Notice
Learning a sound propagation model
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
Part 3 : Sound-Source Localization
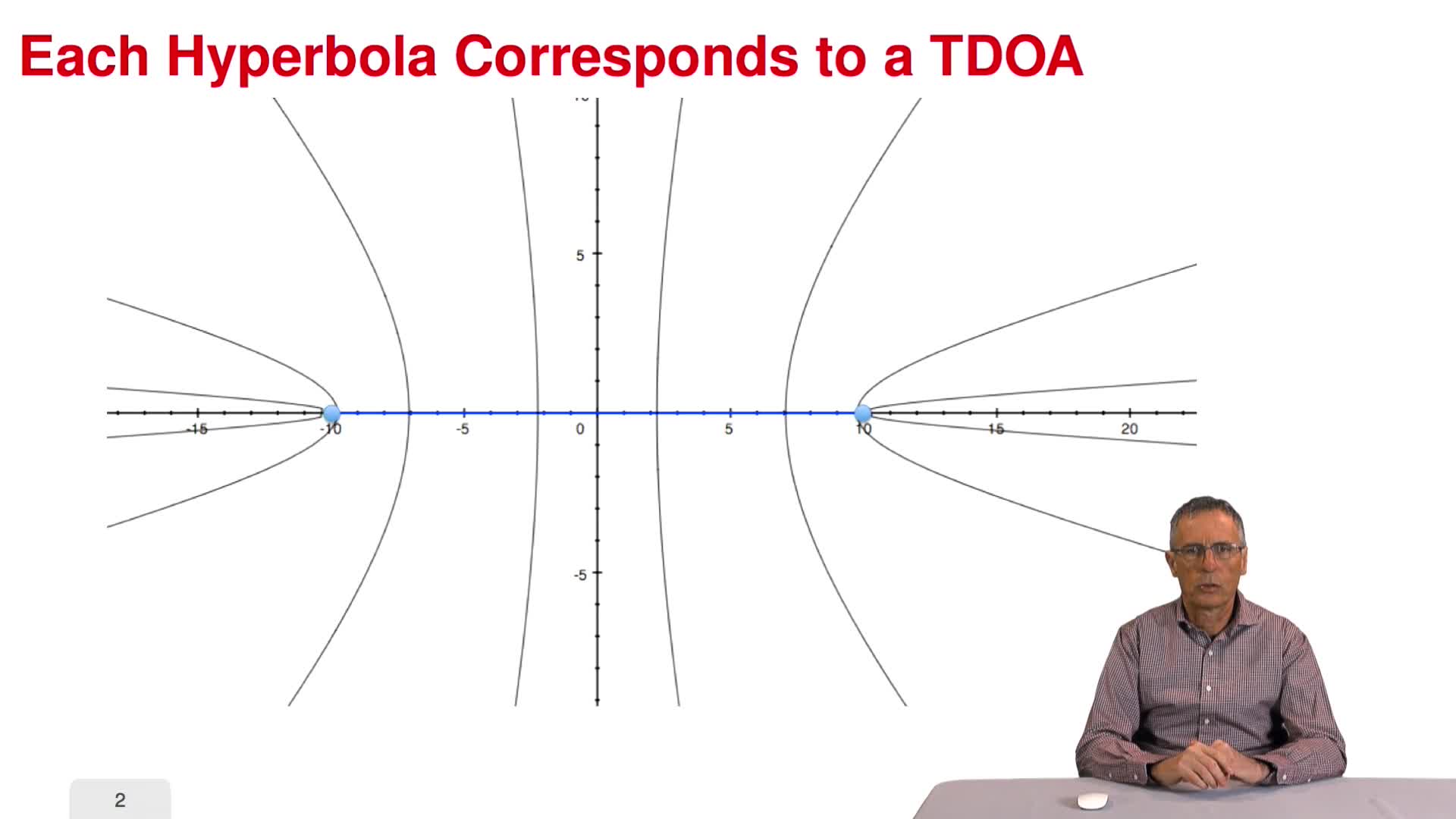
3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA)
3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation
3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain
3.4. The geometry of two microphones
3.5. Direction of arrival
3.6. Using more than two microphones
3.7. Embedding the microphones in a robot head
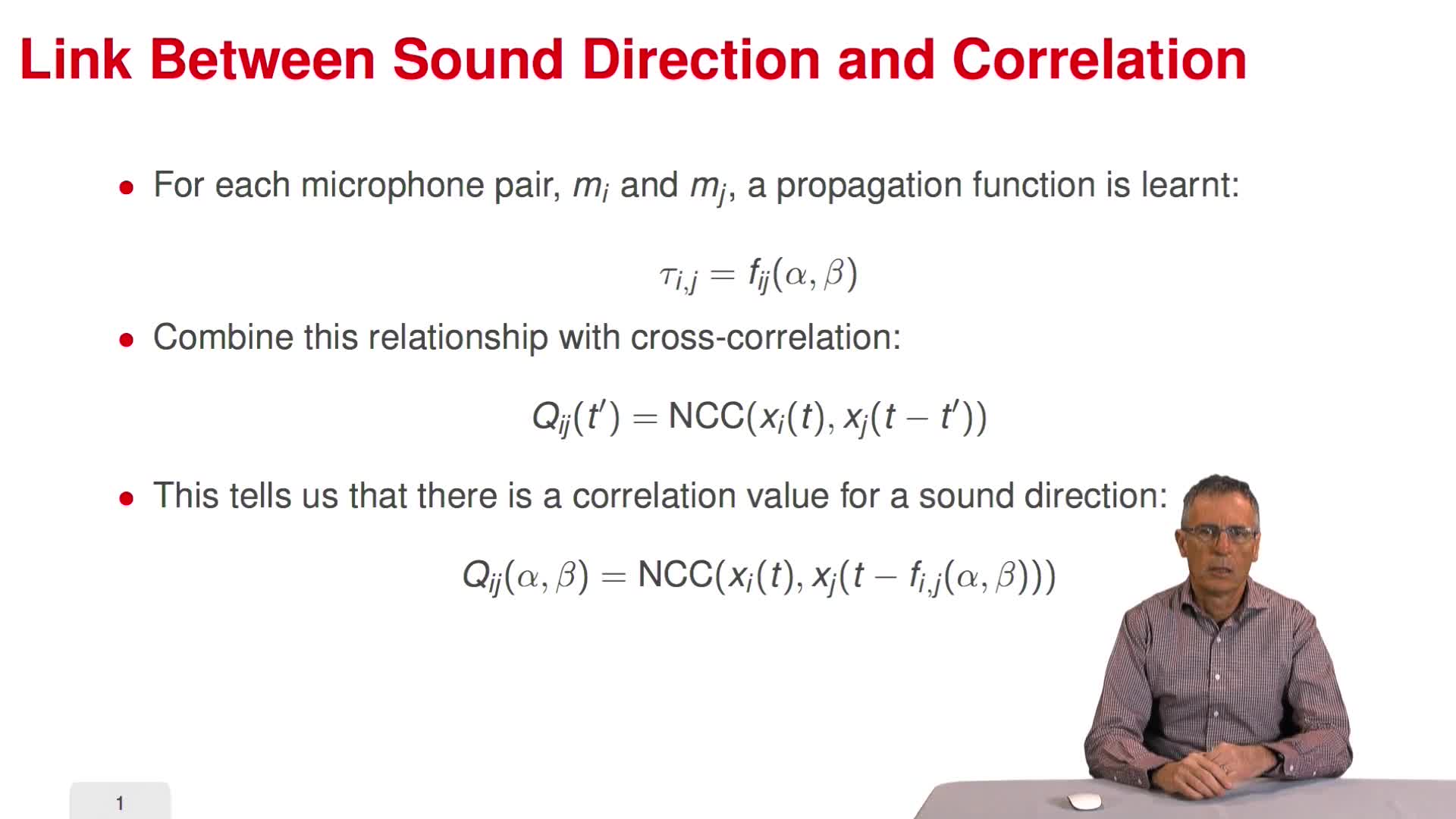
3.8. Learning a sound propagation model
3.9. Predicting direction of a sound with a robot head
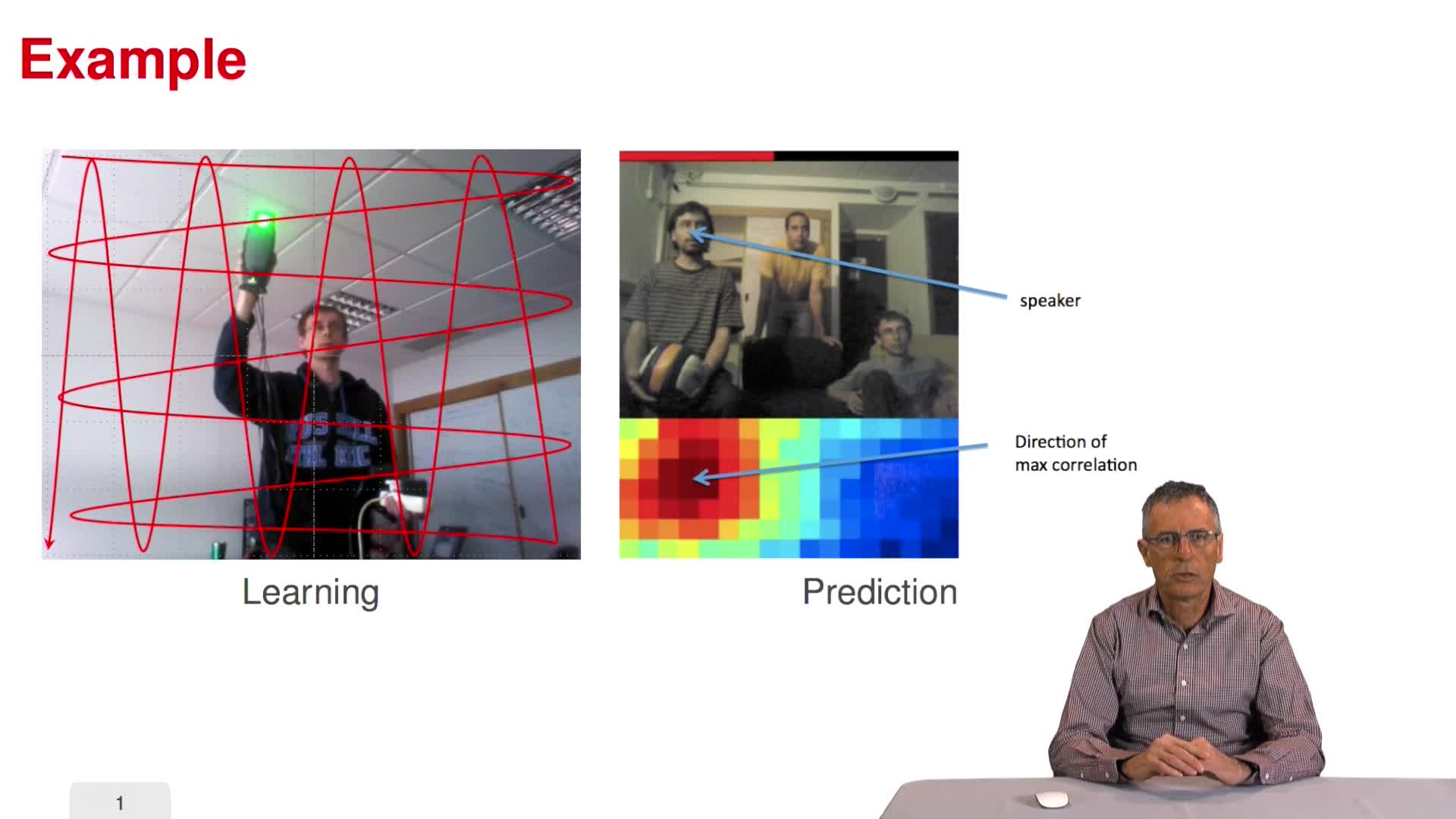
3.10. Example of sound direction estimation
Thème
Documentation
Dans la même collection
-
The geometry of two microphones
HoraudRaduPart 3 : Sound-Source Localization 3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) 3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation 3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain 3.4. The geometry of two
-
Embedding the microphones in a robot head
