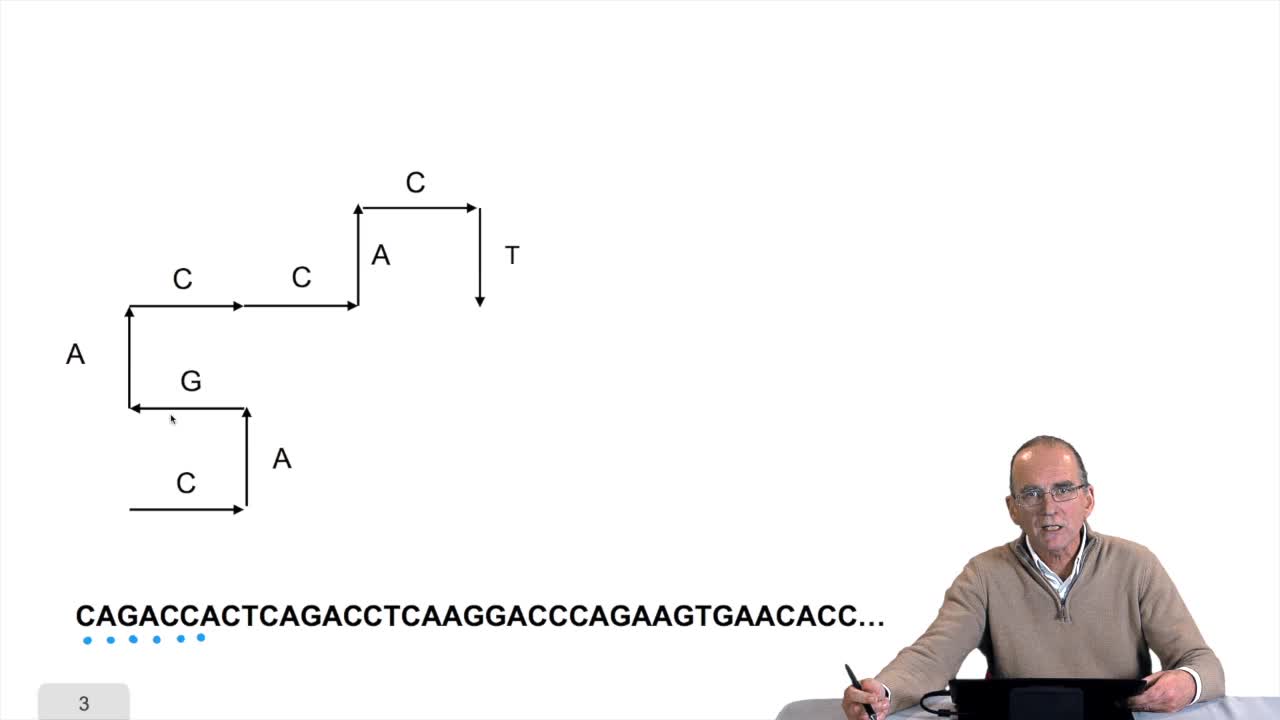Notice
1.2. At the heart of the cell: the DNA macromolecule
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
During the last session, we saw how at the heart of the cell there's DNA in the nucleus, sometimes of cells, or directly in the cytoplasm of the bacteria. The DNA is what we call a macromolecule, that is a very long molecule. It's Avery, in 1944, who discovered that the DNA was the support of genetic information. But the scientists who are most well-known for DNA are Francis Crick and James Watson who discovered together, with Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin, in 1953, the structure of DNA, the famous double helix, the two strands. Here are Crick and Watson explaining on a very crude wire model far away from the kind of modelwe would build nowadays with a computer visualization technic. They're showing the two strands of the DNA. They wrote a three page paper inwhich they had this very famous sentence: "It did not escapeour attention that