Notice
3.4. Predicting all the genes in a sequence
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
We have written an algorithm whichis able to locate potential genes on a sequence but only on one phase because we are looking triplets after triplets. Now remember that the genes maybe located on different phases and on the two strands. It means that to retrieve all the genes on a genome we have to look on six different sequences, three phases on each strand. Let's looknow how we can deal with this kind of search. First we have to modify a little bit our algorithm so that instead of starting at position One, I want to introduce a variable, a parameter which could be One or Two or Three so that I can run this algorithm starting on position One, first phase, or on position Two, second phase,or on position Three, third phase. Of course if you have Four, it's still the first phase again so it's unnecessary to test the numbers Four and Five and soon, you have only threepossible phases.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Thème
Documentation
Dans la même collection
-
3.7. Index and suffix trees
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen with the Boyer-Moore algorithm how we can increase the efficiency of spin searching through the pre-processing of the pattern to be searched. Now we will see that an alternative way of
-
3.1. All genes end on a stop codon
RechenmannFrançoisLast week we studied genes and proteins and so how genes, portions of DNA, are translated into proteins. We also saw the very fast evolutionof the sequencing technology which allows for producing
-
3.10. Gene prediction in eukaryotic genomes
RechenmannFrançoisIf it is possible to have verygood predictions for bacterial genes, it's certainly not the caseyet for eukaryotic genomes. Eukaryotic cells have manydifferences in comparison to prokaryotic cells. You
-
3.5. Making the predictions more reliable
RechenmannFrançoisWe have got a bacterial gene predictor but the way this predictor works is rather crude and if we want to have more reliable results, we have to inject into this algorithmmore biological knowledge. We
-
3.8. Probabilistic methods
RechenmannFrançoisUp to now, to predict our gene,we only rely on the process of searching certain strings or patterns. In order to further improve our gene predictor, the idea is to use, to rely onprobabilistic methods
-
3.2. A simple algorithm for gene prediction
RechenmannFrançoisBased on the principle we statedin the last session, we will now write in pseudo code a firstalgorithm for locating genes on a bacterial genome. Remember first how this algorithm should work, we first
-
3.6. Boyer-Moore algorithm
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen how we can make gene predictions more reliable through searching for all the patterns,all the occurrences of patterns. We have seen, for example, howif we locate the RBS, Ribosome
-
3.9. Benchmarking the prediction methods
