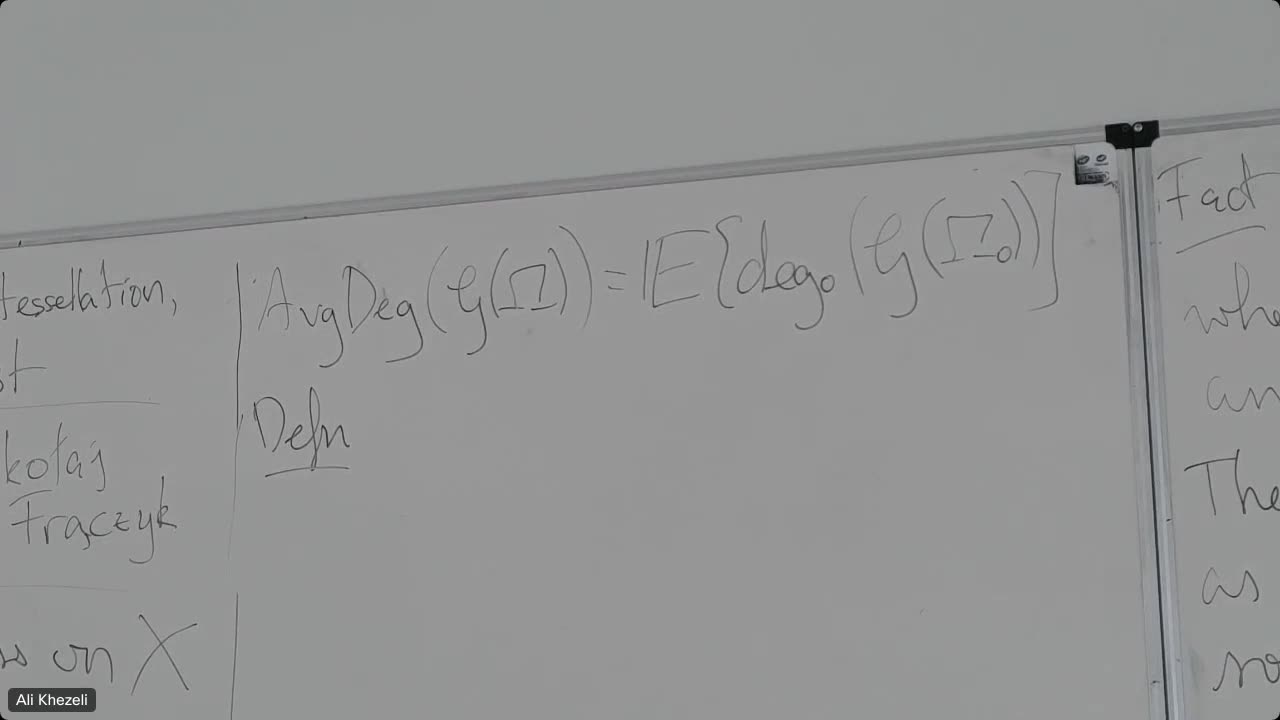Notice
Finitary random interlacements and the Gaboriau-Lyons problem
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
The von Neumann-Day problem asks whether every non-amenable group contains a non-abelian free group. It was answered in the negative by Ol'shanskii in the 1980s. The measurable version (formulated by Gaboriau-Lyons) asks whether every non-amenable measured equivalence relation contains a non-amenable treeable subequivalence relation. This paper obtains a positive answer in the case of arbitrary Bernoulli shifts over a non-amenable group, extending work of Gaboriau-Lyons. The proof uses an approximation to the random interlacement