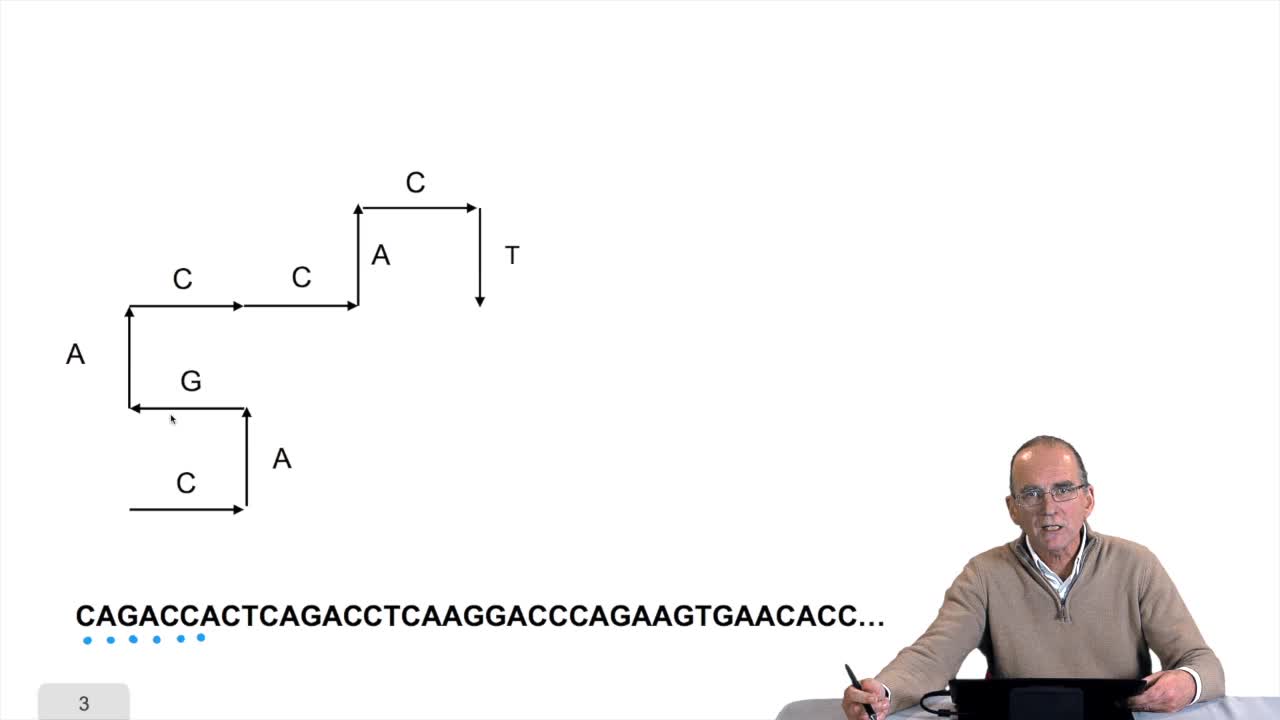Notice
5.6. The diversity of bioinformatics algorithms
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
In this course, we have seen a very little set of bioinformatic algorithms. There exist numerous various algorithms in bioinformatics which deal with a large span of classes of problems. For example, read assembly. We have seen how NGS sequencers produce large sets of reads, small sequences which overlap. And the problem of assembly isto use the overlap in order to ordering this read and reconstructing the whole genomic sequence. This is the overlapping and you see that you can use this overlap to get a longer sequence. Of course, here the example issimple: you have to imagine a set of millions of reads to beassembled into genomic sequences of millions or billions of bases. A second class of problems issequence mapping and comparison. We have seen sequence comparison. What about sequence mapping? You remember this situation in which biologists get what they call "cDNA". Experimentally, this is a sequence of DNA and they want to map this sequence of DNA on the sequence of the genome in order to say: well, this is an exon, this i an exon and so on.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Thème
Documentation
Dans la même collection
-
5.7. The application domains in microbiology
RechenmannFrançoisBioinformatics relies on many domains of mathematics and computer science. Of course, algorithms themselves on character strings are important in bioinformatics, we have seen them. Algorithms and
-
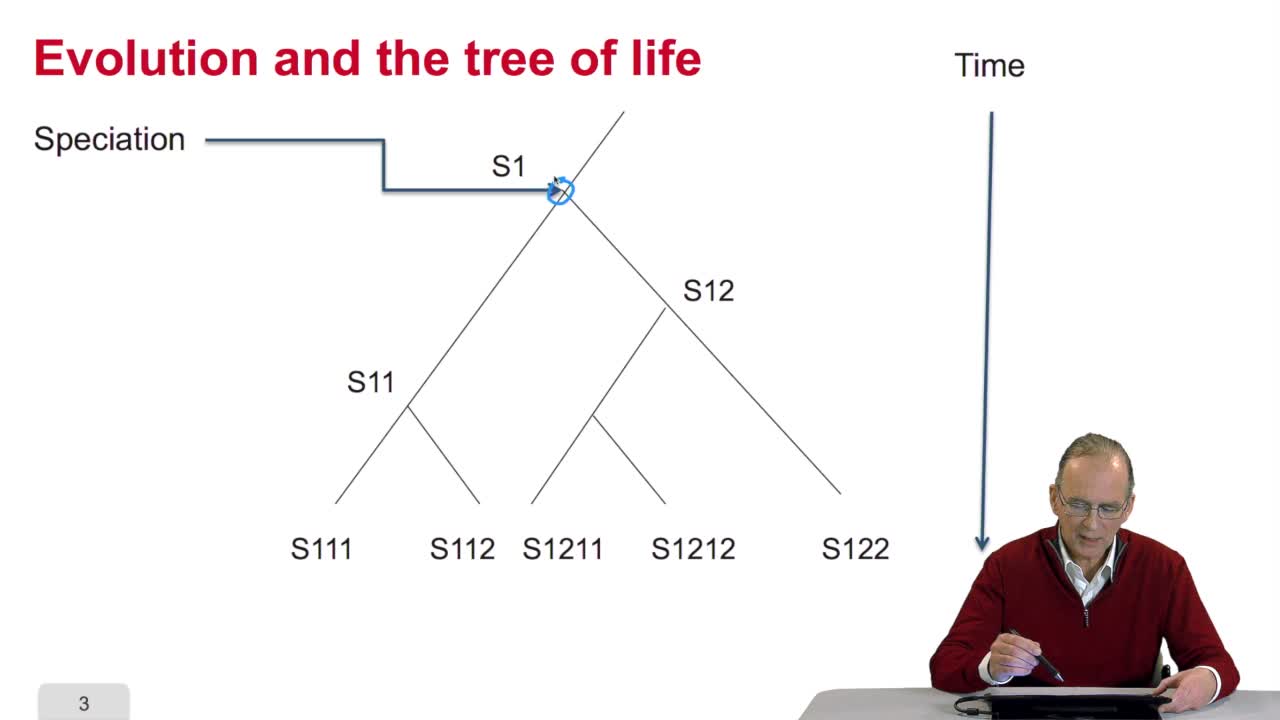
5.1. The tree of life
RechenmannFrançoisWelcome to this fifth and last week of our course on genomes and algorithms that is the computer analysis of genetic information. During this week, we will firstsee what phylogenetic trees are and how
-
5.4. The UPGMA algorithm
RechenmannFrançoisWe know how to fill an array with the values of the distances between sequences, pairs of sequences which are available in the file. This array of distances will be the input of our algorithm for