this double helix structure was a way to explain how a DNA could replicate and then how its cell, one cell could give birth to two cells. " Wilkins was a scientist associated with this research in doing all the experimentally say to getthe structure of the molecule, to give clues on the structure of the molecule.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Thème
Documentation
Dans la même collection
-
1.1. The cell, atom of the living world
RechenmannFrançoisWelcome to this introduction to bioinformatics. We will speak of genomes and algorithms. More specifically, we will see how genetic information can be analysed by algorithms. In these five weeks to
-
1.10. Overlapping sliding window
RechenmannFrançoisWe have made some drawings along a genomic sequence. And we have seen that although the algorithm is quite simple, even if some points of the algorithmare bit trickier than the others, we were able to
-
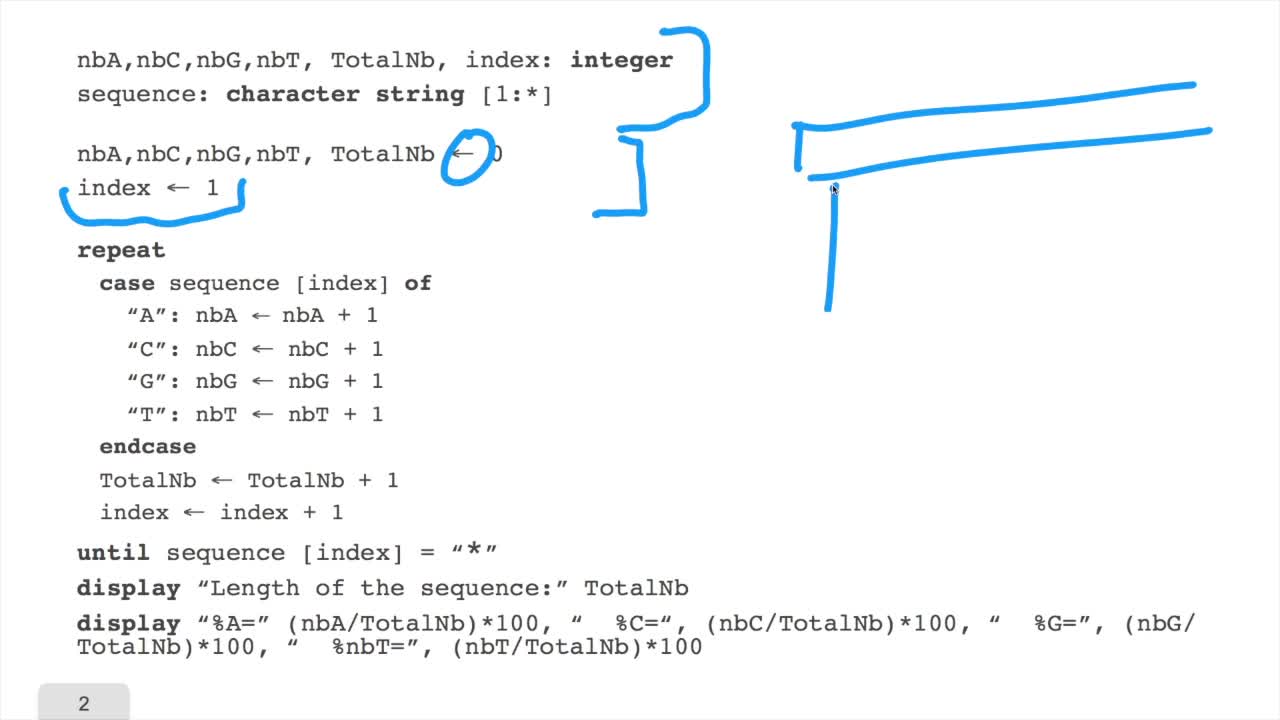
1.5. Counting nucleotides
