Notice
Xsun Drones Solaires - Journées Drones et Cap' 2023
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
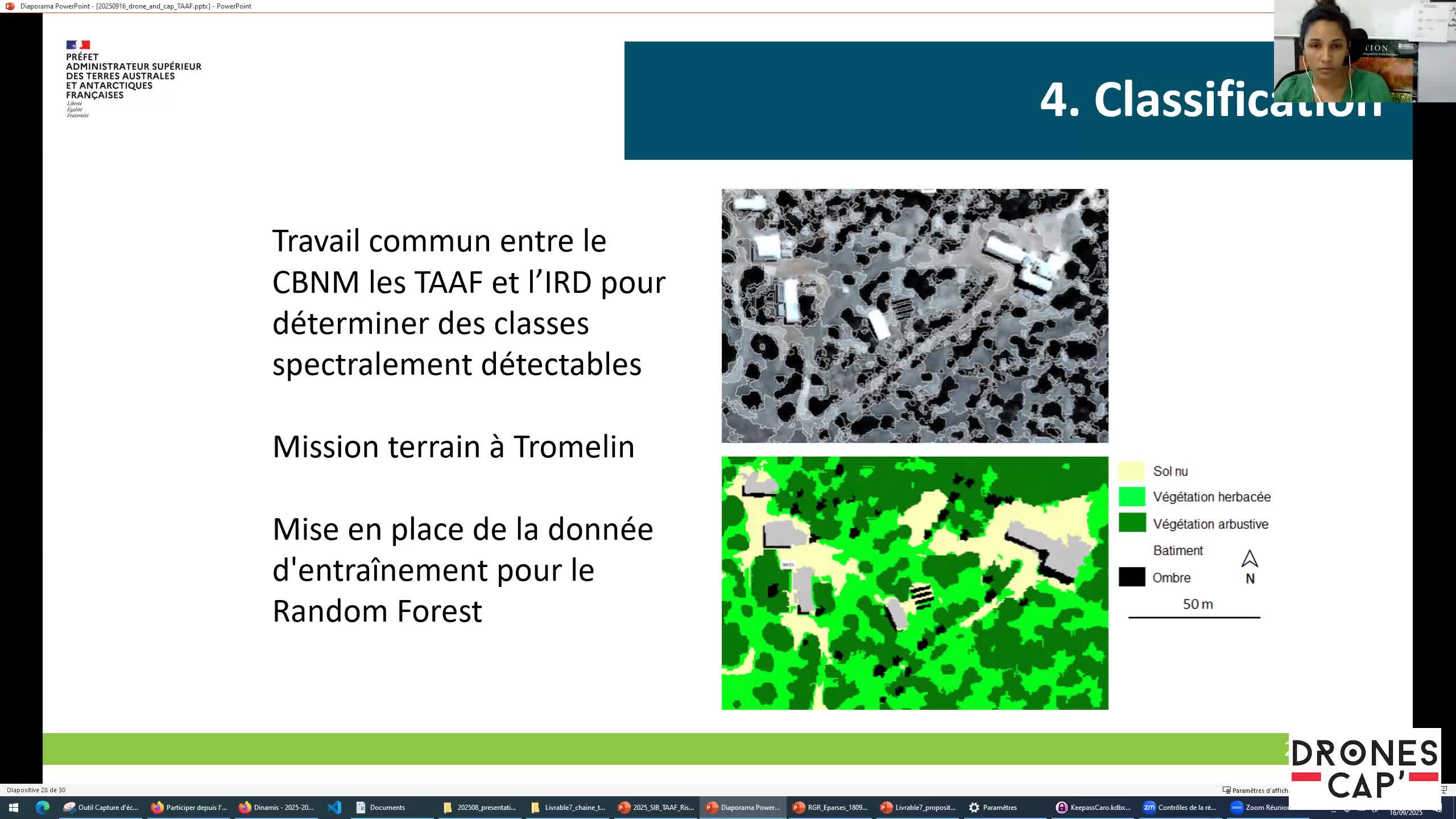
Descriptif
During the last decade, small and medium drones with less than 25kg take-off weight have become indispensable tools to serve a variety of commercial and scientific applications in the Geospatial domain. However, due to their restricted autonomy and ability to carry adequate payloads, their operations were limited to small-scale projects and VLOS opera- tions. So far, large-scale applications in precision agriculture and environmental monitoring require manned aerial platforms that are costly and cumbersome. A capable low-altitude, long-endurance platform that provides extensive autonomy and is able to carry a range of high-quality bespoke sensors to enable new scientific and operational commercial applica- tions is required. During the last years, the XSun team has developed a solar electric powered fixed wing platform that enhances the operational limits of small UAS and closes observation gaps between small UAS and manned airborne as well as spaceborne platforms. By exploiting the large wing area for photovoltaic energy generation, the platform is capable of 8 hours of autonomous flight during good solar conditions. Redundant communication links consist of a long-range antenna and Satellite communications enable safe BVLOS operations up to 120km from its base station. Due to its powerful yet extremely quiet engines, the UAS is able to operate with a very low environmental impact at altitudes down to 90m above the ground. An adaptable payload bay enables the operation of bespoke sensor payloads, which include RGB, multispectral, thermal, and LiDAR sensors up to 5kg. In a partnership with PhaseOn, XSun integrated the iXM camera series (iXM-RS150,iXM- GS120,iXM-100) as its prime optical sensor. Its base version with 100 MPixel is available as RGB and 4-Band CIR configuration with 35, 80, and 150mm lenses that enable ultra-high geometric resolutions of 0.6cm GSD from 90m latitude. This paper introduces two case studies that demonstrate the utility of the Solar Sx1.2 in scientific research to monitor plastic pollution and marine wildlife in the coastal zones and a vegetation mapping project to estimate biomass and carbon capture using the PhaseOne iXM100 camera system. In a proof of concept study commissioned and supported by the Joint Research Centre (JRC) along the southern French Mediterranean Sea near Perpignan, the XSun team performed a range of resolution tests that demonstrate the detectability of plastic elements in the sea as well as monitoring flights that reached up to 30km out to the sea at flying heights from 100 up to 300m under different wind conditions. The second study, commissioned by Skylogic Australia, was carried out as a mapping project in the Australian outback intending to map vegetation, estimate vegetation health and biomass and thus cap- tured carbon. Both case studies show encouraging results and demonstrate the capabilities of the new long-endurance low-altitude platform. The large payload bay enables the integration of ver- satile and bespoke sensor combinations. Following on, the team will continue to improve the performance and versatility of the system to enable so far unfeasible applications.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Sur le même thème
