Notice
4.3. Measuring sequence similarity
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
So we understand why gene orprotein sequences may be similar. It's because they evolve togetherwith the species and they evolve in time, there aremodifications in the sequence and that the sequence may still besimilar, similar enough again to retrieve information on onesequence to transfer it to another sequence of interest. So thequestion now is how can we measure this similarity between twosequences for the moment. The first approach to similarityis a very simple one is to apply a distance which is calledhere the Editing System or the Hamming Distance.The idea is very basic. You would take two sequences likethese two sequences here and you look at the differences and youcount the number of differences. Here, for example, you have twodifferences so you will say that the distance, the similaritybetween the two sequences, the distance is two. Here wehave another pair of sequences which are less similar becausethey are three differences. That's quite nice, it'sa hamming distance. Is it really a distance? A distance is a mathematicalconcept and to be a distance, it must satisfy three conditions:the distance between a sequence and itself must be zero, a sequencebetween a sequence and another one must be the same betweenthe last one and the first one and we must have this inequalitywhich is always verified.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Thème
Documentation
Dans la même collection
-
4.7. Alignment costs
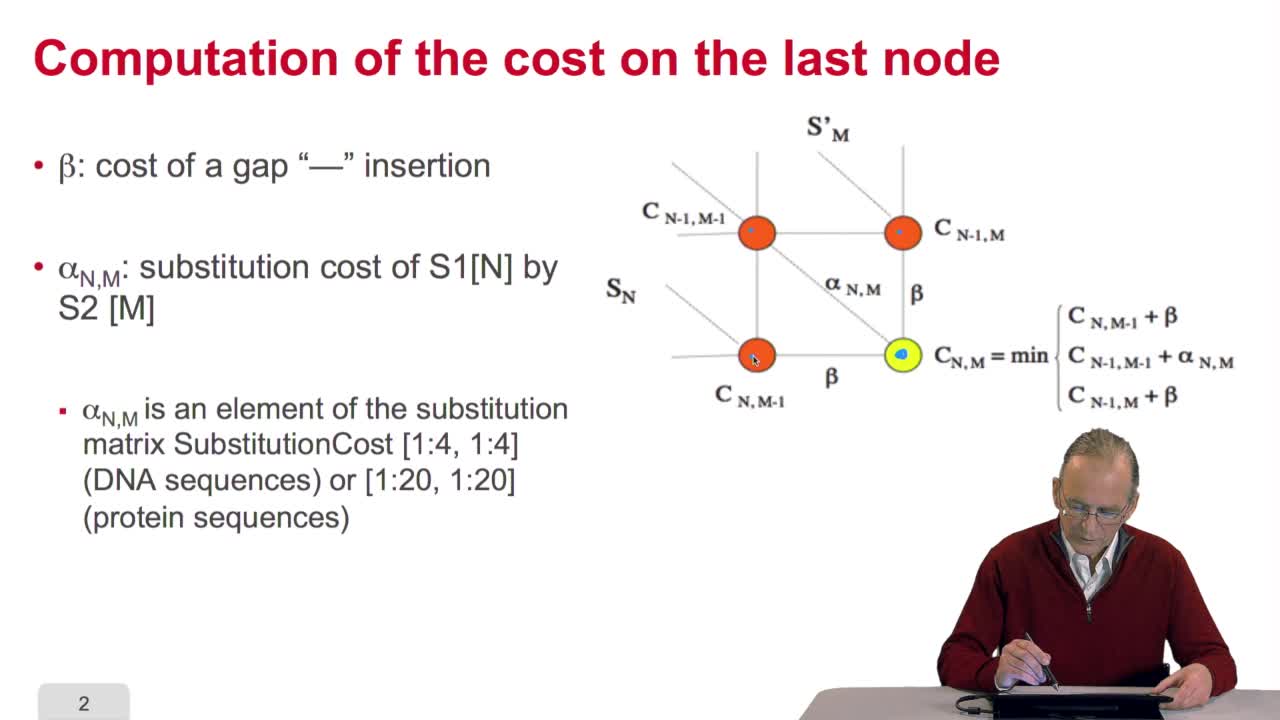
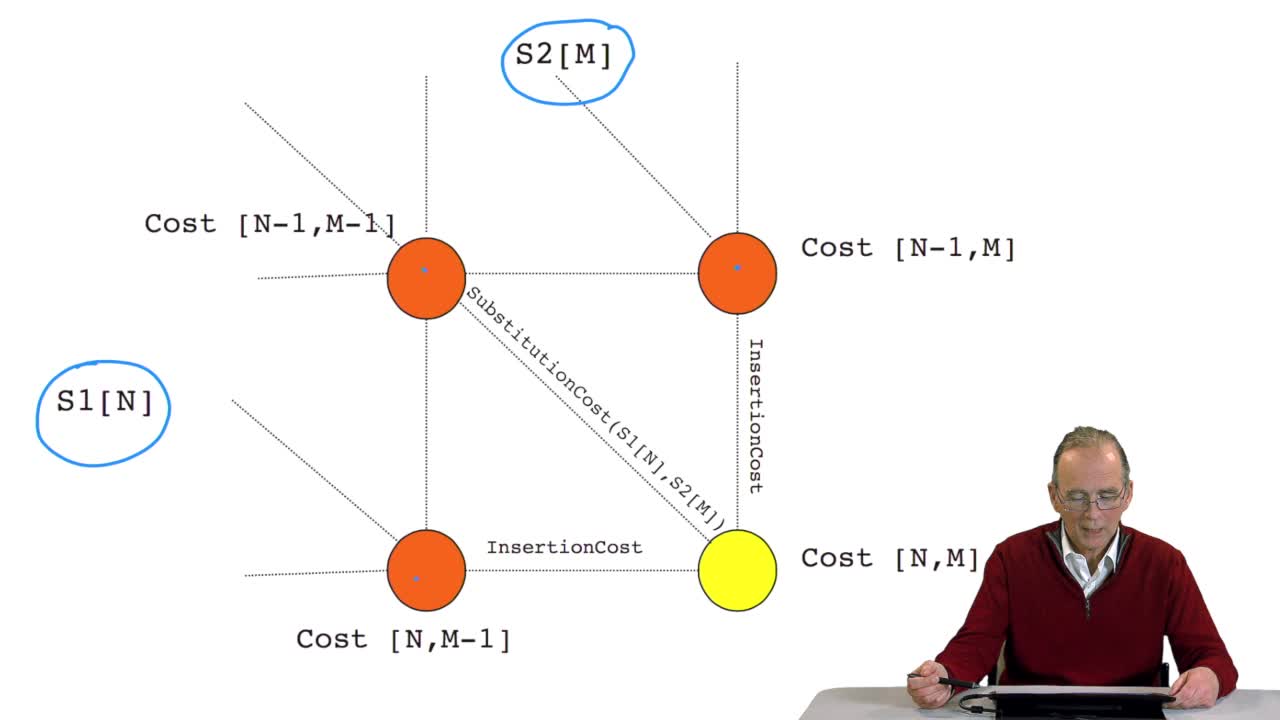
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen how we can compute the cost of the path ending on the last node of our grid if we know the cost of the sub-path ending on the three adjacent nodes. It is time now to see more deeply why
-
4.1. How to predict gene/protein functions?
RechenmannFrançoisLast week we have seen that annotating a genome means first locating the genes on the DNA sequences that is the genes, the region coding for proteins. But this is indeed the first step,the next very