RechenmannFrançoisIn this session, don't panic. We will design our first algorithm. This algorithm is forcounting nucleotides. The idea here is that as an input,you have a sequence of nucleotides, of bases, of letters,
-
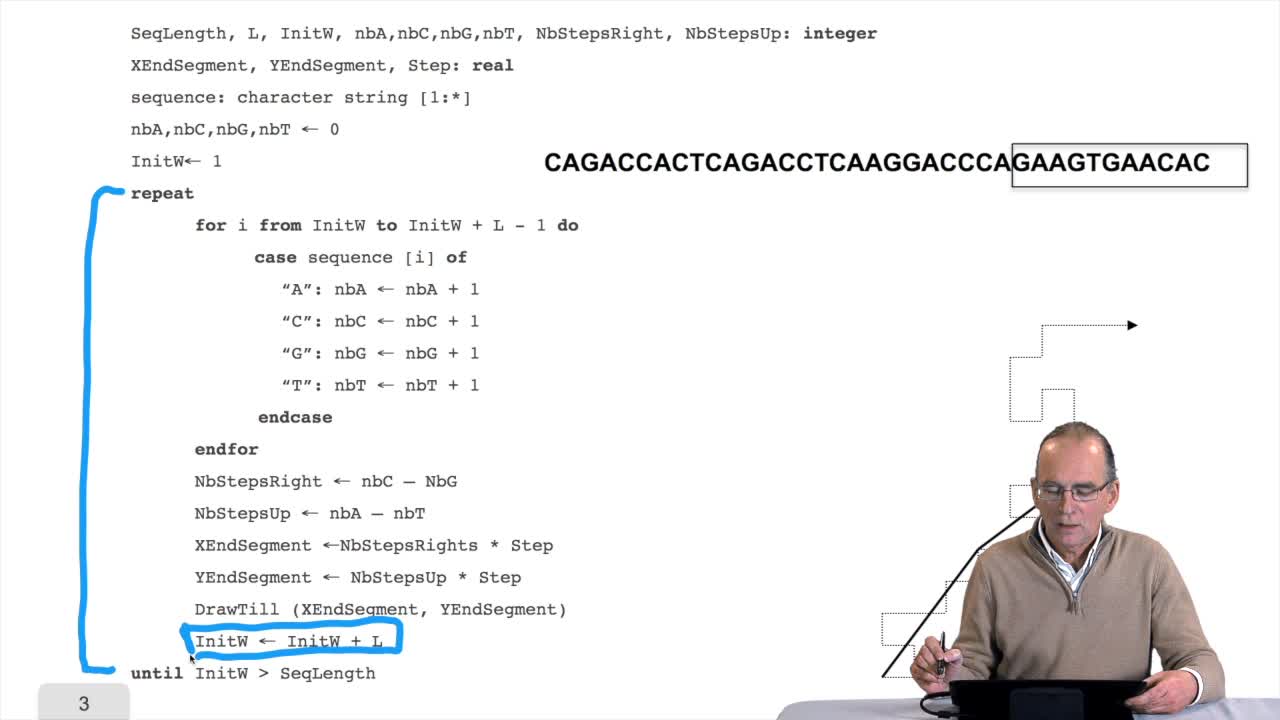
1.8. Compressing the DNA walk
RechenmannFrançoisWe have written the algorithm for the circle DNA walk. Just a precision here: the kind of drawing we get has nothing to do with the physical drawing of the DNA molecule. It is a symbolic
-
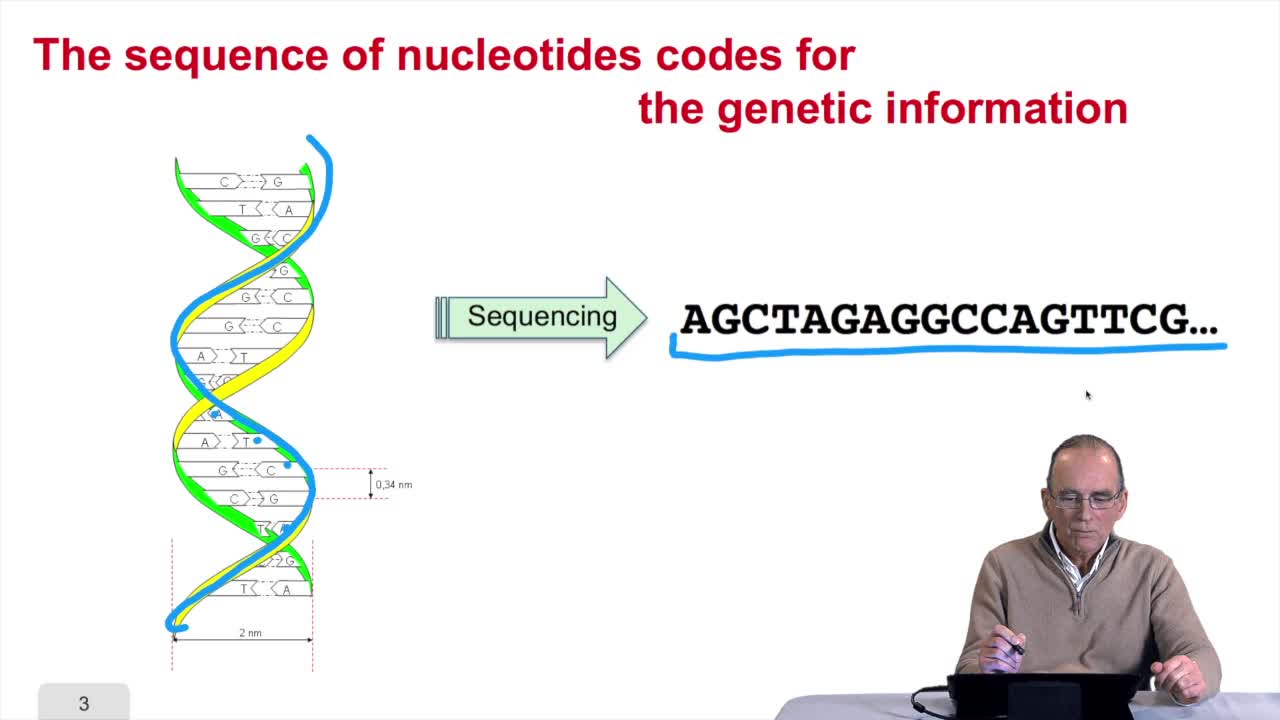
1.3. DNA codes for genetic information
RechenmannFrançoisRemember at the heart of any cell,there is this very long molecule which is called a macromolecule for this reason, which is the DNA molecule. Now we will see that DNA molecules support what is called
-
1.6. GC and AT contents of DNA sequence
RechenmannFrançoisWe have designed our first algorithmfor counting nucleotides. Remember, what we have writtenin pseudo code is first declaration of variables. We have several integer variables that are variables which
