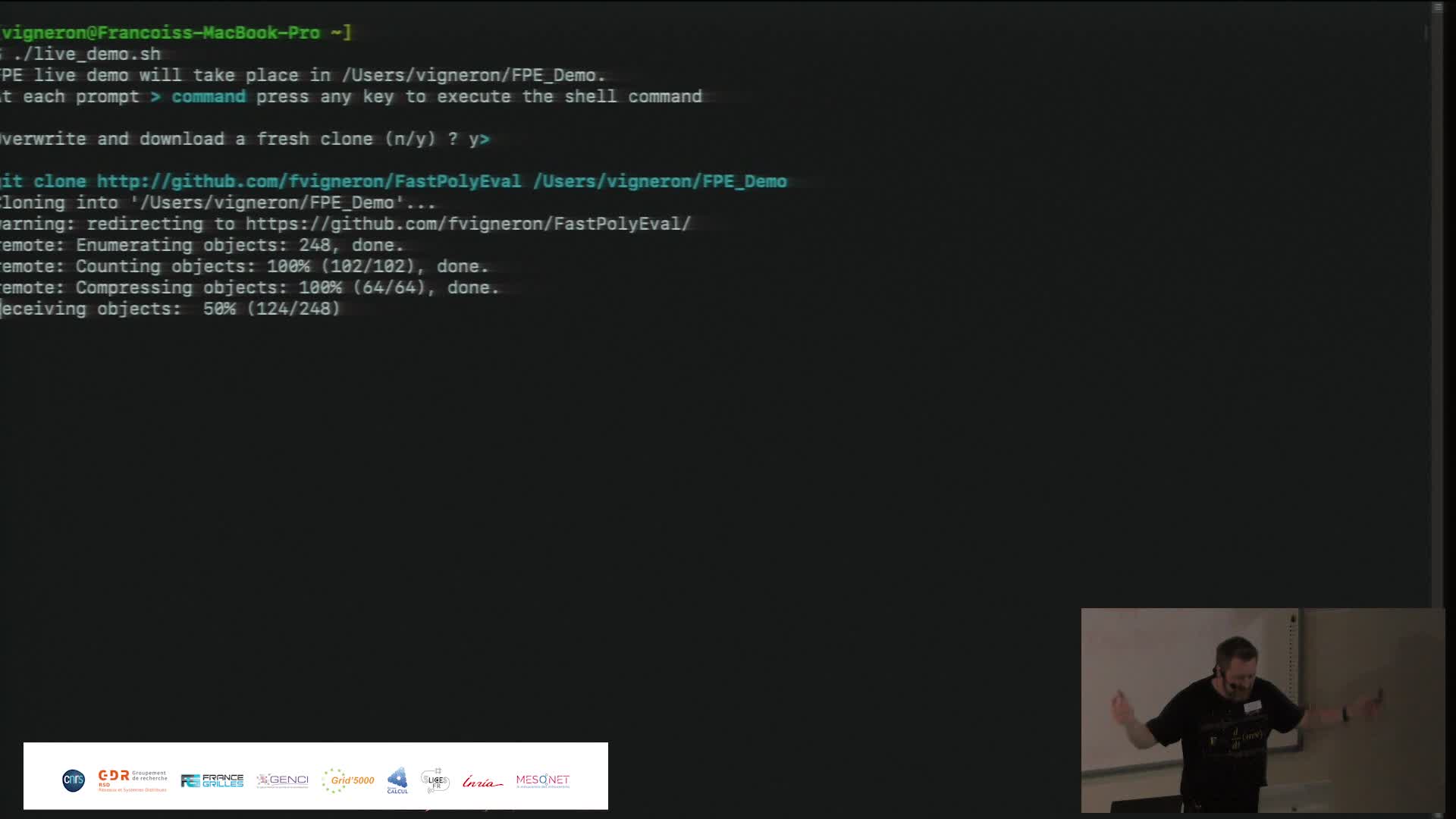
Fast Polynomial Evaluation (présentation + demo)
VigneronFrançoisWe propose a new algorithm for quickly evaluating polynomials. The FPE algorithm pre-conditions a complex polynomial P of degree d in time O(d log d), with a low multiplicative constant independent
-
