Notice
The question of connectedness in the Free Uniform Spanning Forest
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
The uniform measure on the set of all spanning trees of a finite graph is a classical object in probability. In an infinite graph, one can take an exhaustion by finite subgraphs, with some boundary conditions, and take the limit measure. The Free Uniform Spanning Forest (FUSF) is one of the natural limits, but it is less understood than the wired version, the WUSF. If we take a finitely generated group, then several properties of WUSF and FUSF have been known to be independent of the chosen Cayley graph of the group: the average degree in WUSF and in FUSF; the number of ends in the components of the WUSF and of the FUSF; the number of trees in the WUSF. Lyons and Peres asked if this latter should also be the case for the FUSF. In a joint work with Gábor Pete we give two different Cayley graphs of the same group such that the FUSF is connected in one of them and it has infinitely many trees in the other. Furthermore, since our example is a virtually free group, we obtained a counterexample to the general expectation, that such “tree-like” graphs would have connected FUSF. Several open questions are inspired by the results. We also present some preliminary results and conjectures on phase transition phenomena that happen if we put conductances on the edges of the underlying graph.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Thème
Dans la même collection
-
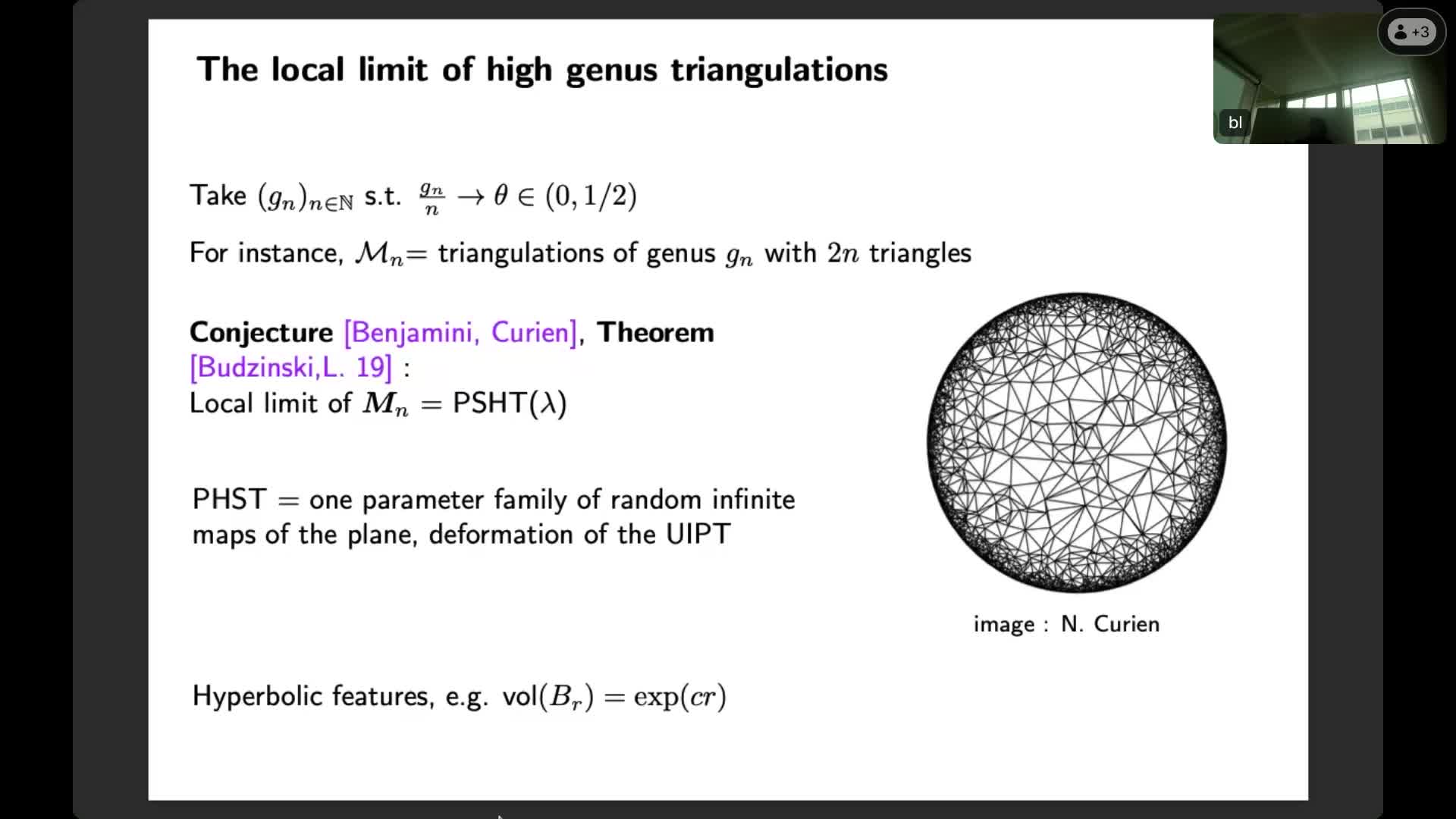
Combinatorial maps in high genus
LoufBaptisteCombinatorial maps are a model of discrete geometry: they are surfaces made by gluing polygons along their sides, or equivalently, graphs drawn on surfaces. In this talk, I'll focus on the study of
-
Do there exist expanders with non-negative curvature ?