-
4.10. How efficient is this algorithm?
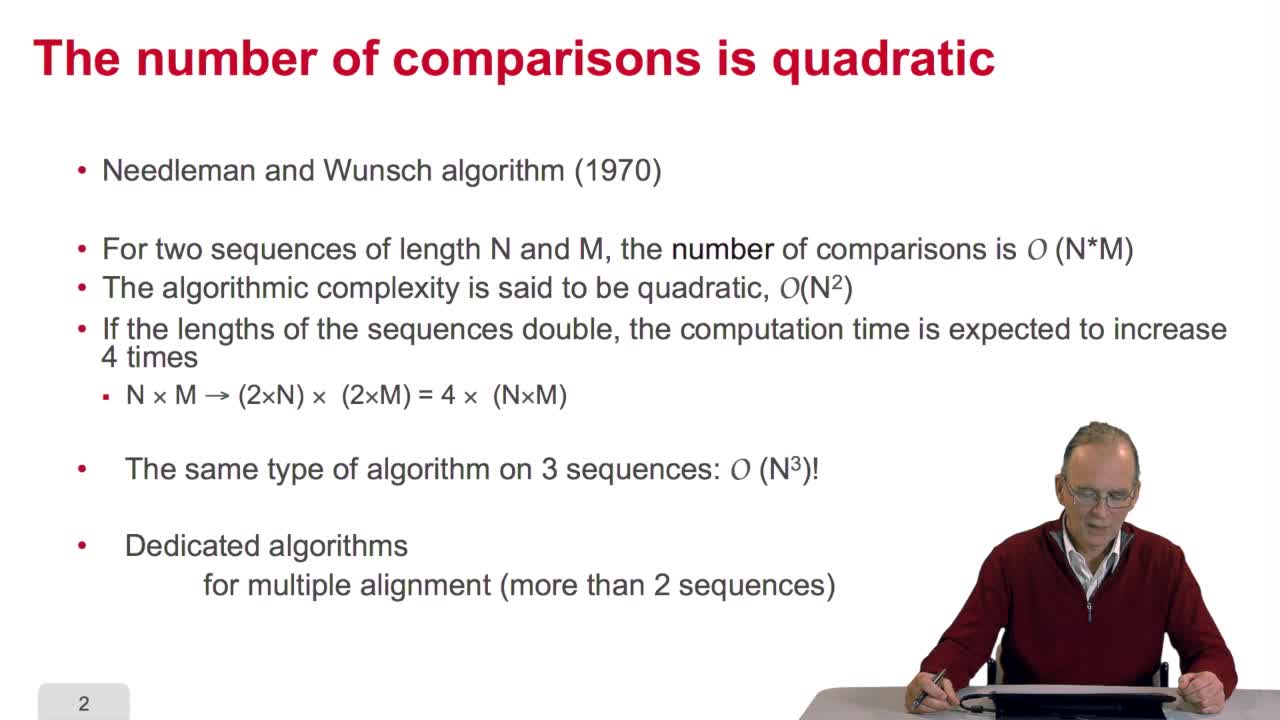
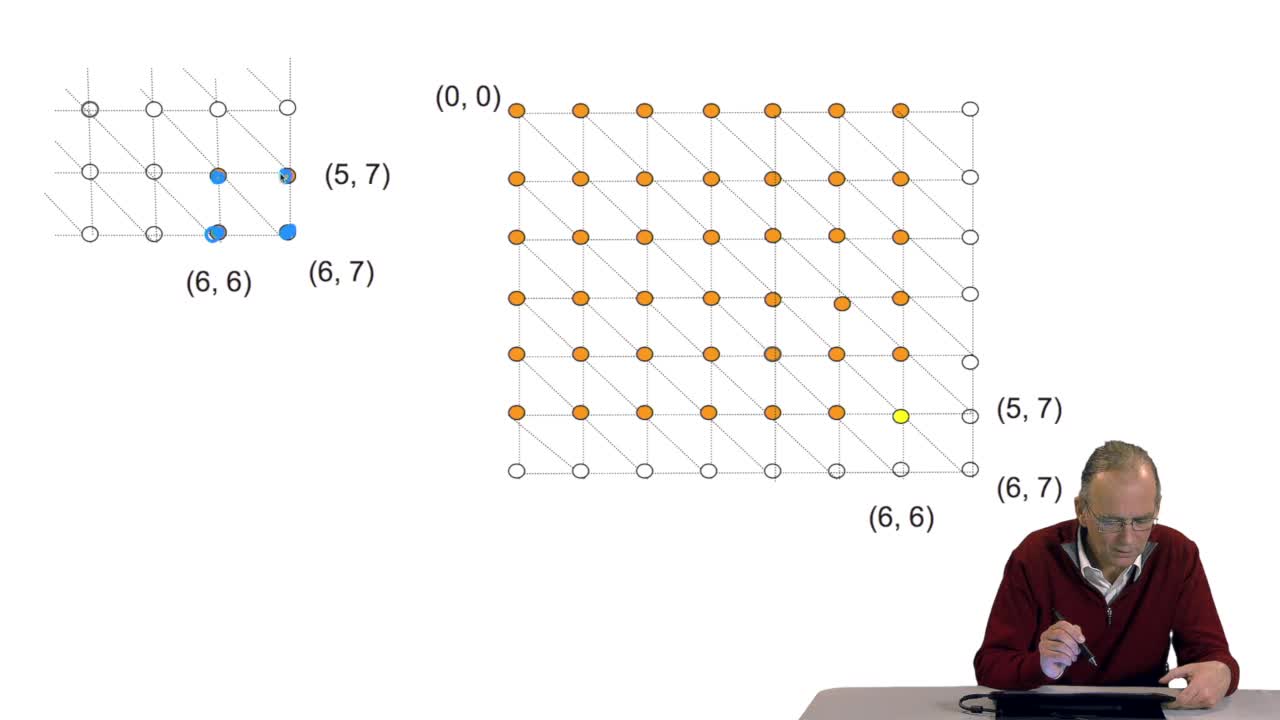
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen the principle of an iterative algorithm in two paths for aligning and comparing two sequences of characters, here DNA sequences. And we understoodwhy the iterative version is much more
-
4.5. A sequence alignment as a path
RechenmannFrançoisComparing two sequences and thenmeasuring their similarities is an optimization problem. Why? Because we have seen thatwe have to take into account substitution and deletion. During the alignment, the
-
4.8. A recursive algorithm