RechenmannFrançoisIt is necessary to underline that gene predictors produce predictions. Predictions mean that you have no guarantees that the coding sequences, the coding regions,the genes you get when applying your
-
3.3. Searching for start and stop codons
RechenmannFrançoisWe have written an algorithm for finding genes. But you remember that we arestill to write the two functions for finding the next stop codonand the next start codon. Let's see how we can do that. We
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
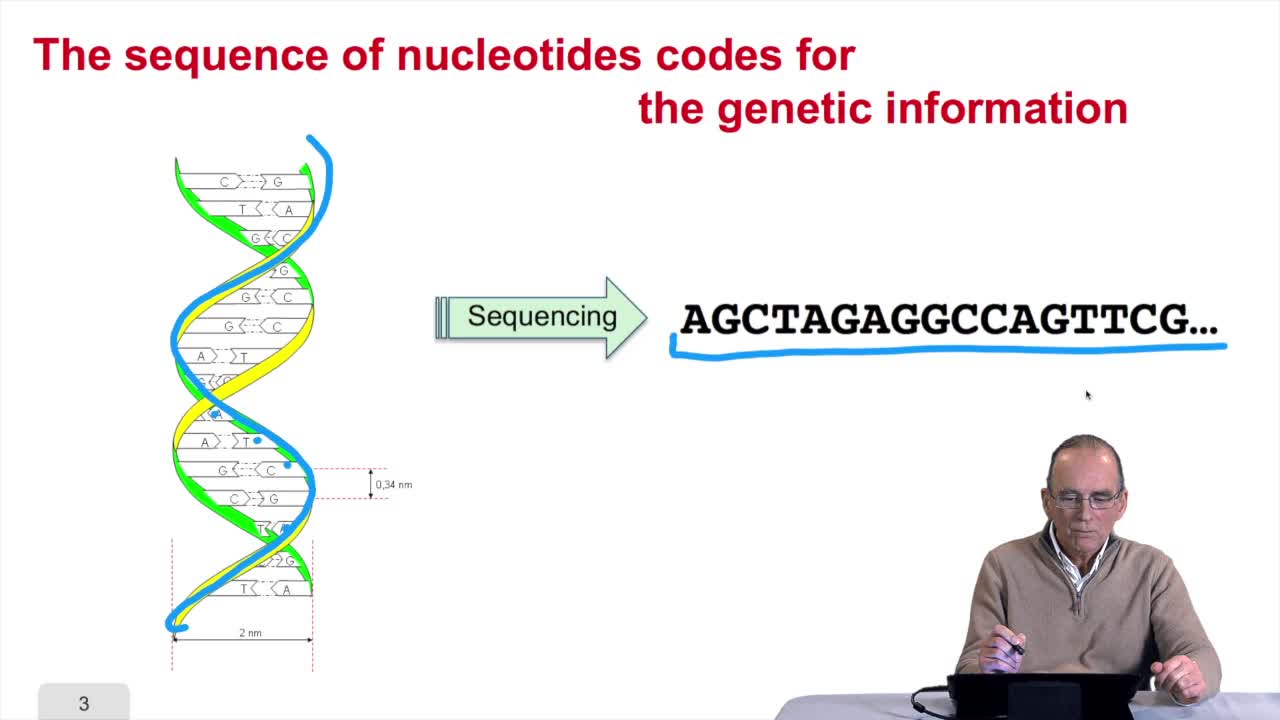
1.3. DNA codes for genetic information
RechenmannFrançoisRemember at the heart of any cell,there is this very long molecule which is called a macromolecule for this reason, which is the DNA molecule. Now we will see that DNA molecules support what is called
-
2.1. The sequence as a model of DNA
RechenmannFrançoisWelcome back to our course on genomes and algorithms that is a computer analysis ofgenetic information. Last week we introduced the very basic concept in biology that is cell, DNA, genome, genes
-
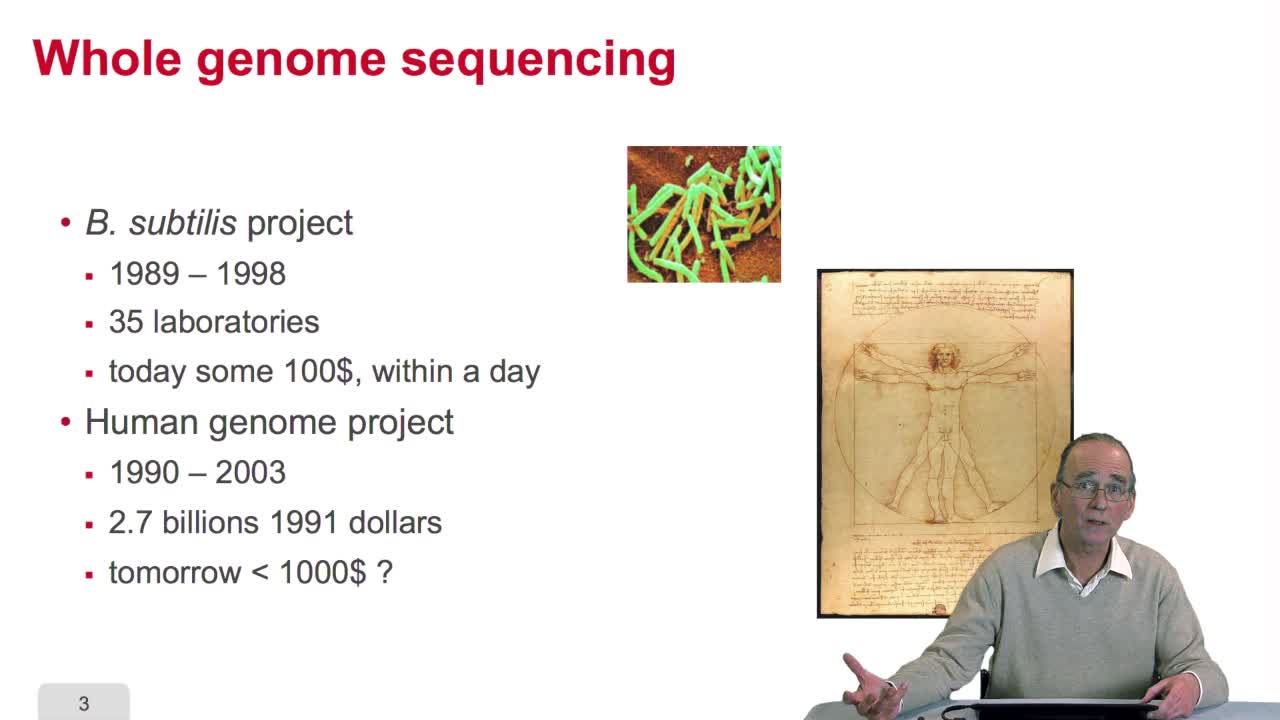
2.9. Whole genome sequencing
RechenmannFrançoisSequencing is anexponential technology. The progresses in this technologyallow now to a sequence whole genome, complete genome. What does it mean? Well let'stake two examples: some twenty years ago,
-
3.8. Probabilistic methods
