Notice
1.10 : Segmentation Mode for Archival Documents with Highly Complex Layout
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
par Daniel Stoekl Ben Ezra
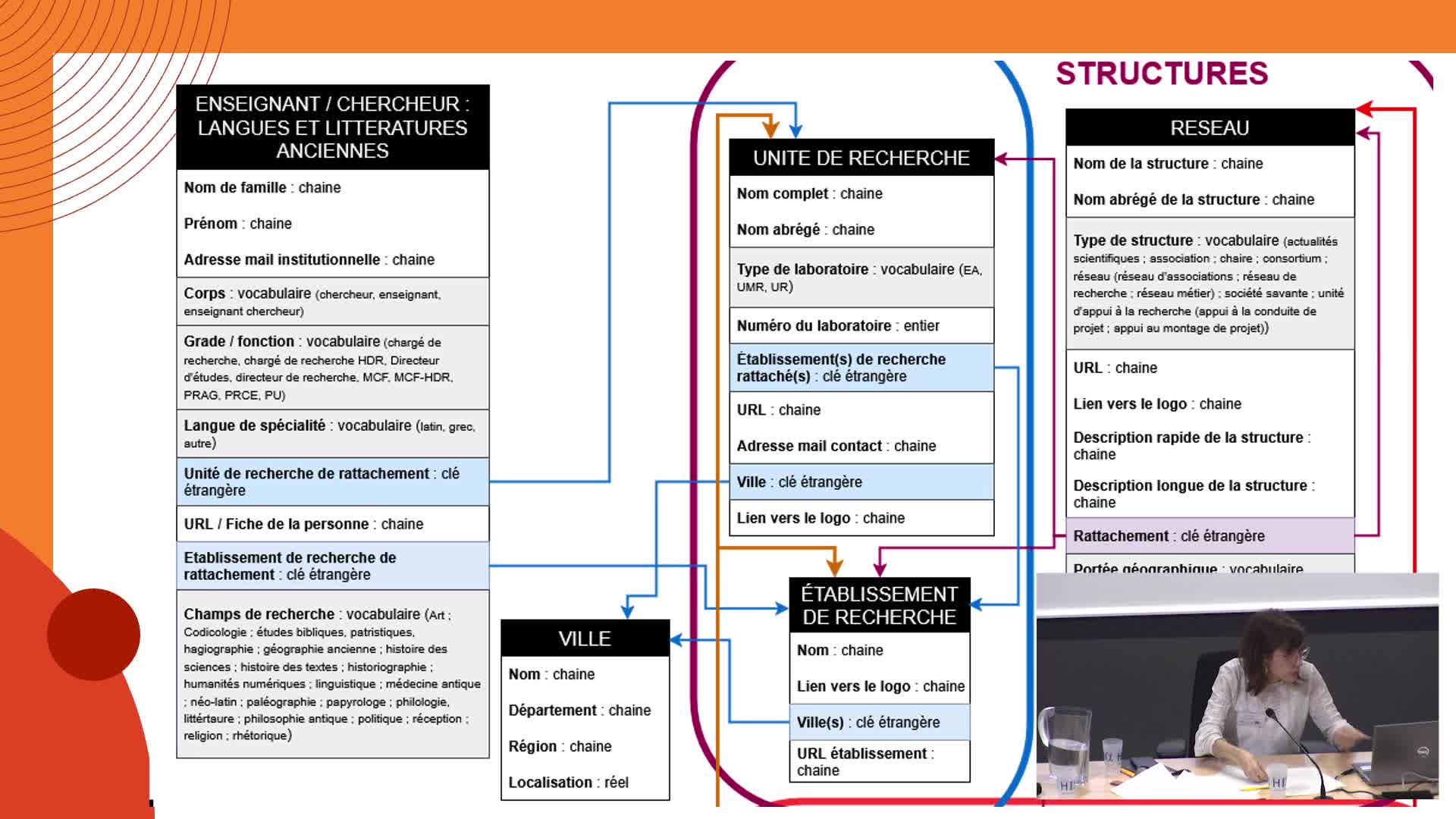
Using eScriptorium together with kraken as an infrastructure, we developed a simple but highly efficient procedure for reducing the amount of human labor necessary for creating large amounts of segmentation ground truth for documents with highly complex layouts, i.e., documents comprising regions with lines at eight different angles. Our specific project deals with medieval documents in Hebrew script in Judeo‑Arabic, Aramaic and Hebrew from the Cairo Genizah, including letters, legal documents, lists, notes and accounts. There are about 40,000 documentary texts from the Genizah, of which only about 5,000 have been transcribed. Therefore, our current aim is to create enough data to be able to train a global segmentation model with a very large number of classes, so that it can segment complex layouts in a single step.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Thème
Dans la même collection
-
2.10 : Clôture Colloque "Documents anciens et reconnaissance automatique des écritures manuscrites"
PincheAriane2.10 : Clôture Colloque "Documents anciens et reconnaissance automatique des écritures manuscrites"
-
2.8 : Reconnaissance et extraction d’informations dans des tableaux manuscrits historiques
PincheAriane2.8 : Reconnaissance et extraction d’informations dans des tableaux manuscrits historiques
-
2.7 : HTR of Handwritten Paleographic Greek Text as a Function of Chronology
PincheAriane2.7 : HTR of Handwritten Paleographic Greek Text as a Function of Chronology
-
2.6 : EpiSearch. Recognising Ancient Inscriptions in Epigraphic Manuscripts
BoschettiFederico2.6 : EpiSearch. Recognising Ancient Inscriptions in Epigraphic Manuscripts
-
2.4 : Expérimentations pour l’analyse automatique de sources chinoises anciennes
Vidal-GorèneChahan2.4 : Expérimentations pour l’analyse automatique de sources chinoises anciennes
-
2.3 : Analyse, Reconnaissance et Indexation des manuscrits CHAM
SchweyerAnne-ValérieBurieJean-Christophe2.3 : Analyse, Reconnaissance et Indexation des manuscrits CHAM
-
2.1 : FoNDUE - A Lightweight HTR Infrastructure for Geneva
GabaySimon2.1 : FoNDUE - A Lightweight HTR Infrastructure for Geneva
-
1.3 : HTR fine tuning for medieval manuscripts models: strategies and evaluation
Torres AguilarSergioJolivetVincent1.3 : HTR fine tuning for medieval manuscripts models: strategies and evaluation
-
2.5 : Sharing HTR datasets with standardized metadata: the HTR United initiative
ChaguéAlixClériceThibault2.5 : Sharing HTR datasets with standardized metadata: the HTR United initiative
-
2.9 : Retour d’expériences sur l’utilisation comparée de plusieurs de dispositifs de transcription …
TufféryChristophe2.9 : Retour d’expériences sur l’utilisation comparée de plusieurs de dispositifs de transcription numérique d’archives de fouilles archéologiques
-
2.2 : From HTR to Critical Edition: A Semi-Automatic Pipeline
StoeklDaniel2.2 : From HTR to Critical Edition: A Semi-Automatic Pipeline
-
1.7 : De Transkribus à eScriptorium : retour(s) d’expérience sur l’usage d’outils d’HTR appliqués à…
LeblancElina1.7: De Transkribus à eScriptorium : retour(s) d’expérience sur l’usage d’outils d’HTR appliqués à un corpus d’imprimés espagnols du XIXe siècle