SalezJustinIn this talk I will briefly recall the framework of local weak limits of finite graphs introduced by I. Benjamini and O. Schramm
-
Tail bounds for detection times in mobile hyperbolic graphs
MitscheDieterMotivated by Krioukov et al.'s model of random hyperbolic graphs for real-world networks, and inspired by the analysis of a dynamic model of graphs in Euclidean space by Peres et al., we introduce a
-
Online matching for the multiclass Stochastic Block Model
SOPRANO LOTONahuelA matching in a graph is a set of edges that do not share endpoints. Developing algorithms that find large matchings is an important problem. An algorithm is said to be online if it has to construct
-
Critical cluster cascades
KirchnerMatthiasWe consider a sequence of Poisson cluster point processes...
-
Point processes on higher rank symmetric spaces and their cost
MellickSamuelCost is a natural invariant associated to group actions and invariant point processes on symmetric spaces (such as Euclidean space and hyperbolic space). Informally, it measures how difficult it is to
-
Parallel server systems in extended heavy traffic
CastielEyalThe standard setting for studying parallel server systems (PSS) at the diffusion scale is based on the heavy traffic condition (HTC)...
-
The Maximal Agreement Subtree problem for random trees
BudzinskiThomasConsider two binary trees whose leaves are labelled from 1 to n.
-
An Improved Lower Bound on the Largest Common Subtree of Random Leaf-Labeled Binary Trees
KhezeliAliIt is known that the size of the largest common subtree...
-
Reversible Markov decision processes
AnantharamVenkatA Markov decision process is called reversible if for every stationary Markov control strategy the resulting Markov chain is reversible.
-
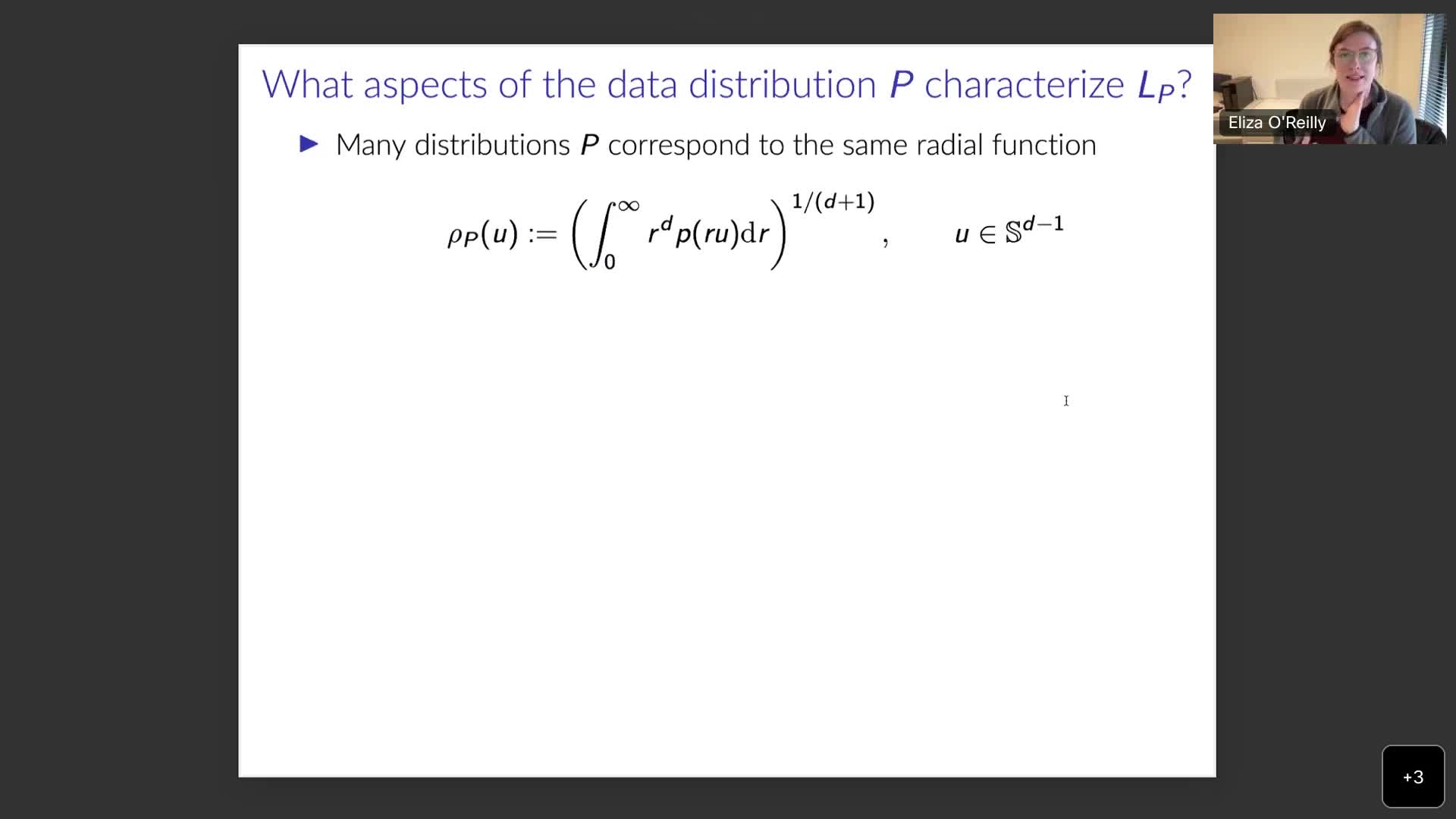
Optimal Convex and Nonconvex Regularizers for a Data Source
O'ReillyElizaRegularization is a widespread technique used in statistical estimation problems that helps to capture low dimensional structure in the data and improve signal recovery.
-
Tropical convexity: application to linear programming and mean payoff games
GaubertStéphaneLinear programming, and more generally convex semialgebraic programming, makes sense...
Sur le même thème
-
Bruit, erreur, anomalie et incertitude dans les données-PUDD