HoraudRaduPart 3 : Sound-Source Localization 3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) 3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation 3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain 3.4. The geometry of two
-
Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation
HoraudRaduPart 3 : Sound-Source Localization 3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) 3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation 3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain 3.4. The geometry of two
-
Direction of arrival
HoraudRaduPart 3 : Sound-Source Localization 3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) 3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation 3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain 3.4. The geometry of two
-
Predicting direction of a sound with a robot head
HoraudRaduPart 3 : Sound-Source Localization 3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) 3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation 3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain 3.4. The geometry of two
-
Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain
HoraudRaduPart 3 : Sound-Source Localization 3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) 3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation 3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain 3.4. The geometry of two
-
Using more than two microphones
HoraudRaduPart 3 : Sound-Source Localization 3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) 3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation 3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain 3.4. The geometry of two
-
Time difference of arrival (TDOA)
HoraudRaduPart 3 : Sound-Source Localization 3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) 3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation 3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain 3.4. The geometry of two
-
Example of sound direction estimation
HoraudRaduPart 3 : Sound-Source Localization 3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) 3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation 3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain 3.4. The geometry of two
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
Audio signal processing in brief
HoraudRaduPart 1 : Introduction to Robot Hearing 1.1. Why do robots need to hear? 1.2. Human-robot interaction 1.3. Auditory scene analysis 1.4. Audio signal processing in brief 1.5.
