Notice
Carpentier - Introduction to some problems of composite and minimax hypothesis testing
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
A fundamental question in statistics is: how well can we fulfil a given aim given the data that one possesses? Answering this question sheds light on the possibilities, but also on the fundamental limitations, of statistical methods and algorithms. In this talk, we will consider some examples of this question and its answers in the hypothesis testing setting. We will consider the Gaussian model in (high) dimension p where the data are of the form X = \theta + \sigma \epsilon, where \epsilon is a standard Gaussian vector with identity covariance matrix. An important hypothesis testing question consists in deciding whether \theta belongs to a given subset \Theta_0 of R^p (null hypothesis) or whether the l_2 distance between \theta and the set \Theta_0 is larger than some quantity \rho (alternative hypothesis). We will investigate how difficult, or easy, this testing problem is, namely how large \rho has to be so that the testing problem has a meaningful solution - i.e. that a non-trivial tests exists. We will see through several examples that the answer to this question depends on the shape of \Theta_0 in an interesting way.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Sur le même thème
-
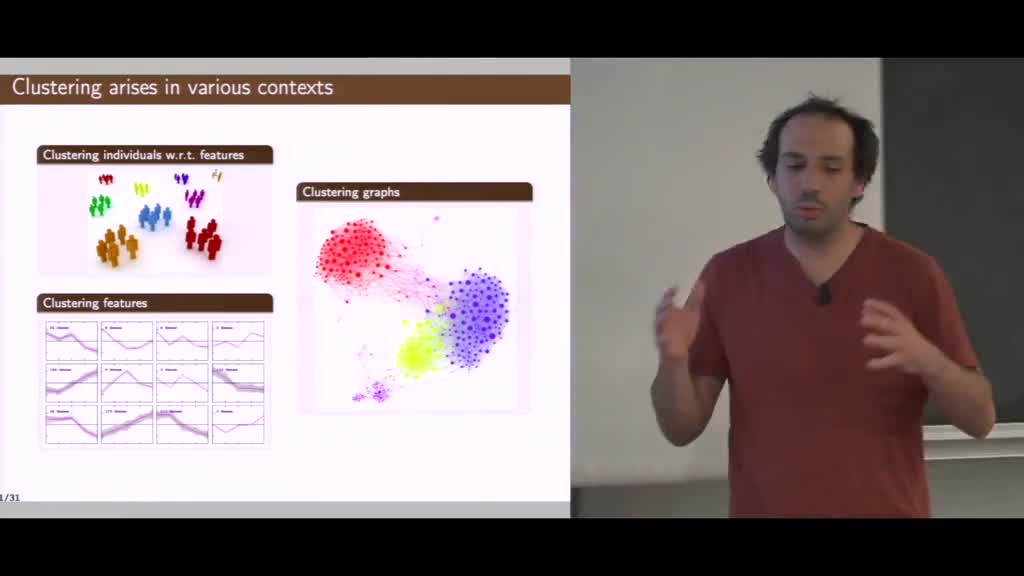
Verzelen - Clustering with the relaxed K-means
VerzelenNicolasThis talk is devoted to clustering problems. It amounts to partitionning a set of given points or the nodes of a given graph, in such a way that the groups are as homogeneous as possible. After
-
teaser statistique pour l'ingénieur
bande annonce du MOOC Statistique pour l'ingénieur
-
-
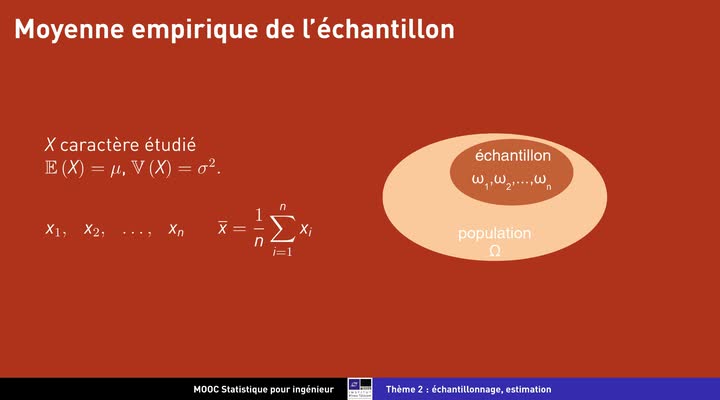
Echantillonnage, estimation : distributions d'échantillonnage
DelacroixFrédéricLecomteMicheldistributions d'échantillonnage
-
Notions de probabilités : couples de variables aléatoires
GarnierChristelleNotions de probabilités : couples de variables aléatoires
-
Optimisation et apprentissage
AspremontAlexandre d'L'apprentissage est un domaine émergent à l'interface de l'informatique et des statistiques, porté par la croissance exponentielle du flot de données générées par des applications aussi variées
-
Quelques modèles solubles pour le trafic routier
LasgouttesJean-MarcLe phénomène de formation spontanée de bouchons « en accordéon » sur les axes routiers est décrit notamment par la théorie des 3 phases de Kerner, qui décrit la structure du diagramme fondamental du
-
COURLIS : Satistiques dans le domaine de la santé
COURLIS est un MOOC de statistique appliquée, gratuit, totalement en ligne, ouvert à tous. Exemples d'applications dans le domaine de la santé. En coproduction avec
-
COURLIS : Satistiques dans le domaine de l'ingénierie
COURLIS est un MOOC de statistique appliquée, gratuit, totalement en ligne, ouvert à tous. Exemples d'applications dans le domaine de l'ingénierie En coproduction avec
-
COURLIS : MOOC de statistique appliquée
COURLIS est un MOOC de statistique appliquée, gratuit, totalement en ligne, ouvert à tous. en coproduction avec :
-
COURLIS : Satistiques dans le domaine du marketing
COURLIS est un MOOC de statistique appliquée, gratuit, totalement en ligne, ouvert à tous. Exemples d'applications dans le domaine du marketing En coproduction avec