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen how we can computethe optimal cost, the ending node of our grid if we know the optimal cost of the three adjacent nodes. This is this computation scheme we can see here using the notation
-
4.2. Why gene/protein sequences may be similar?
RechenmannFrançoisBefore measuring the similaritybetween the sequences, it's interesting to answer the question: why gene or protein sequences may be similar? It is indeed veryinteresting because the answer is related
-
4.6. A path is optimal if all its sub-paths are optimal
RechenmannFrançoisA sequence alignment between two sequences is a path in a grid. So that, an optimal sequence alignmentis an optimal path in the same grid. We'll see now that a property of this optimal path provides
-
4.9. Recursion can be avoided: an iterative version
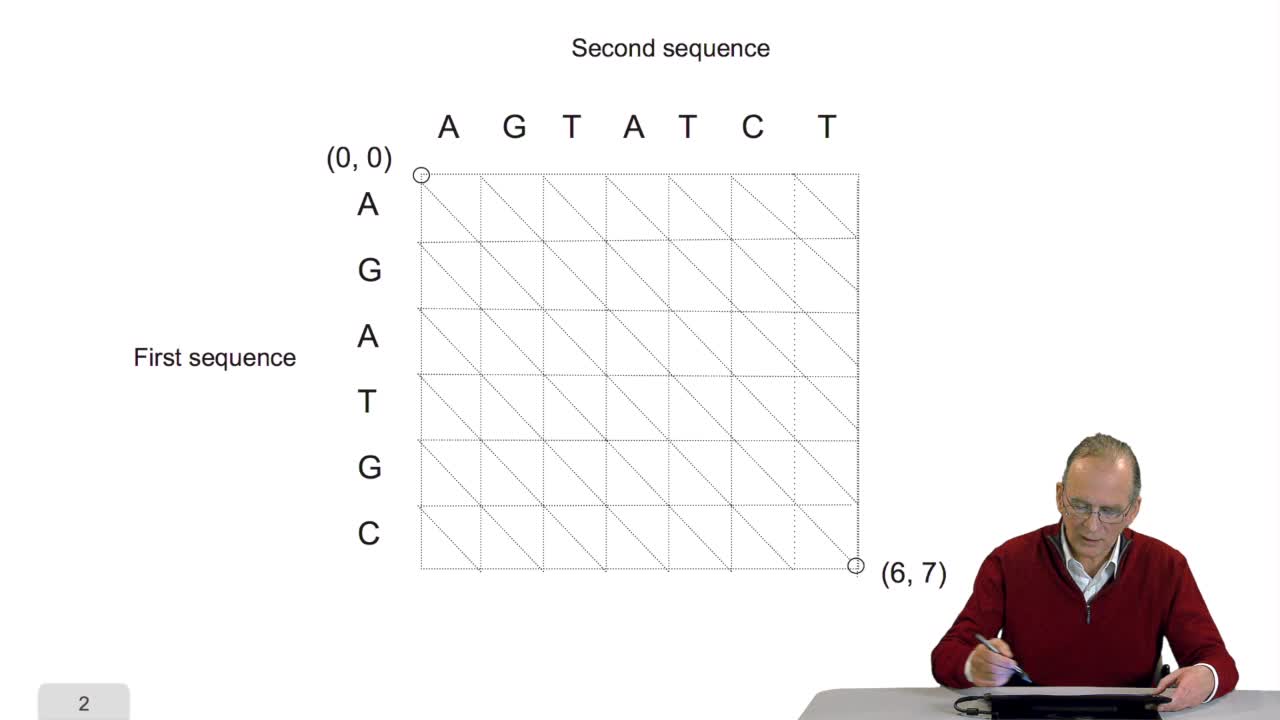