-
Discrete-time signals
HoraudRaduPart 2 : Methodological Foundations 2.1. Robot heads and acoustic laboratories 2.2. Binaural Processing Pipeline 2.3. Continuous-time Fourier transform 2.4. Continuous short-time
-
Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain
HoraudRaduPart 3 : Sound-Source Localization 3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) 3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation 3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain 3.4. The geometry of two
-
-
-
Audio-visual clustering
HoraudRaduPart 5 : Fusion of Audio and Vision 5.1. Audio-visual processing challenges 5.2. Representation of visual information 5.3. The geometry of vision 5.4. Audio-visual feature association 5.5. Audio
-
Audio processing in the brain
HoraudRaduPart 1 : Introduction to Robot Hearing 1.1. Why do robots need to hear? 1.2. Human-robot interaction 1.3. Auditory scene analysis 1.4. Audio signal processing in brief 1.5.
-
Cross-correlation
HoraudRaduPart 2 : Methodological Foundations 2.1. Robot heads and acoustic laboratories 2.2. Binaural Processing Pipeline 2.3. Continuous-time Fourier transform 2.4. Continuous short-time
-
Using more than two microphones
HoraudRaduPart 3 : Sound-Source Localization 3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) 3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation 3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain 3.4. The geometry of two
-
-
The geometry of vision
HoraudRaduPart 5 : Fusion of Audio and Vision 5.1. Audio-visual processing challenges 5.2. Representation of visual information 5.3. The geometry of vision 5.4. Audio-visual feature association 5.5. Audio
-
Sur le même thème
-
Les capteurs THOË et TRACESENSE
Présentation de THOË le robot sous-marin et de TRACESENSE un capteur vibrant de préconcentration
-
Les jeudis du Grhapes 2021/2022-Handicap, Éducation et Numérique "La télé-présence mobile au servic…
La télé-présence mobile au service des enfants malades et empêchés de se rendre en classe Intervenants : Laurent Gallon et Françoise Dubergey
-
Les jeudis du Grhapes 2021/2022-Handicap, Éducation et Numérique "La télé-présence mobile au servic…
La télé-présence mobile au service des enfants malades et empêchés de se rendre en classe Intervenants : Laurent Gallon et Françoise Dubergey
-
« es-tu vivant? » interagir avec des humains, interagir avec des machines
Table ronde organisée à l'occasion de la Nuit des Idées 2020.
-
cognition naturelle, cognition artificielle
JouenFrançoisConférence inaugurale de François Jouen (EPHE PSL) dans le cadre du cycle « La bioéthique : aux frontières de la vie ». organisé par l’Institut d’études avancées de Paris et l’École pratique des
-
Pascal Bourgoin, Responsable opérationnel à la délégation académique du numérique éducatif (Dane), …
Autisme et robotique humanoïde : un projet d'observation des prérequis à la communication. Ce projet comporte une partie expérimentation de l'usages d'un robot dans un cadre d'apprentissages avec des
- Robots
- Les écoles et leurs activités, enseignement spécialisé, éducation spéciale
- Élèves et étudiants souffrant de troubles affectifs (autistes, éducation spéciale pour les personnes atteintes de troubles affectifs, de trouble déficitaire de l'attention...)