-
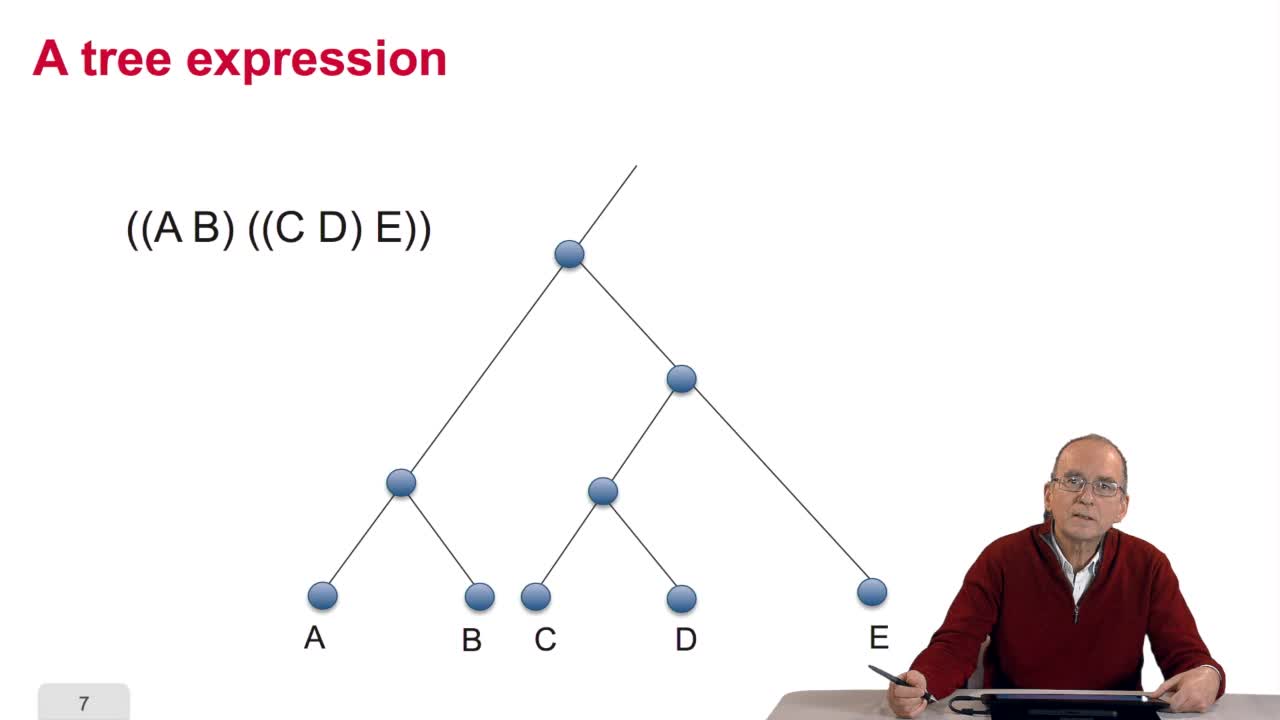
5.2. The tree, an abstract object
RechenmannFrançoisWhen we speak of trees, of species,of phylogenetic trees, of course, it's a metaphoric view of a real tree. Our trees are abstract objects. Here is a tree and the different components of this tree.
-
5.5. Differences are not always what they look like
RechenmannFrançoisThe algorithm we have presented works on an array of distance between sequences. These distances are evaluated on the basis of differences between the sequences. The problem is that behind the
-
5.3. Building an array of distances
RechenmannFrançoisSo using the sequences of homologous gene between several species, our aim is to reconstruct phylogenetic tree of the corresponding species. For this, we have to comparesequences and compute distances
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
1.5. Counting nucleotides
RechenmannFrançoisIn this session, don't panic. We will design our first algorithm. This algorithm is forcounting nucleotides. The idea here is that as an input,you have a sequence of nucleotides, of bases, of letters,
