Notice
Direction de la communication - Inria
Quel est le prix à payer pour la sécurité de nos données ?
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
À l'ère du tout connecté, la question de la sécurité de nos données personnelles est devenue primordiale. Comment faire pour garder le contrôle de nos données ? Comment déjouer les pièges de plus en plus sophistiqués tendus par des attaquants de toutes sortes ? Ces questions, nous nous les posons souvent et comme l'explique Brice Minaud, chercheur en cryptographie, la réponse n'est pas toujours simple. Parfois, il s'agit de trouver un juste équilibre entre l'efficacité et la sécurité...
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Thème
Sur le même thème
-
Les données sensibles : anonymisation ou pseudonymisation ?
MboméMarieLes données sensibles et/ou à caractère personnel ont une importance croissante dans nos travaux de recherche. Que l’on soit chercheur ou étudiant, la collecte, le traitement et l’analyse de ces
-
Penser les données numériques de santé – partie 3 – Penser la santé #13
BastianiFloraDubruelNoémieFerréFabriceQu’il s’agisse des dossiers médicaux en ligne ou des informations issues des appareils connectés, les données de santé sont désormais de plus en plus analysées par les chercheurs. Y a-t-il un risque à
-
Penser les données numériques de santé – partie 2 – Penser la santé #13
BastianiFloraDubruelNoémieFerréFabriceQu’il s’agisse des dossiers médicaux en ligne ou des informations issues des appareils connectés, les données de santé sont désormais de plus en plus analysées par les chercheurs. Y a-t-il un risque à
-
Penser les données numériques de santé – partie 1 – Penser la santé #13
BastianiFloraDubruelNoémieFerréFabriceQu’il s’agisse des dossiers médicaux en ligne ou des informations issues des appareils connectés, les données de santé sont désormais de plus en plus analysées par les chercheurs. Y a-t-il un risque à
-
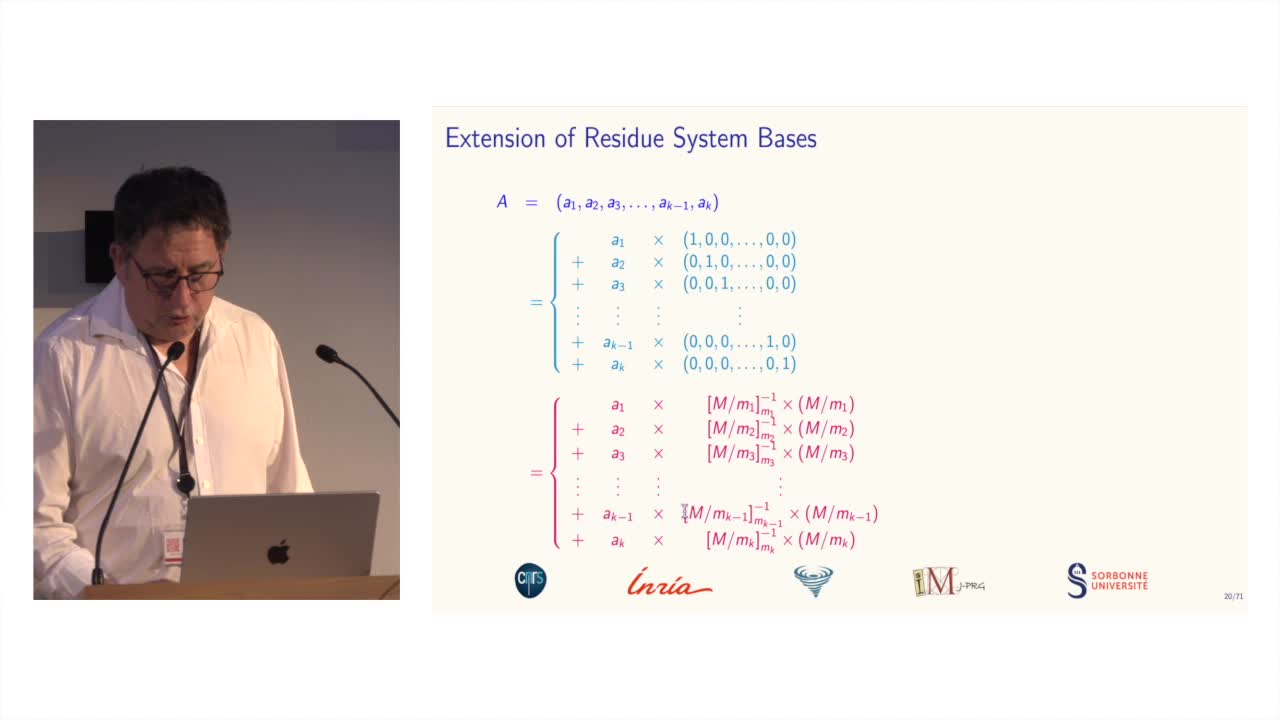
Des systèmes de numération pour le calcul modulaire
BajardJean-ClaudeLe calcul modulaire est utilisé dans de nombreuses applications des mathématiques...
