Notice
"Le mathématicien Petre (Pierre) Sergescu, historien des sciences, personnalité du XXe siècle"
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
Né en Roumanie, en 1893, Petre Sergescu, appartient à une pléiade de Roumains dont l’œuvre fait partie intégrante de la culture française, voire européenne. Il a joué un rôle majeur dans l’organisation institutionnelle de l’Histoire des Sciences, au plan international.
Après de brillantes études à Bucarest et Paris il est Professeur titulaire de mathématiques et Président de l’École Polytechnique de Bucarest. En 1946, après l’occupation de la Roumanie par l’armée soviétique, il se réfugie en France où tout en étant très actif au sein de l’émigration roumaine se consacre à la réanimation de l’Académie Internationale d’Histoire des Sciences - AIHS dont il est, depuis 1937, vice-président, pour être élu Président en 1947 et secrétaire perpétuel, en 1950. En 1947 il est élu également secrétaire général de l’Union Internationale d’Histoire des Sciences - UIHS et devient rédacteur en chef des „Archives Internationales d’Histoire des Sciences”
Petre Sergescu décède à Paris en décembre 1954, en pleine activité.
Thème
Sur le même thème
-
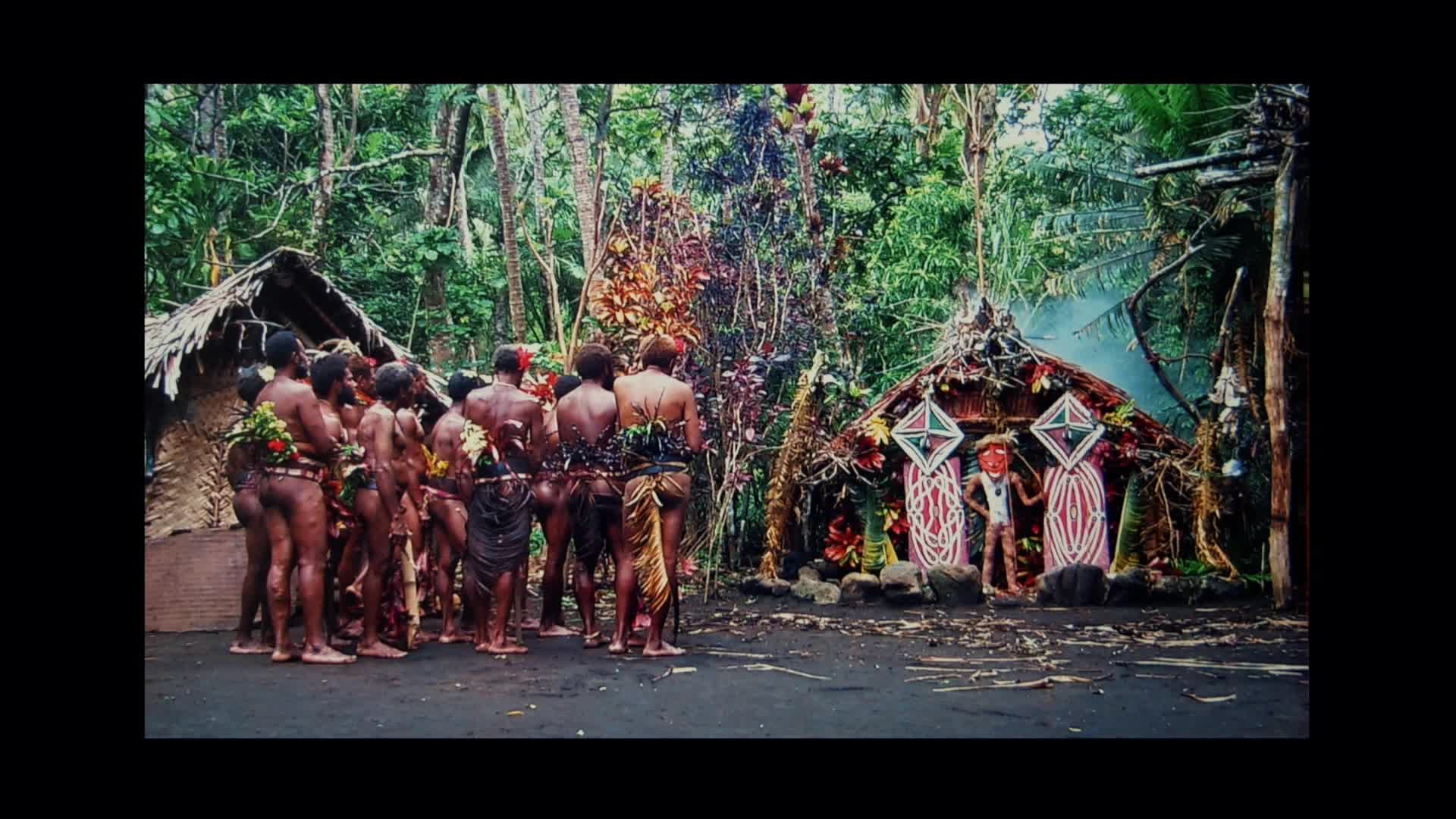
Tuan Ta Pesao : écritures de sable et de ficelle à l'Ile d'Ambrym
VandendriesscheEricCe film se déroule au Nord de l’île d’Ambrym, dans l’archipel de Vanuatu, en Mélanésie...