-
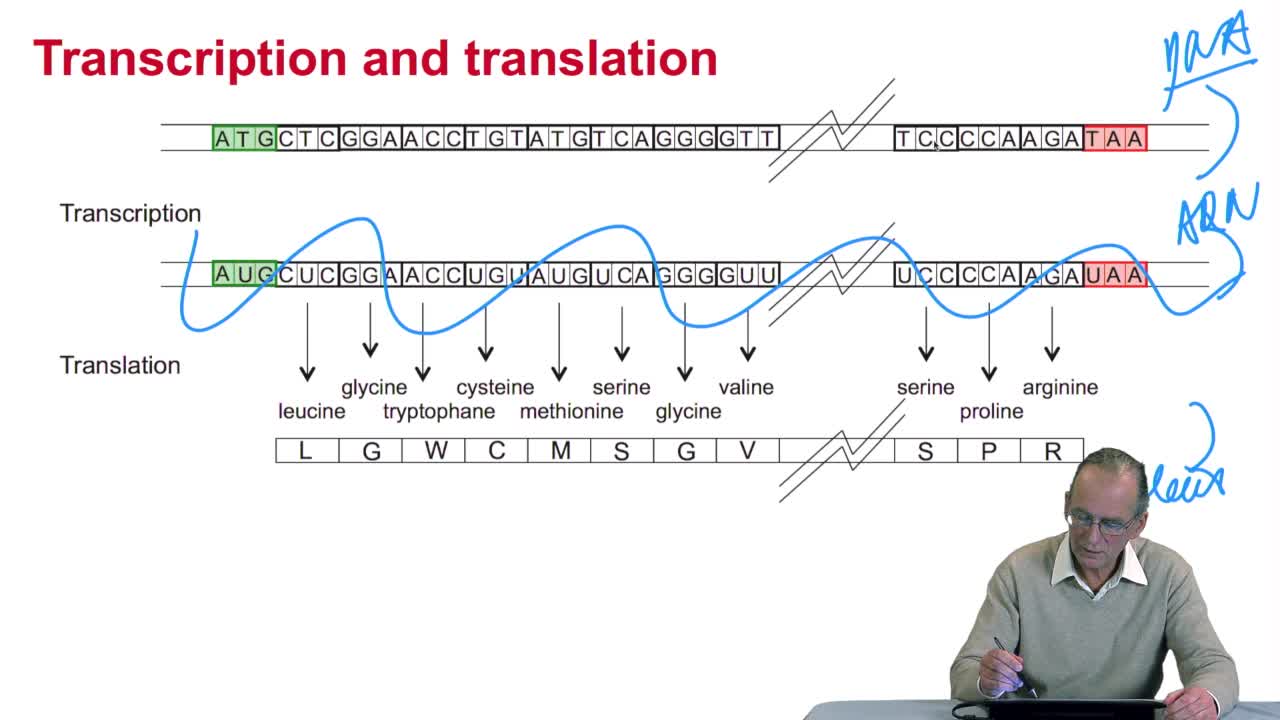
2.4. A translation algorithm
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen that the genetic codeis a correspondence between the DNA or RNA sequences and aminoacid sequences that is proteins. Our aim here is to design atranslation algorithm, we make the
-
3.1. All genes end on a stop codon
RechenmannFrançoisLast week we studied genes and proteins and so how genes, portions of DNA, are translated into proteins. We also saw the very fast evolutionof the sequencing technology which allows for producing
-
3.9. Benchmarking the prediction methods
RechenmannFrançoisIt is necessary to underline that gene predictors produce predictions. Predictions mean that you have no guarantees that the coding sequences, the coding regions,the genes you get when applying your
-
4.2. Why gene/protein sequences may be similar?