-
Inauguration de l'exposition - Vanessa Vitse : Nombres de Sophie Germain et codes secrets
VitseVanessaExposé de Vanessa Vitse (Institut Fourier) : Nombres de Sophie Germain et codes secrets
-
Information Structures for Privacy and Fairness
PalamidessiCatusciaInformation Structures for Privacy and Fairness
-
AI and Human Decision-Making: An Interdisciplinary Perspective
CastellucciaClaudeThis seminar will talk about some of the privacy risks of these systems and will describe some recent attacks. It will also discuss why they sometimes fail to deliver. Finally, we will also show that
-
4.9. Goppa codes still resist
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuAll the results that we have seen this week doesn't mean that code based cryptography is broken. So in this session we will see that Goppa code still resists to all these attacks. So recall that
-
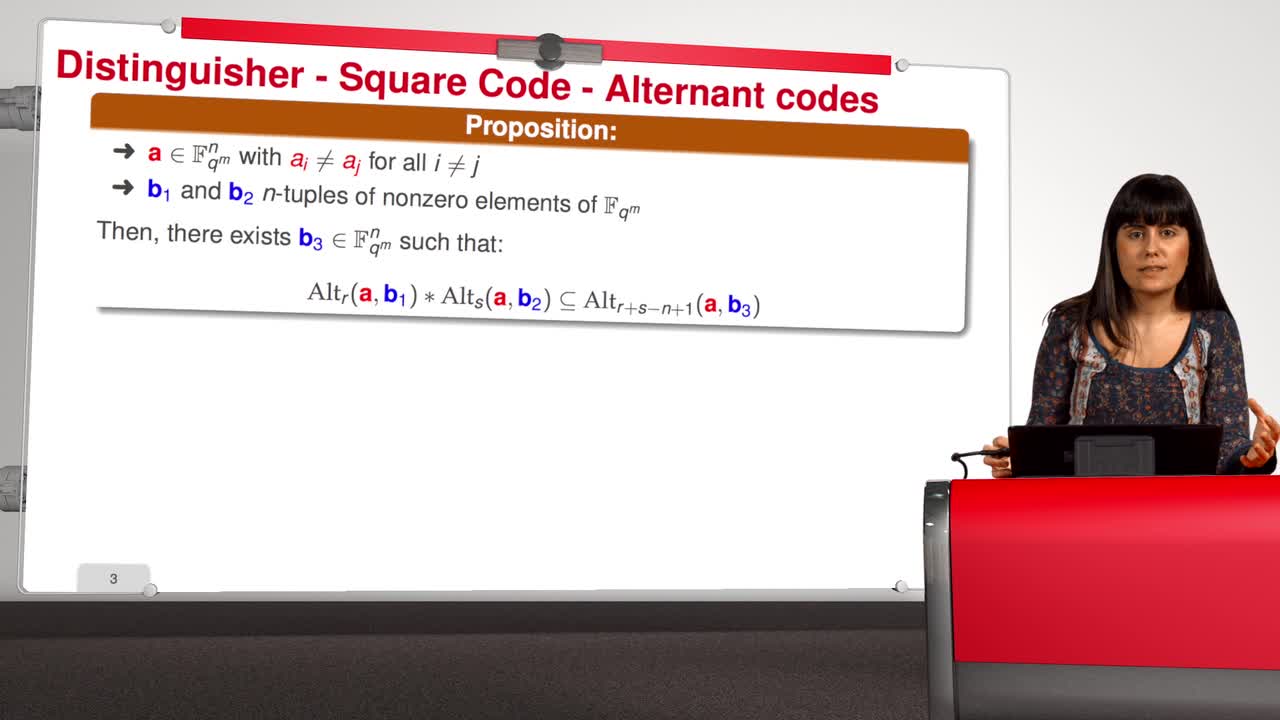
4.4. Attack against subcodes of GRS codes
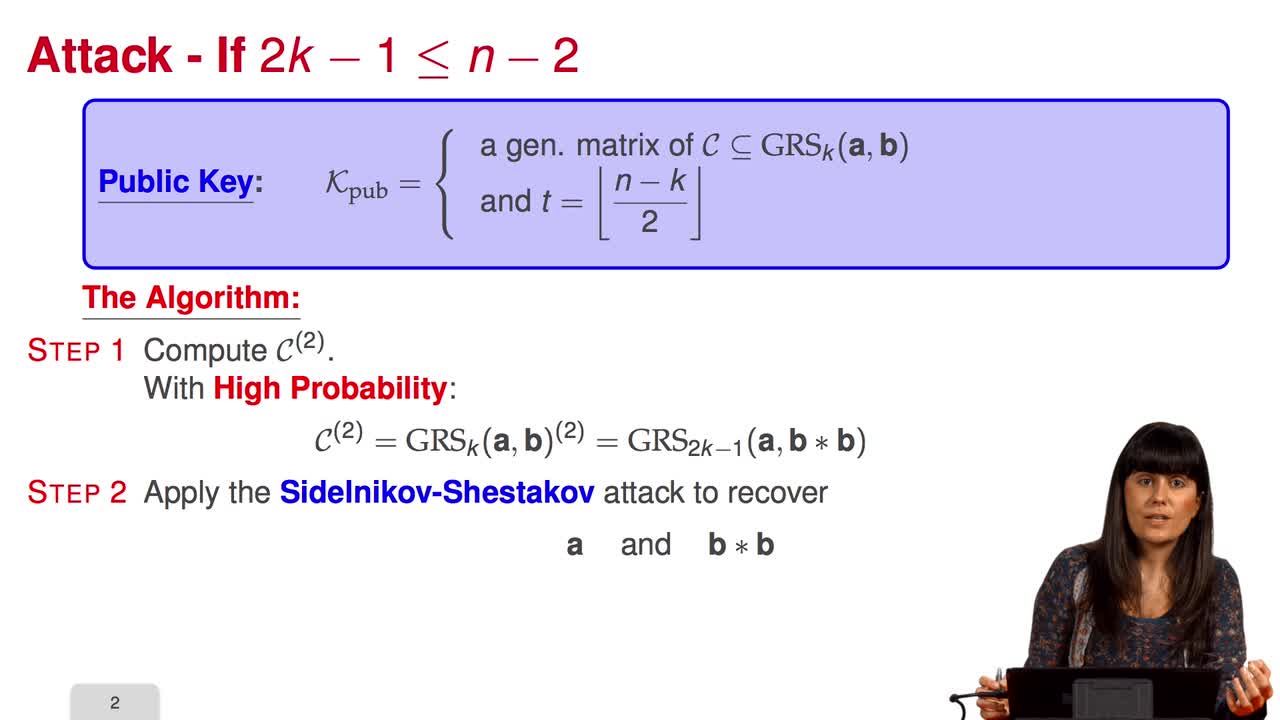
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will talk about using subcodes of a Generalized Reed–Solomon code for the McEliece Cryptosystem. Recall that to avoid the attack of Sidelnikov and Shestakov, Berger and
-
5.3. Attacks against the CFS Scheme
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will have a look at the attacks against the CFS signature scheme. As for public-key encryption, there are two kinds of attacks against signature schemes. First kind of attack is
-
4.7. Attack against Reed-Muller codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will introduce an attack against binary Reed-Muller codes. Reed-Muller codes were introduced by Muller in 1954 and, later, Reed provided the first efficient decoding algorithm