- Interaction sociale (défauts et troubles de la communication, principes psychologiques de la sociologie, psychologie sociale, rapports sociaux, relations interpersonnelles, relations sociales, représentations sociales, réseaux sociaux)
- Handicap
-
Vers la navigation sociale des véhicules autonomes
SpalanzaniAnne-MarieLe véhicule autonome n'est pas un "simple" robot, tel un robot compagnon, mais un robot qui transporte des personnes. Cela implique que les passagers doivent se sentir intégrés dans le trafic comme
-
-
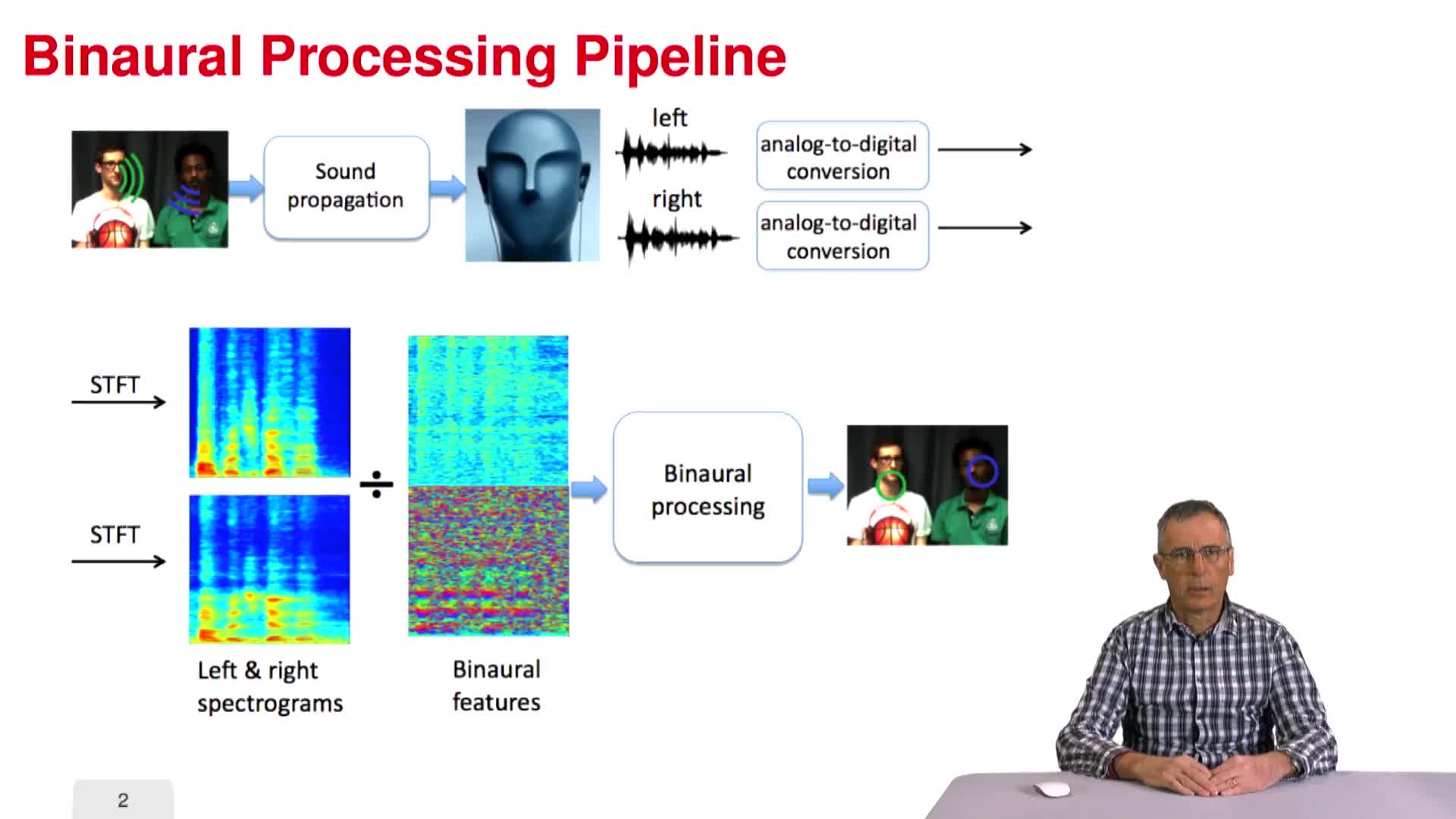
Binaural Processing Pipeline
HoraudRaduPart 2 : Methodological Foundations 2.1. Robot heads and acoustic laboratories 2.2. Binaural Processing Pipeline 2.3. Continuous-time Fourier transform 2.4. Continuous short-time Fourier transform 2
-
Time difference of arrival (TDOA)
HoraudRaduPart 3 : Sound-Source Localization 3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) 3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation 3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain 3.4. The geometry of two
-
Example of sound direction estimation
HoraudRaduPart 3 : Sound-Source Localization 3.1. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) 3.2. Estimation of TDOA by cross-correlation 3.3. Estimation of TDOA in the spectral domain 3.4. The geometry of two
-