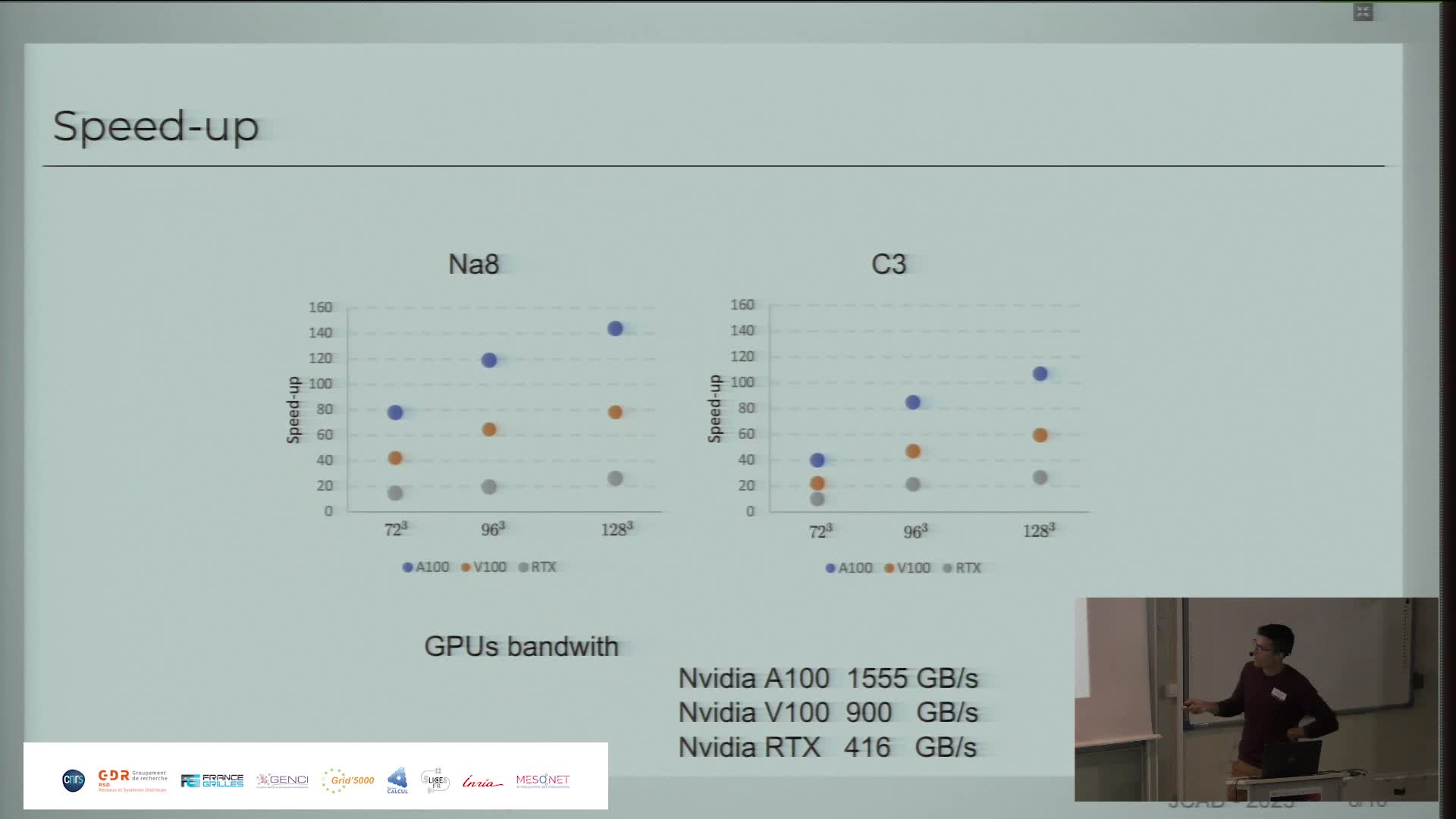
Présentation des performances paralléles du code QDD CUDA Fortran sur différentes Architectures GPU
PaipuriMahendraQDD est l'acronyme de Quantum Dissipative Dynamics, un ensemble de théories développées pour prendre en compte les corrélations dynamiques incohérentes dans les clusters et les molécules.