RechenmannFrançoisWe have written a recursive function to compute the optimal path that is an optimal alignment between two sequences. Here all the examples I gave were onDNA sequences, four letter alphabet. OK. The
-
4.4. Aligning sequences is an optimization problem
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen a nice and a quitesimple solution for measuring the similarity between two sequences. It relied on the so-called hammingdistance that is counting the number of differencesbetween two
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
1.3. DNA codes for genetic information
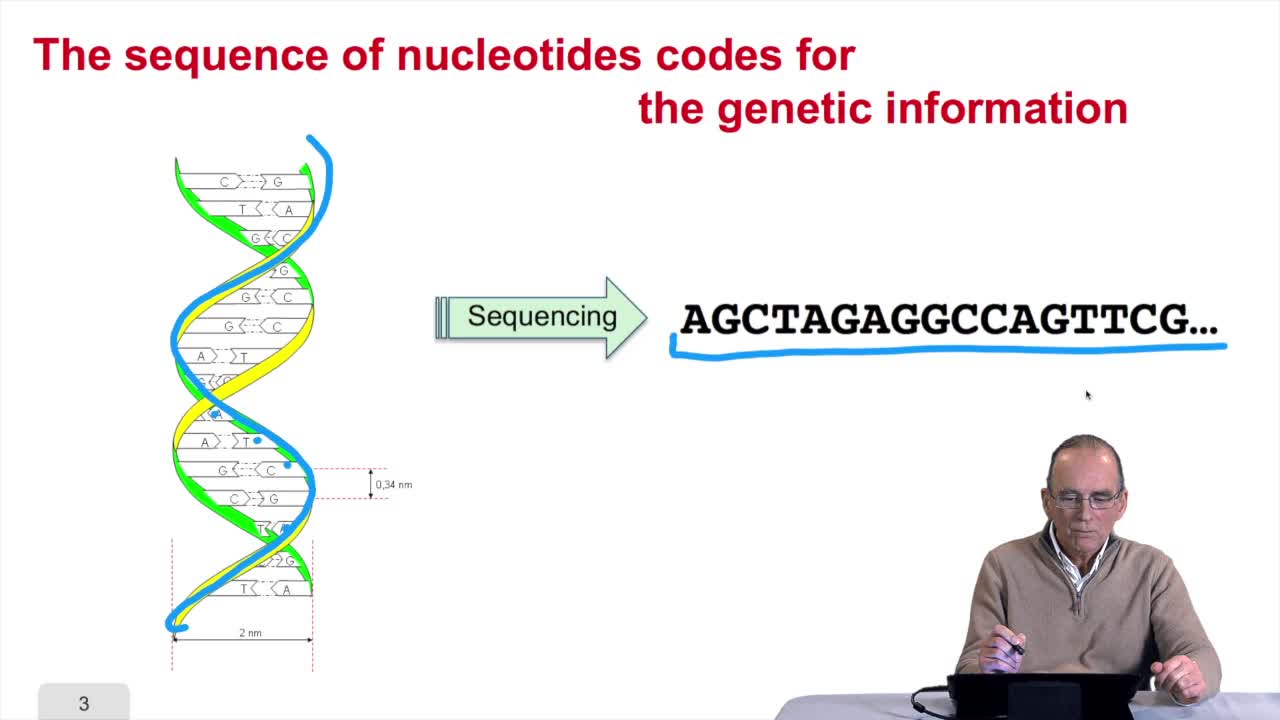