-
Lancement de la collection "Truchements"
Monod-BecquelinAuroreCunillCarolineDéléagePierreRivertiCamilleGhermanVasileZimmermannThéoStoichităVictor AlexandreChemillierMarcLancement de la nouvelle collection "Truchements" des éditions de la Société d'ethnologie de Nanterre, avec la présentation en mots et en musique de son premier titre, "Passeurs de mémoire", de
-
Webinaire sur la rédaction des PGD
LouvetViolaineRédaction des Plans de Gestion de Données (PGD) sous l’angle des besoins de la communauté mathématique.
-
Alexandre Booms : « Usage de matériel pédagogique adapté en géométrie : une transposition à interro…
« Usage de matériel pédagogique adapté en géométrie : une transposition à interroger ». Alexandre Booms, doctorant (Université de Reims Champagne-Ardenne - Cérep UR 4692)
-
D. Semola - Boundary regularity and stability under lower Ricci bounds
SemolaDanieleThe theory of non smooth spaces with lower Ricci Curvature bounds has undergone huge developments in the last thirty years. On the one hand the impetus came from Gromov’s precompactness theorem
-
D. Stern - Harmonic map methods in spectral geometry
SternDanielOver the last fifty years, the problem of finding sharp upper bounds for area-normalized Laplacian eigenvalues on closed surfaces has attracted the attention of many geometers, due in part to
-
Y. Lai - A family of 3d steady gradient Ricci solitons that are flying wings
LaiYiWe find a family of 3d steady gradient Ricci solitons that are flying wings. This verifies a conjecture by Hamilton. For a 3d flying wing, we show that the scalar curvature does not vanish at
-
R. Bamler - Compactness and partial regularity theory of Ricci flows in higher dimensions
BamlerRichard H.We present a new compactness theory of Ricci flows. This theory states that any sequence of Ricci flows that is pointed in an appropriate sense, subsequentially converges to a synthetic flow.
-
C. Li - Classifying sufficiently connected PSC manifolds in 4 and 5 dimensions
LiChaoIn this talk, I will discuss some recent developments on the topology of closed manifolds admitting Riemannian metrics of positive scalar curvature. In particular, we will prove if a closed PSC
-
T. Ozuch - Noncollapsed degeneration and desingularization of Einstein 4-manifolds
OzuchTristanWe study the noncollapsed singularity formation of Einstein 4-manifolds. We prove that any smooth Einstein 4-manifold close to a singular one in a mere Gromov-Hausdorff (GH) sense is the result
-
D. Tewodrose - Limits of Riemannian manifolds satisfying a uniform Kato condition
TewodroseDavidPresentation of a joint work with G. Carron and I. Mondello where we study Kato limit spaces.
-
J. Wang - Topological rigidity and positive scalar curvature
WangJianIn this talk, we shall describe some topological rigidity and its relationship with positive scalar curvature. Precisely, we will present a proof that a complete contractible 3-manifold with