-
1.9. Predicting the origin of DNA replication?
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen a nice algorithm to draw, let's say, a DNA sequence. We will see that first, we have to correct a little bit this algorithm. And then we will see how such as imple algorithm can provide
-
1.4. What is an algorithm?
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen that a genomic textcan be indeed a very long sequence of characters. And to interpret this sequence of characters, we will need to use computers. Using computers means writing program.
-
1.7. DNA walk
RechenmannFrançoisWe will now design a more graphical algorithm which is called "the DNA walk". We shall see what does it mean "DNA walk". Walk on to DNA. Something like that, yes. But first, just have a look again at
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
1.7. DNA walk
RechenmannFrançoisWe will now design a more graphical algorithm which is called "the DNA walk". We shall see what does it mean "DNA walk". Walk on to DNA. Something like that, yes. But first, just have a look again at
-
2.6. Algorithms + data structures = programs
RechenmannFrançoisBy writing the Lookup GeneticCode Function, we completed our translation algorithm. So we may ask the question about the algorithm, does it terminate? Andthe answer is yes, obviously. Is it pertinent,
-
3.3. Searching for start and stop codons
RechenmannFrançoisWe have written an algorithm for finding genes. But you remember that we arestill to write the two functions for finding the next stop codonand the next start codon. Let's see how we can do that. We
-
4.1. How to predict gene/protein functions?
RechenmannFrançoisLast week we have seen that annotating a genome means first locating the genes on the DNA sequences that is the genes, the region coding for proteins. But this is indeed the first step,the next very