RechenmannFrançoisUp to now, to predict our gene,we only rely on the process of searching certain strings or patterns. In order to further improve our gene predictor, the idea is to use, to rely onprobabilistic methods
-
4.3. Measuring sequence similarity
RechenmannFrançoisSo we understand why gene orprotein sequences may be similar. It's because they evolve togetherwith the species and they evolve in time, there aremodifications in the sequence and that the sequence
-
5.3. Building an array of distances
RechenmannFrançoisSo using the sequences of homologous gene between several species, our aim is to reconstruct phylogenetic tree of the corresponding species. For this, we have to comparesequences and compute distances
-
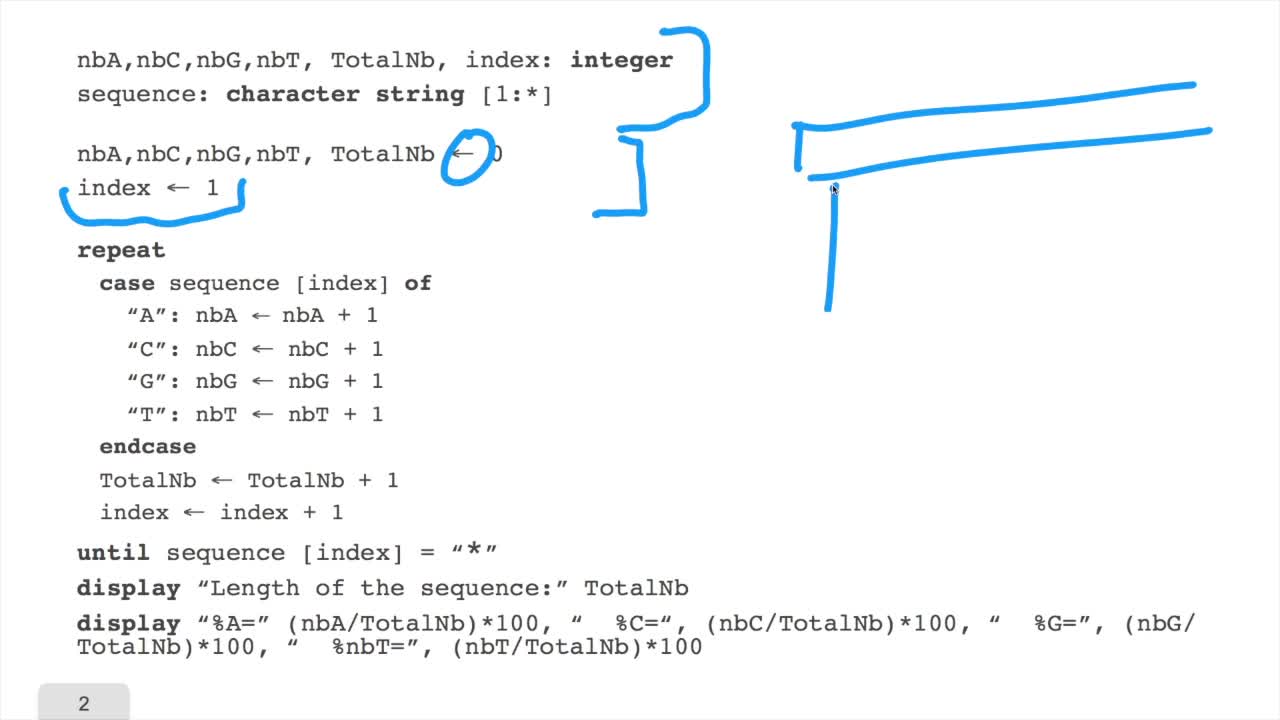
1.6. GC and AT contents of DNA sequence
RechenmannFrançoisWe have designed our first algorithmfor counting nucleotides. Remember, what we have writtenin pseudo code is first declaration of variables. We have several integer variables that are variables which
-
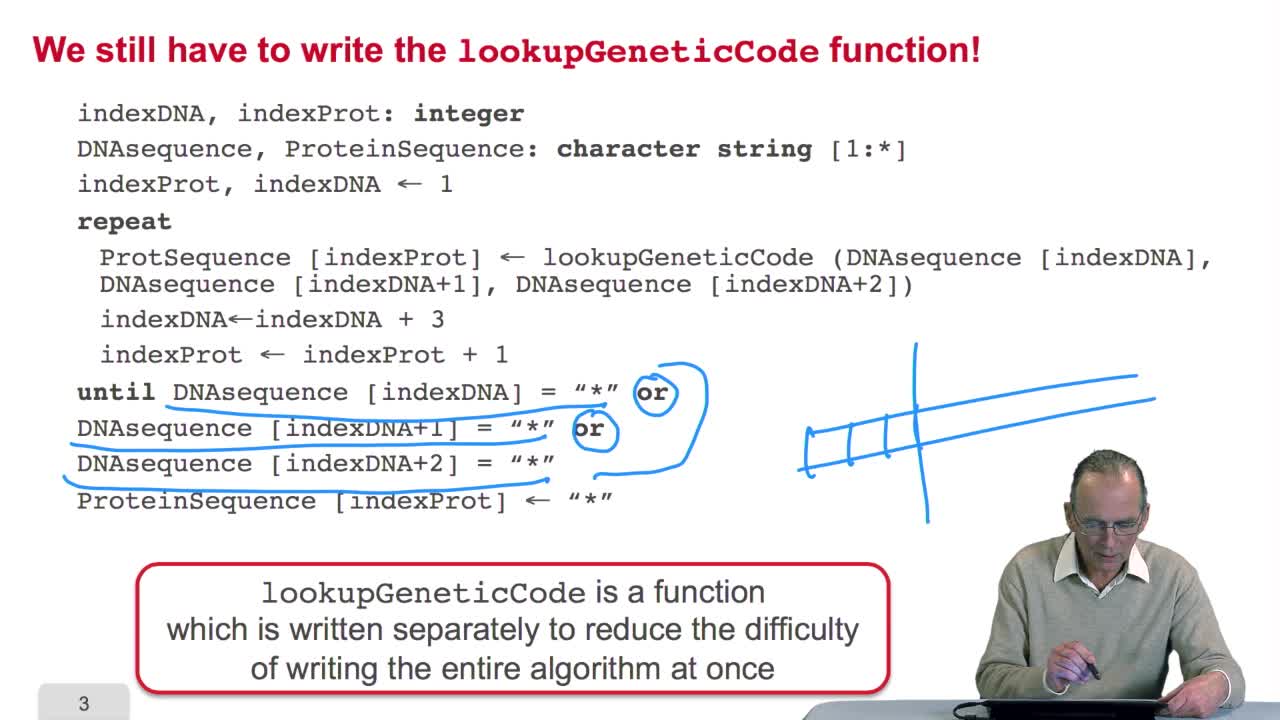
2.5. Implementing the genetic code
RechenmannFrançoisRemember we were designing our translation algorithm and since we are a bit lazy, we decided to make the hypothesis that there was the adequate function forimplementing the genetic code. It's now time
-
3.2. A simple algorithm for gene prediction
RechenmannFrançoisBased on the principle we statedin the last session, we will now write in pseudo code a firstalgorithm for locating genes on a bacterial genome. Remember first how this algorithm should work, we first