RechenmannFrançoisBefore measuring the similaritybetween the sequences, it's interesting to answer the question: why gene or protein sequences may be similar? It is indeed veryinteresting because the answer is related
-
5.4. The UPGMA algorithm
RechenmannFrançoisWe know how to fill an array with the values of the distances between sequences, pairs of sequences which are available in the file. This array of distances will be the input of our algorithm for
-
1.8. Compressing the DNA walk
RechenmannFrançoisWe have written the algorithm for the circle DNA walk. Just a precision here: the kind of drawing we get has nothing to do with the physical drawing of the DNA molecule. It is a symbolic
-
2.7. The algorithm design trade-off
RechenmannFrançoisWe saw how to increase the efficiencyof our algorithm through the introduction of a data structure. Now let's see if we can do even better. We had a table of index and weexplain how the use of these
-
3.4. Predicting all the genes in a sequence
RechenmannFrançoisWe have written an algorithm whichis able to locate potential genes on a sequence but only on one phase because we are looking triplets after triplets. Now remember that the genes maybe located on
-
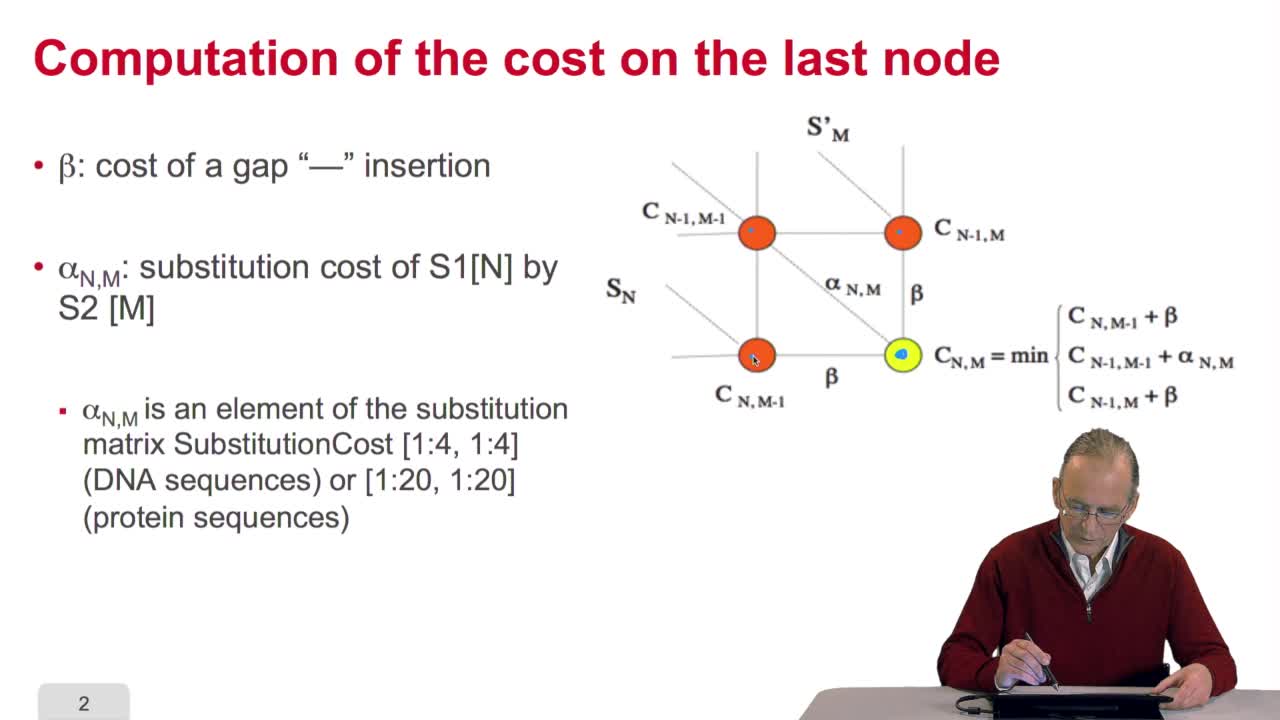
4.7. Alignment costs
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen how we can compute the cost of the path ending on the last node of our grid if we know the cost of the sub-path ending on the three adjacent nodes. It is time now to see more deeply why
-
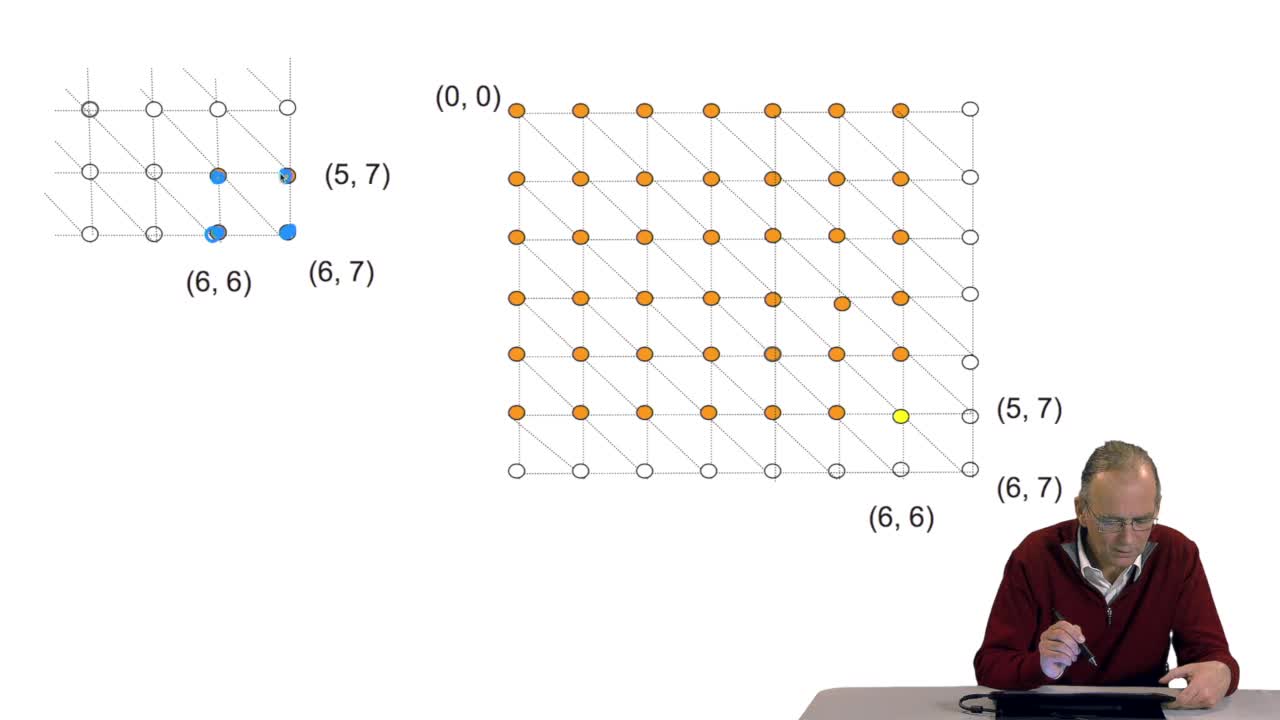
4.9. Recursion can be avoided: an iterative version
RechenmannFrançoisWe have written a recursive function to compute the optimal path that is an optimal alignment between two sequences. Here all the examples I gave were onDNA sequences, four letter alphabet. OK. The
-
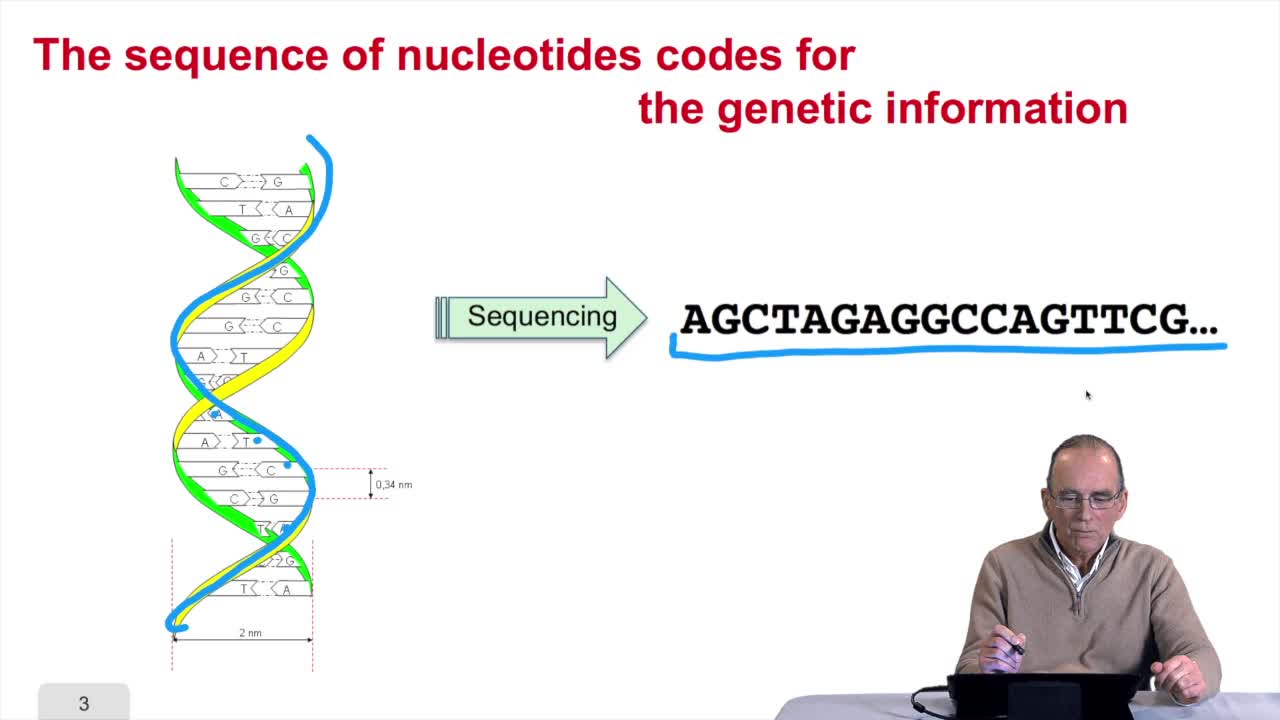
1.3. DNA codes for genetic information
RechenmannFrançoisRemember at the heart of any cell,there is this very long molecule which is called a macromolecule for this reason, which is the DNA molecule. Now we will see that DNA molecules support what is called