RechenmannFrançoisRemember at the heart of any cell,there is this very long molecule which is called a macromolecule for this reason, which is the DNA molecule. Now we will see that DNA molecules support what is called
-
2.1. The sequence as a model of DNA
RechenmannFrançoisWelcome back to our course on genomes and algorithms that is a computer analysis ofgenetic information. Last week we introduced the very basic concept in biology that is cell, DNA, genome, genes
-
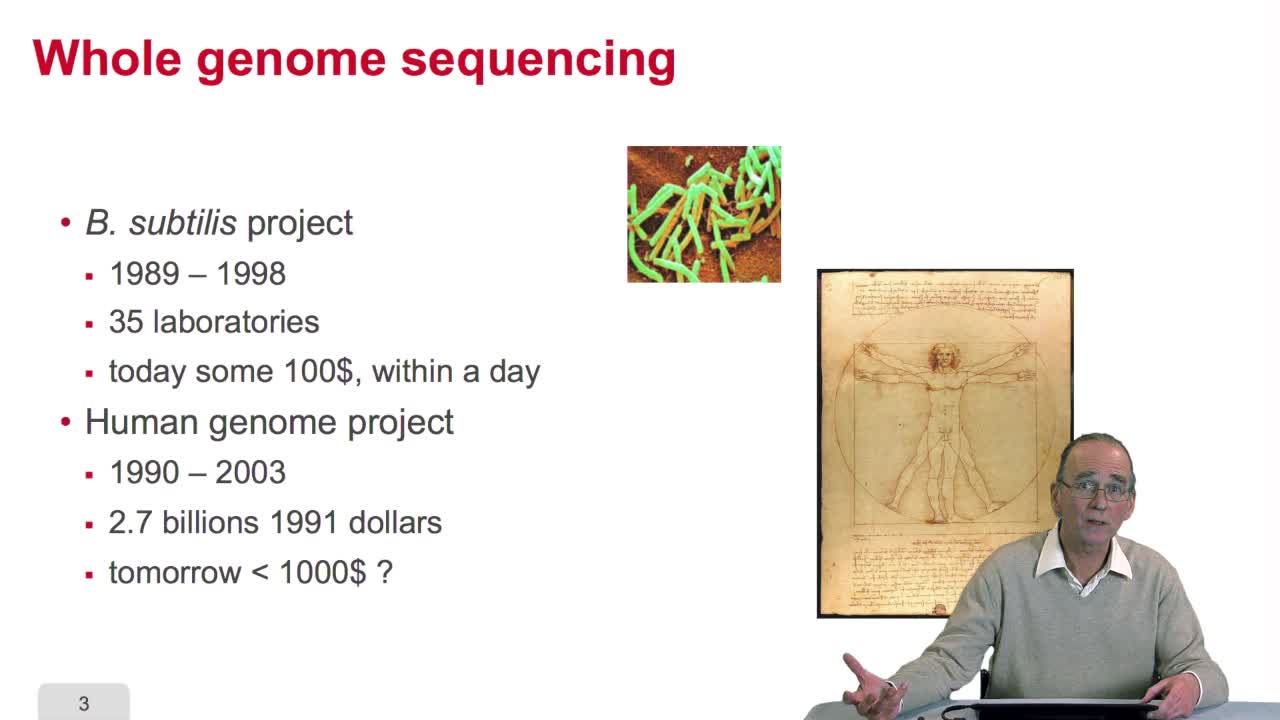
2.9. Whole genome sequencing
RechenmannFrançoisSequencing is anexponential technology. The progresses in this technologyallow now to a sequence whole genome, complete genome. What does it mean? Well let'stake two examples: some twenty years ago,
-
3.7. Index and suffix trees