-
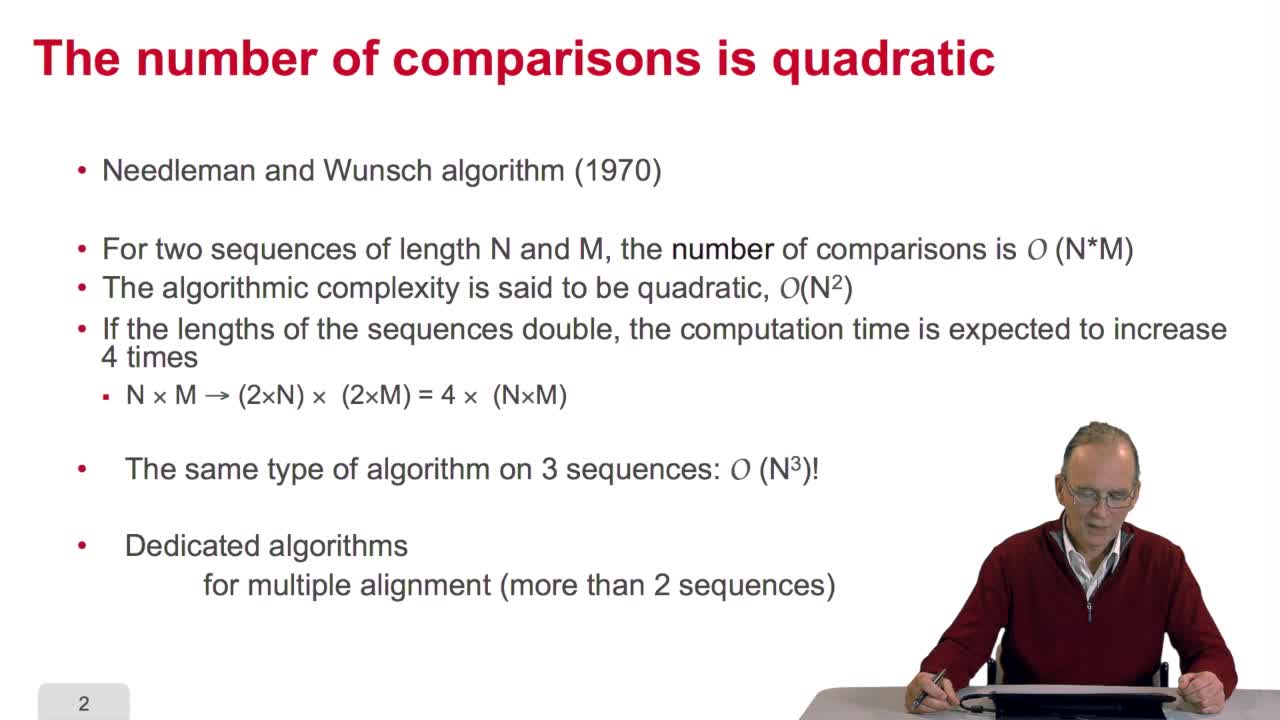
4.10. How efficient is this algorithm?
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen the principle of an iterative algorithm in two paths for aligning and comparing two sequences of characters, here DNA sequences. And we understoodwhy the iterative version is much more
-
5.7. The application domains in microbiology
RechenmannFrançoisBioinformatics relies on many domains of mathematics and computer science. Of course, algorithms themselves on character strings are important in bioinformatics, we have seen them. Algorithms and
-
1.1. The cell, atom of the living world
RechenmannFrançoisWelcome to this introduction to bioinformatics. We will speak of genomes and algorithms. More specifically, we will see how genetic information can be analysed by algorithms. In these five weeks to
-
1.10. Overlapping sliding window
RechenmannFrançoisWe have made some drawings along a genomic sequence. And we have seen that although the algorithm is quite simple, even if some points of the algorithmare bit trickier than the others, we were able to
-
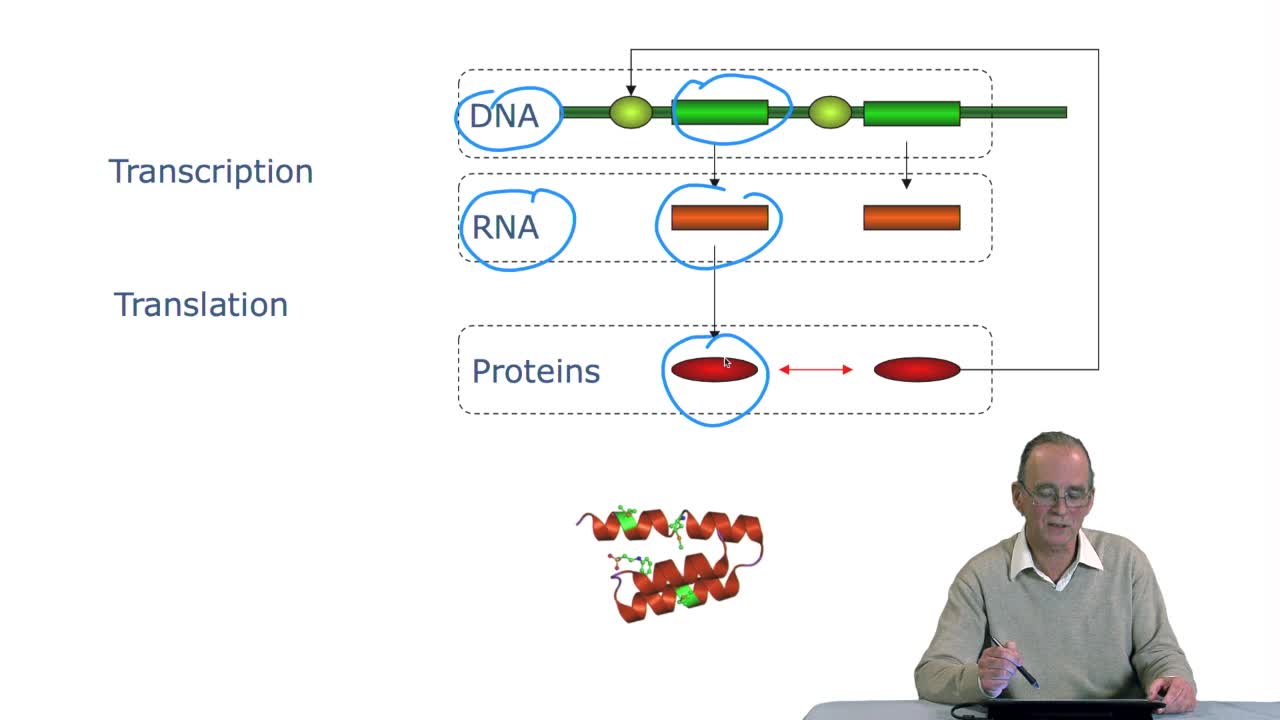
2.3. The genetic code
RechenmannFrançoisGenes code for proteins. What is the correspondence betweenthe genes, DNA sequences, and the structure of proteins? The correspondence isthe genetic code. Proteins have indeedsequences of amino acids.
