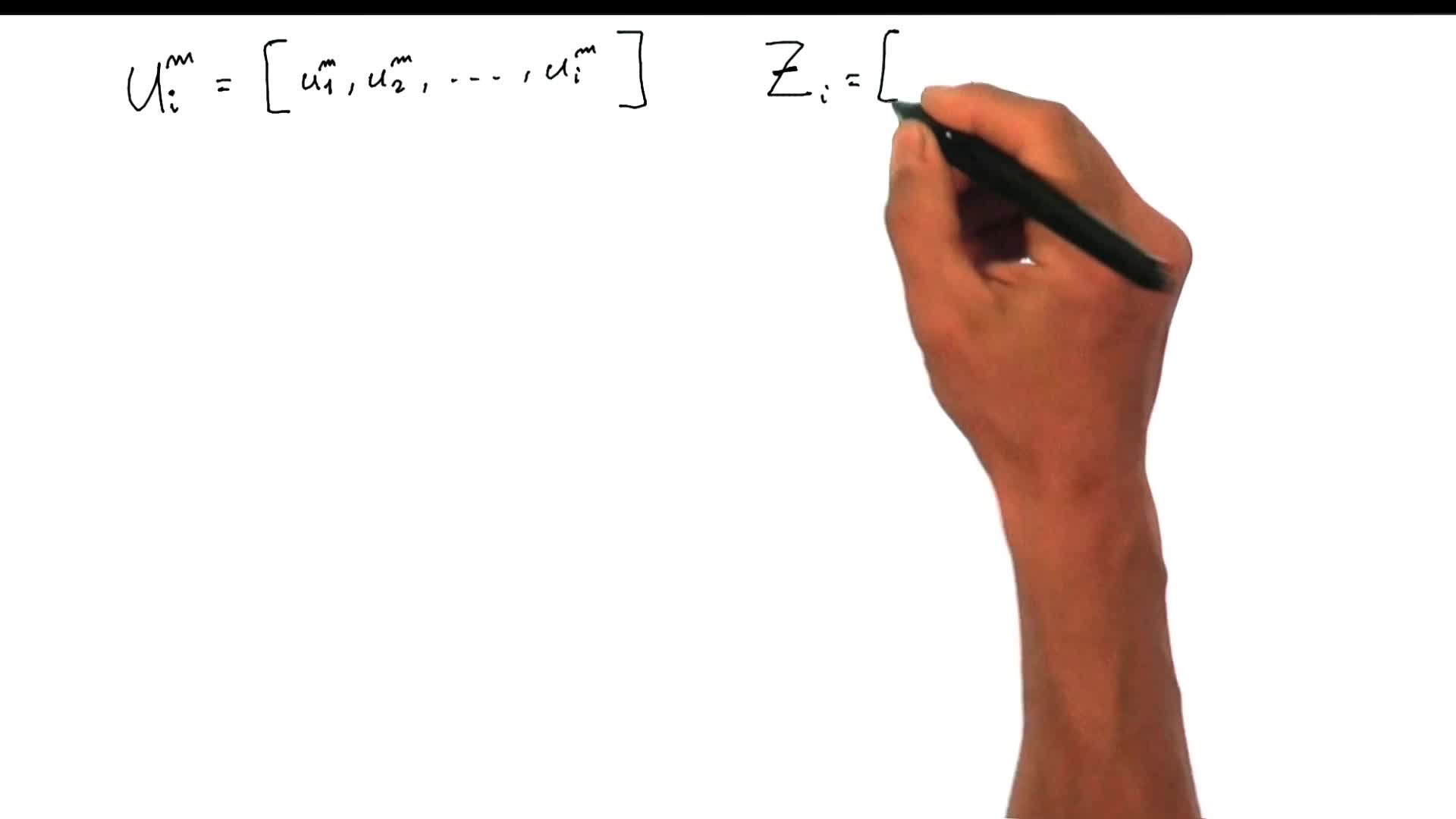2. Bayes and Kalman Filters
Descriptif
Contents of this second part:
2.1. Localization process in a probabilistic framework: basic concepts
2.2. Characterization of proprioceptive and exteroceptive sensors
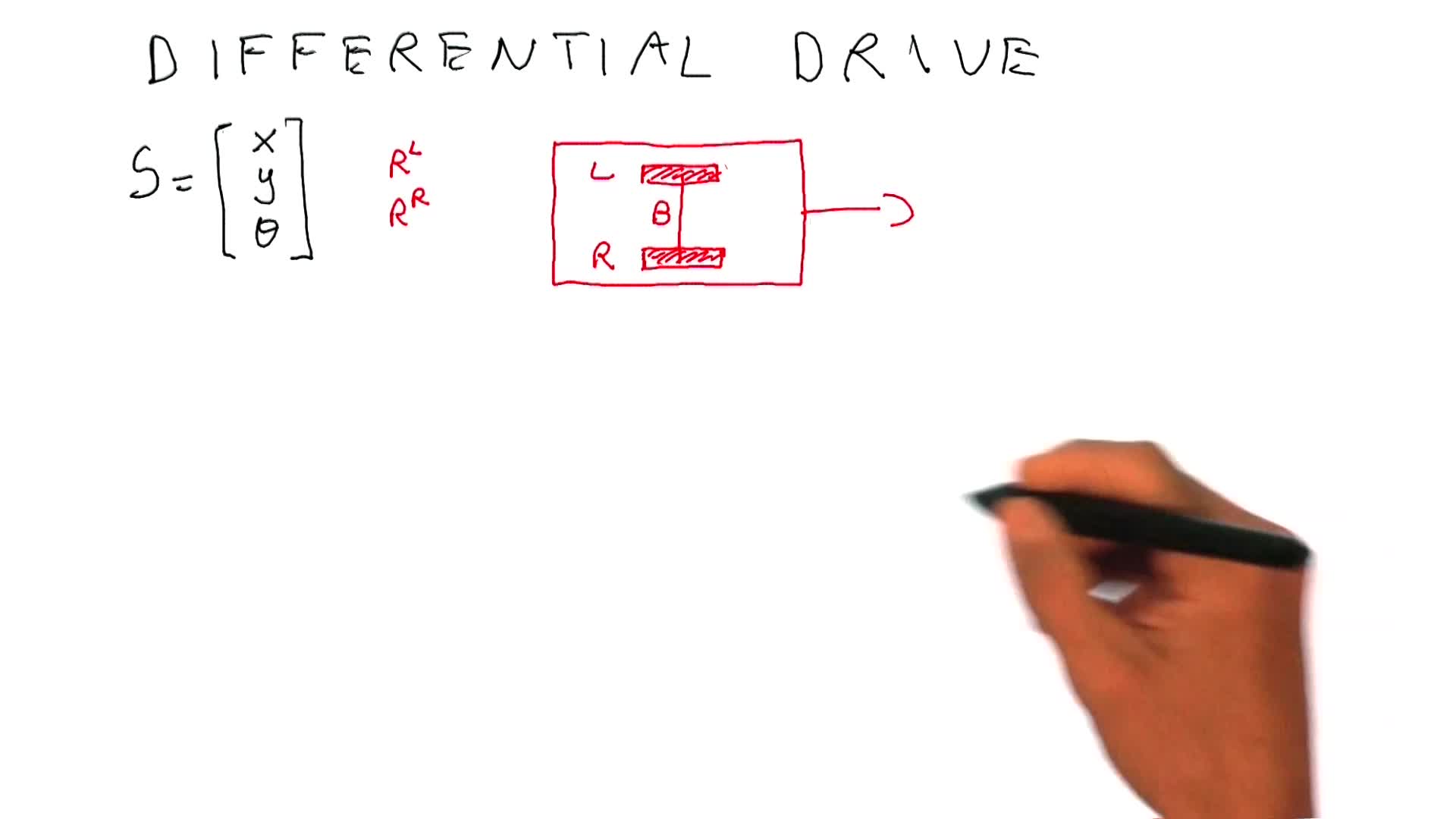
2.3. Wheel encoders for a differential drive vehicle
2.4. Sensor statistical models
2.5. Reminds on probability
2.6. The Bayes Filter
2.7. Grid Localization: an example in 1D
2.8. The Extended Kalman Filter (EKF)
Vidéos
2.3. Wheel encoders for a differential drive vehicle
In this video, we want to discuss the case of a wheel encoders in 2D, and in particular the case of a robot equipped with a differential drive which is very popular in mobile robotics.
2.2. Characterization of proprioceptive and exteroceptive sensors
Before deriving the equations of the Bayes filter, I want to remind you a few concepts in the theory of probability, and also some mathematical characterization for the statistical error of the
2.1. Localization process in a probabilistic framework: basic concepts
In this part, we will talk about localization which is a fundamental problem that a robot has to be able to solve in order to accomplish almost any tasks. In particular, we will start by
2.4. Sensor statistical models
So far in the characterization of our sensor measurements, we didn't talk about the errors. This is precisely what we want to do in this video. In particular, we want to compute two probability
2.5. Reminds on probability
In this sequence I want to remind you a few concepts in the theory of probability and then in the next one we finally derive the equations of the Bayes filter. So the concept that I want to
2.6. The Bayes Filter
The equations of the Bayes filters are the equation that allow us to update the probability distribution for the robot to be in a given configuration by integrating the information that are in the
2.7. Grid Localization: an example in 1D
Now that we have the equations of the Bayes filter, we need a method in order to implement in real cases these equations. So, in the following, I want to discuss two methods, which are commonly
2.8. The Extended Kalman Filter (EKF)
We have seen the grid localization, and the advantage of this approach is that we can deal with any kind of probability distribution; in particular we don't need to do a Gaussian assumption. The
Intervenants et intervenantes
Directeur de thèse à l'Université de Grenoble