process by random multistep of geometrically-killed random walk paths. There are two applications: (1) the Gaboriau-Lyons problem for actions with positive Rokhlin entropy admits a positive solution, (2) for any non-amenable group, all Bernoulli shifts factor onto each other.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Thème
Dans la même collection
-
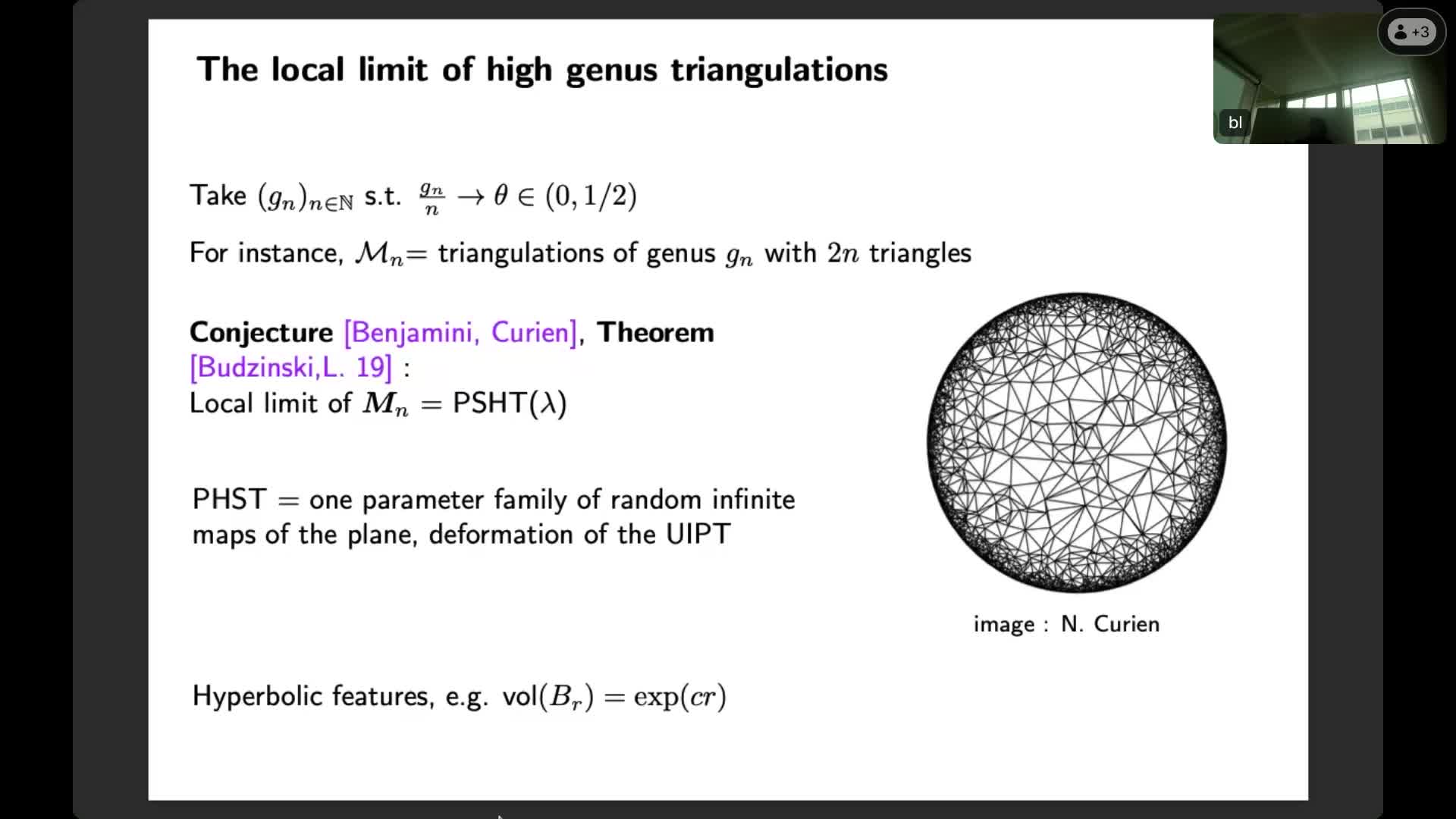
Combinatorial maps in high genus
LoufBaptisteCombinatorial maps are a model of discrete geometry: they are surfaces made by gluing polygons along their sides, or equivalently, graphs drawn on surfaces. In this talk, I'll focus on the study of
-
Do there exist expanders with non-negative curvature ?