-
3.6. Boyer-Moore algorithm
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen how we can make gene predictions more reliable through searching for all the patterns,all the occurrences of patterns. We have seen, for example, howif we locate the RBS, Ribosome
-
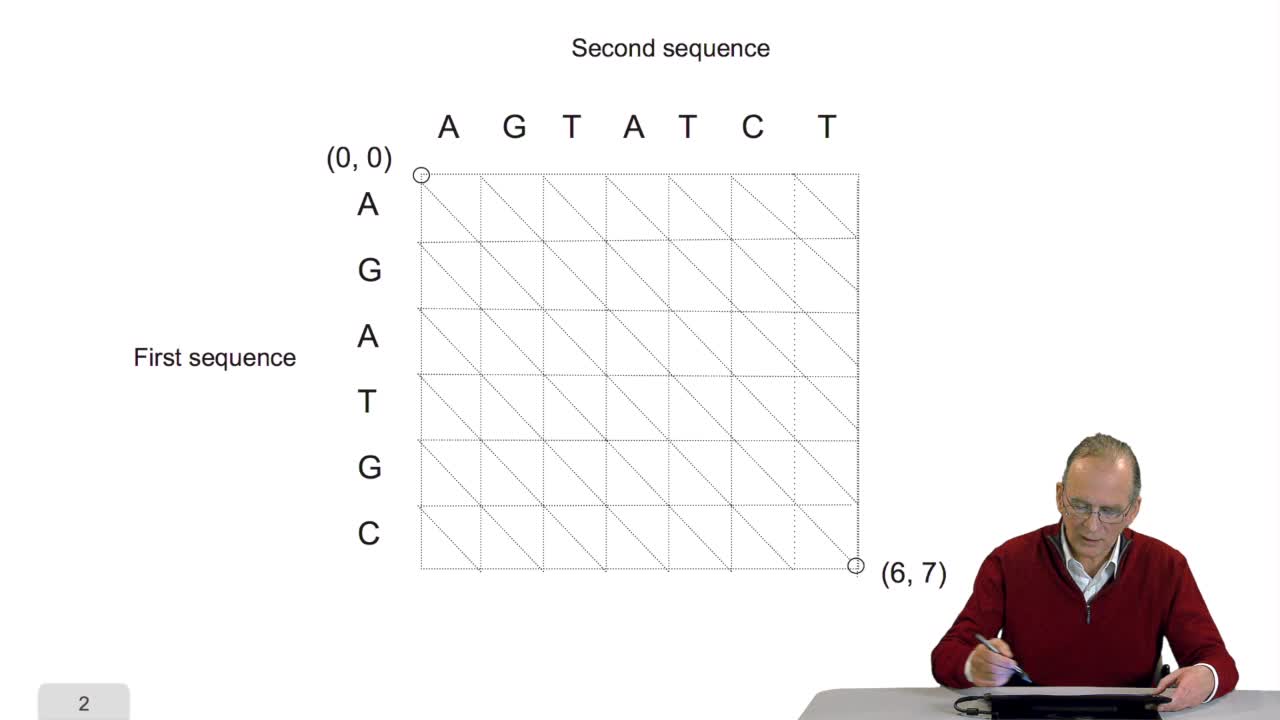
4.5. A sequence alignment as a path
RechenmannFrançoisComparing two sequences and thenmeasuring their similarities is an optimization problem. Why? Because we have seen thatwe have to take into account substitution and deletion. During the alignment, the
-
5.5. Differences are not always what they look like
RechenmannFrançoisThe algorithm we have presented works on an array of distance between sequences. These distances are evaluated on the basis of differences between the sequences. The problem is that behind the