RossiFabriceLes données collectées sont systématiquement soumises à des perturbations de diverses natures, depuis le bruit de mesure de capteurs jusqu’aux erreurs de saisie.
-
Combinatorial maps in high genus
LoufBaptisteCombinatorial maps are a model of discrete geometry: they are surfaces made by gluing polygons along their sides, or equivalently, graphs drawn on surfaces. In this talk, I'll focus on the study of
-
Do there exist expanders with non-negative curvature ?
SalezJustinIn this talk I will briefly recall the framework of local weak limits of finite graphs introduced by I. Benjamini and O. Schramm
-
Tail bounds for detection times in mobile hyperbolic graphs
MitscheDieterMotivated by Krioukov et al.'s model of random hyperbolic graphs for real-world networks, and inspired by the analysis of a dynamic model of graphs in Euclidean space by Peres et al., we introduce a
-
Sofic entropy of processes on infinite random trees
BordenaveCharlesThis is a joint work with Agnes Backhausz et Balasz Szegedy. We define a natural notion of micro-state entropy...
-
Online matching for the multiclass Stochastic Block Model
SOPRANO LOTONahuelA matching in a graph is a set of edges that do not share endpoints. Developing algorithms that find large matchings is an important problem. An algorithm is said to be online if it has to construct
-
Critical cluster cascades
KirchnerMatthiasWe consider a sequence of Poisson cluster point processes...
-
Point processes on higher rank symmetric spaces and their cost
MellickSamuelCost is a natural invariant associated to group actions and invariant point processes on symmetric spaces (such as Euclidean space and hyperbolic space). Informally, it measures how difficult it is to
-
Parallel server systems in extended heavy traffic
CastielEyalThe standard setting for studying parallel server systems (PSS) at the diffusion scale is based on the heavy traffic condition (HTC)...
-
The Maximal Agreement Subtree problem for random trees
BudzinskiThomasConsider two binary trees whose leaves are labelled from 1 to n.
-
An Improved Lower Bound on the Largest Common Subtree of Random Leaf-Labeled Binary Trees
KhezeliAliIt is known that the size of the largest common subtree...
-
Reversible Markov decision processes
AnantharamVenkatA Markov decision process is called reversible if for every stationary Markov control strategy the resulting Markov chain is reversible.