SalezJustinIn this talk I will briefly recall the framework of local weak limits of finite graphs introduced by I. Benjamini and O. Schramm
-
Tail bounds for detection times in mobile hyperbolic graphs
MitscheDieterMotivated by Krioukov et al.'s model of random hyperbolic graphs for real-world networks, and inspired by the analysis of a dynamic model of graphs in Euclidean space by Peres et al., we introduce a
-
Online matching for the multiclass Stochastic Block Model
SOPRANO LOTONahuelA matching in a graph is a set of edges that do not share endpoints. Developing algorithms that find large matchings is an important problem. An algorithm is said to be online if it has to construct
-
Critical cluster cascades
KirchnerMatthiasWe consider a sequence of Poisson cluster point processes...
-
Point processes on higher rank symmetric spaces and their cost
MellickSamuelCost is a natural invariant associated to group actions and invariant point processes on symmetric spaces (such as Euclidean space and hyperbolic space). Informally, it measures how difficult it is to
-
Parallel server systems in extended heavy traffic
CastielEyalThe standard setting for studying parallel server systems (PSS) at the diffusion scale is based on the heavy traffic condition (HTC)...
-
The Maximal Agreement Subtree problem for random trees
BudzinskiThomasConsider two binary trees whose leaves are labelled from 1 to n.
-
An Improved Lower Bound on the Largest Common Subtree of Random Leaf-Labeled Binary Trees
KhezeliAliIt is known that the size of the largest common subtree...
-
Reversible Markov decision processes
AnantharamVenkatA Markov decision process is called reversible if for every stationary Markov control strategy the resulting Markov chain is reversible.
-
The question of connectedness in the Free Uniform Spanning Forest
TimárÁdám DávidThe uniform measure on the set of all spanning trees of a finite graph is a classical object in probability.
-
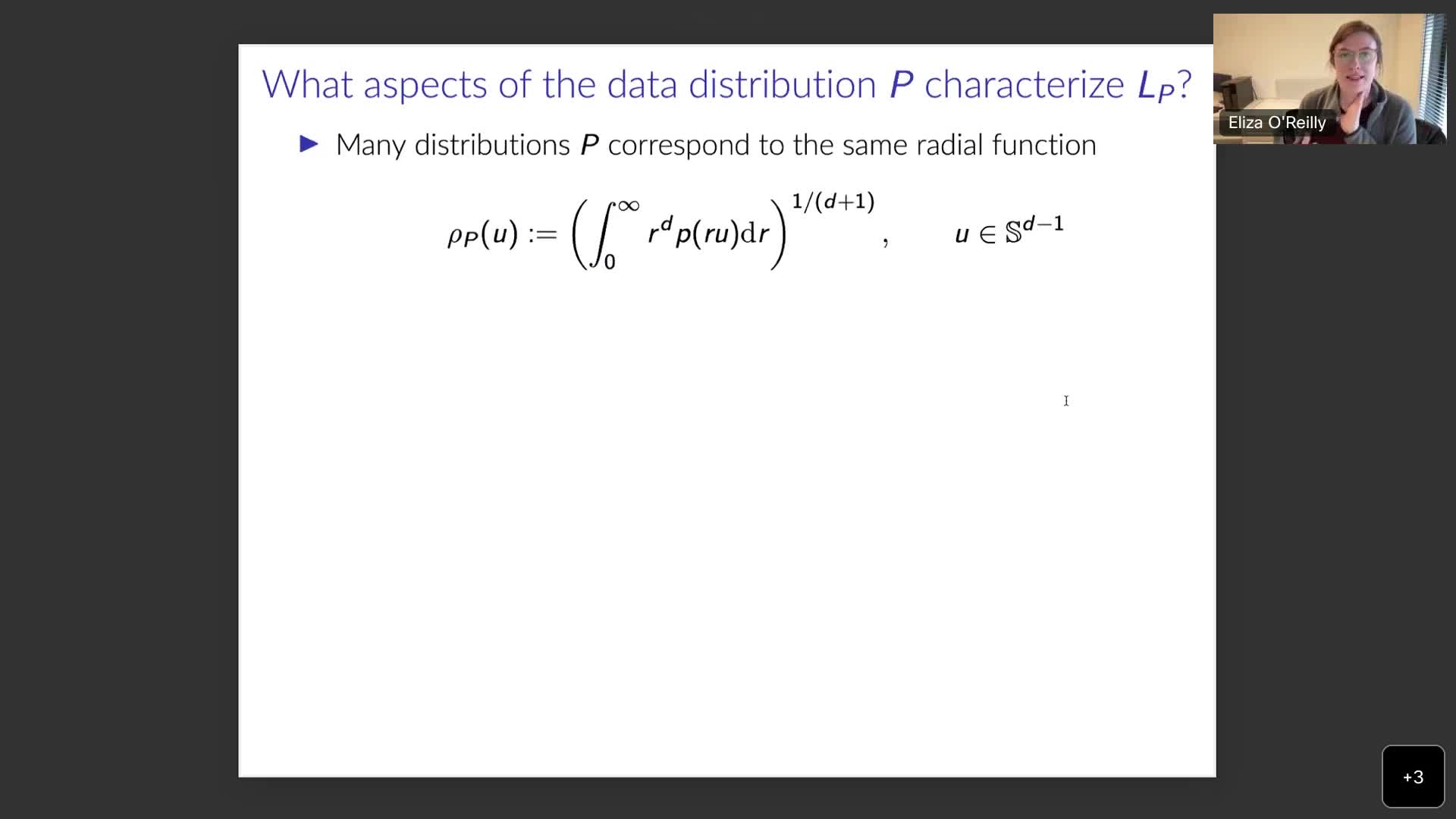
Optimal Convex and Nonconvex Regularizers for a Data Source
O'ReillyElizaRegularization is a widespread technique used in statistical estimation problems that helps to capture low dimensional structure in the data and improve signal recovery.
Sur le même thème
-
Bruit, erreur, anomalie et incertitude dans les données-PUDD