-
Retours d'expérience sur l'usage du drone multispectral DJI Mavic 3M pour la caractérisation de la …
MouquetPascalKurzrockCarolineEn tant que gestionnaire d'espaces protégés isolés, les Terres Australes et Antarctiques Françaises recherchent des méthodes de suivi pratiques et reproductibles pour améliorer la connaissance et la
-
Reconfigurable Underwater Robot (RUR): robot architecture and propulsion technology for maneuverabi…
Fagundes GasparotoHenriqueVerduTitouanReconfigurable Underwater Robot (RUR): robot architecture and propulsion technology for maneuverability and water tightness
-
Sécurité et Réglementation Drones - Journées Drones et Cap' 2023
CornuFrançoisSécurité et Réglementation Drones - Journées Drones et Cap' 2023
-
Photogrammétrie vs. lasergrammétrie par drone aérien sur la Côte d'Émeraude - Journées Drones et Ca…
JamesDorothéePhotogrammétrie vs. lasergrammétrie par drone aérien sur la Côte d'Émeraude
-
L'utilisation des drones pour un suivi spatio-temporel des activités de bioturbation par les crabes…
MichaudEmmaL'utilisation des drones pour un suivi spatio-temporel des activités de bioturbation par les crabes des vasières tropicales
-
Réaliser une campagne de drones à Paris - Journées Drones et Cap' 2023
GoretMarineRéaliser une campagne de drones à Paris
-
Système actif hyper-fréquences porté par drone - Journées Drones et Cap' 2023
PaillouPhilippeSystème actif hyper-fréquences porté par drone
-
Apport de la radio-logicielle pour l’analyse des problèmes de communication d’un drone d’observatio…
Le GallThierryApport de la radio-logicielle pour l’analyse des problèmes de communication d’un drone d’observation du littoral
-
Prospection thermique par drone en Archéologie - Journées Drones et Cap' 2023
FovetEliseVoldoireOlivierVautierFranckToumazetFrédéricDackoMarionČučkovićZoranCette communication présente les premiers résultats d’une étude en cours sur la reconnaissance des vestiges archéologiques via des capteurs thermiques embarqués sur drone. L’utilisation de cette
-
Evaluation topographique du tandem Drone Matrice 300RTK + LIDAR L1 - Journées Drones et Cap' 2023
FleuryJulesÉvaluer la précision topographique d'un relevé combinant le capteur LiDAR L1 et le drone Matrice 300RTK
-
Caractérisation des habitats piscicoles d'une rivière intermittente par imagerie drone - Journées D…
LejotJérômeCaractérisation des habitats piscicoles d'une rivière intermittente par imagerie drone
-
Contribution des infrarouges de l’Altum-PT pour la cartographie des littoraux de carbone bleu - Jou…
CollinAntoineLes écosystèmes de carbone bleu, tels que les marais maritimes, les mangroves et les herbiers marins, jouent un rôle crucial dans la séquestration du carbone et la protection des côtes...