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
2.2 : From HTR to Critical Edition: A Semi-Automatic Pipeline
StoeklDaniel2.2 : From HTR to Critical Edition: A Semi-Automatic Pipeline
Sur le même thème
-
Causeries Culture - Humanités Numériques, Intelligence Artificielle, littérature et technologies #6
PorlierChristopheBertaniNicolaCauseries Culture - Humanités Numériques, Intelligence Artificielle, littérature et technologies #6
-
Faire une histoire des territoires en contexte montagneux : l’organisation de l’espace par les fonc…
SuméraPaula[séminaire] Faire une histoire des territoires en contexte montagneux : l’organisation de l’espace par les fonctionnaires natifs (tusi 土司) dans la région des monts Wuling (Chine impériale tardive,
-
Digital Benin: a digital platform connecting the displaced royal artefacts from Benin Kingdom
Digital Benin: a digital platform connecting the displaced royal artefacts from Benin Kingdom
-
Multilinguality and data access: an area studies librarian’s perspective
WagnerCosimaMultilinguality and data access: an area studies librarian’s perspective
-
InVisto : Base de données pour l’histoire du livre et de l’édition vietnamienne en Cochinchine (18…
CaoThúy VyL’histoire du livre et de l’édition vietnamienne en Cochinchine (1890-1945)
-
Comment s’orienter dans la forêt des ressources et des outils numériques ?
BurriInèsAntiqui.TXTes - Sciences des textes anciens
-
Base de données et cartographie. Pour une nouvelle approche des monastères latins dans les États la…
ArtaudFlorianÀ travers son projet doctoral, Florian Artaud propose une relecture des institutions monastiques latines dans les États latins d’Orient, en les abordant sous l’angle de la territorialité. Au cœur de
-
L'IA comme aide à la recherche : l'expérimentation du traitement automatique des langues appliqué a…
MenuArianeAriane Menu (direction scientifique et technique, Inrap) présente ici un exemple d'utilisation du traitement automatique des langues pour repérer des mots-clés dans un corpus de texte et montre
-
The Crusades Regesta: A Database for the Study of the Latin East
GutgartsAnnaBomMyra MirandaDans cette communication, Anna Gutgarts et Myra M. Bom présentent l'histoire et les enjeux de la base de données The Crusades Regesta. Cette base de données, initiée par Jonathan Riley-Smith, est
-
Présentation du projet MistraNum. L’usage et l’apport des nouvelles technologies sur le site archéo…
YotaÉlisabethÉlisabeth Yota présente, dans cette communication, un projet de recherche alliant études byzantines et humanités numériques, consacré à l'étude et à la valorisation patrimoniale du site médiéval de
-
Le portail numérique Φραγκικά-Frankika : un nouvel élan pour l’histoire de la Grèce franque et lati…
TrélatPhilippeVoisinLudivineMeyer-FernandezGeoffreyDans cette communication, Geoffrey Meyer-Fernandez, Philippe Trélat et Ludivine Voisin présentent le portail Φραγκικά-Frankika, un projet de recherche numérique porté par l’École française d’Athènes
-
The Templar Citadel of Tartous through Images: Digital Tools to Reveal its Origins and Reconstruct …
MercuriLorenzoDans cette communication, Lorenzo Mercuri explore sous un angle renouvelé la citadelle templière de Tartous, en Syrie, grâce aux apports des outils numériques. En croisant histoire, archéologie et