RossiFabriceLes données collectées sont systématiquement soumises à des perturbations de diverses natures, depuis le bruit de mesure de capteurs jusqu’aux erreurs de saisie.
-
Combinatorial maps in high genus
LoufBaptisteCombinatorial maps are a model of discrete geometry: they are surfaces made by gluing polygons along their sides, or equivalently, graphs drawn on surfaces. In this talk, I'll focus on the study of
-
Do there exist expanders with non-negative curvature ?
SalezJustinIn this talk I will briefly recall the framework of local weak limits of finite graphs introduced by I. Benjamini and O. Schramm
-
Tail bounds for detection times in mobile hyperbolic graphs
MitscheDieterMotivated by Krioukov et al.'s model of random hyperbolic graphs for real-world networks, and inspired by the analysis of a dynamic model of graphs in Euclidean space by Peres et al., we introduce a
-
Sofic entropy of processes on infinite random trees
BordenaveCharlesThis is a joint work with Agnes Backhausz et Balasz Szegedy. We define a natural notion of micro-state entropy...
-
Online matching for the multiclass Stochastic Block Model
SOPRANO LOTONahuelA matching in a graph is a set of edges that do not share endpoints. Developing algorithms that find large matchings is an important problem. An algorithm is said to be online if it has to construct
-
Critical cluster cascades
KirchnerMatthiasWe consider a sequence of Poisson cluster point processes...
-
Point processes on higher rank symmetric spaces and their cost
MellickSamuelCost is a natural invariant associated to group actions and invariant point processes on symmetric spaces (such as Euclidean space and hyperbolic space). Informally, it measures how difficult it is to
-
Parallel server systems in extended heavy traffic
CastielEyalThe standard setting for studying parallel server systems (PSS) at the diffusion scale is based on the heavy traffic condition (HTC)...
-
The Maximal Agreement Subtree problem for random trees
BudzinskiThomasConsider two binary trees whose leaves are labelled from 1 to n.
-
An Improved Lower Bound on the Largest Common Subtree of Random Leaf-Labeled Binary Trees
KhezeliAliIt is known that the size of the largest common subtree...
-
Reversible Markov decision processes
AnantharamVenkatA Markov decision process is called reversible if for every stationary Markov control strategy the resulting Markov chain is reversible.