-
4.1. How to predict gene/protein functions?
RechenmannFrançoisLast week we have seen that annotating a genome means first locating the genes on the DNA sequences that is the genes, the region coding for proteins. But this is indeed the first step,the next very
-
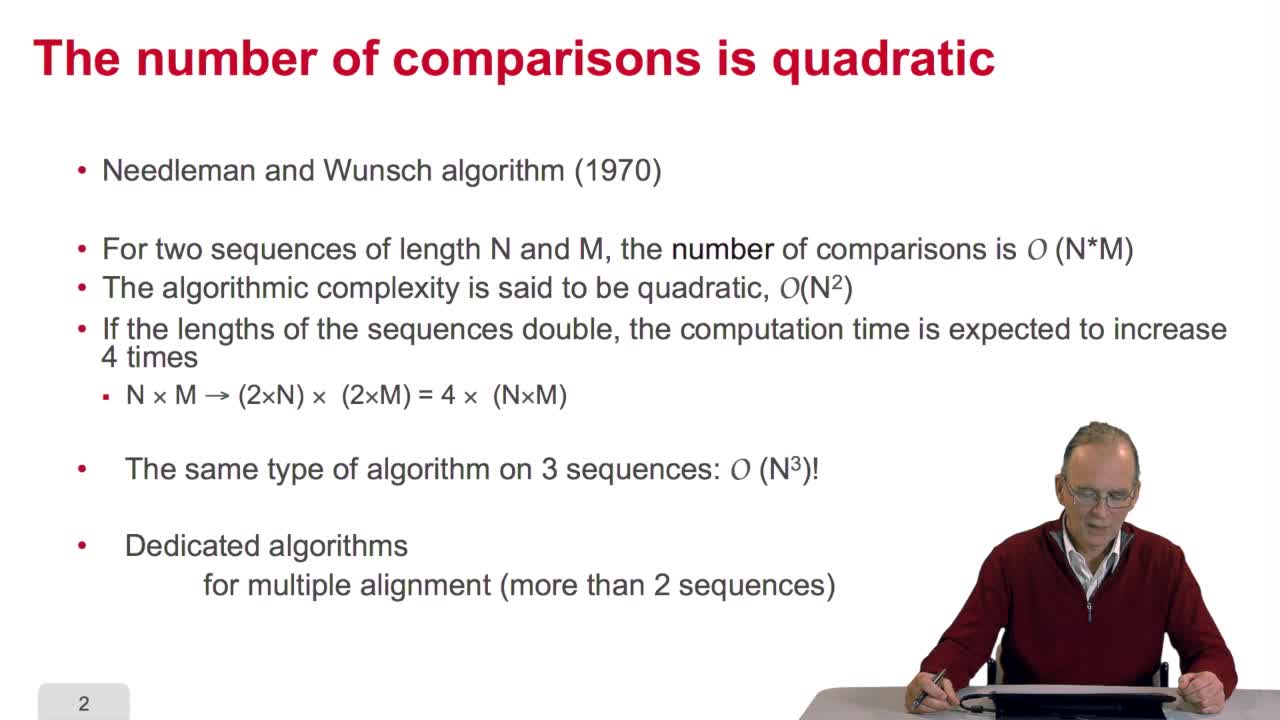
4.10. How efficient is this algorithm?
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen the principle of an iterative algorithm in two paths for aligning and comparing two sequences of characters, here DNA sequences. And we understoodwhy the iterative version is much more
-
5.7. The application domains in microbiology
RechenmannFrançoisBioinformatics relies on many domains of mathematics and computer science. Of course, algorithms themselves on character strings are important in bioinformatics, we have seen them. Algorithms and