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen with the Boyer-Moore algorithm how we can increase the efficiency of spin searching through the pre-processing of the pattern to be searched. Now we will see that an alternative way of
-
4.4. Aligning sequences is an optimization problem
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen a nice and a quitesimple solution for measuring the similarity between two sequences. It relied on the so-called hammingdistance that is counting the number of differencesbetween two
-
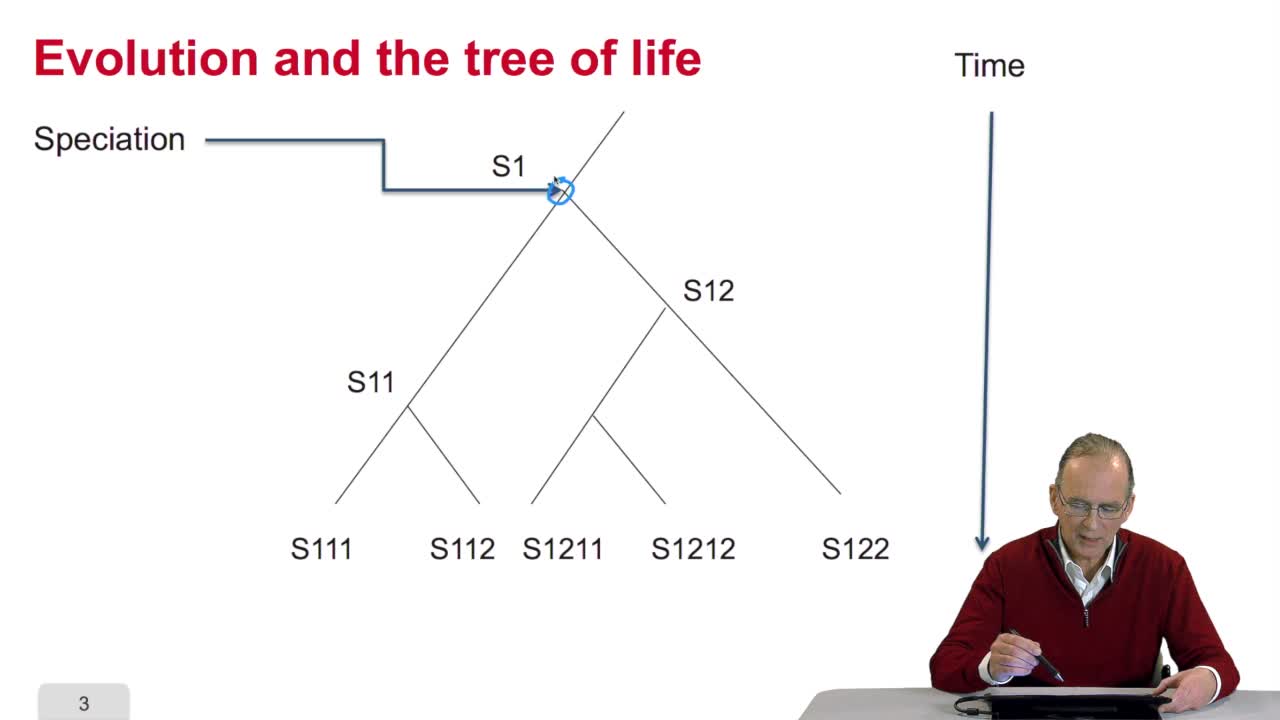
5.3. Building an array of distances
RechenmannFrançoisSo using the sequences of homologous gene between several species, our aim is to reconstruct phylogenetic tree of the corresponding species. For this, we have to comparesequences and compute distances
-
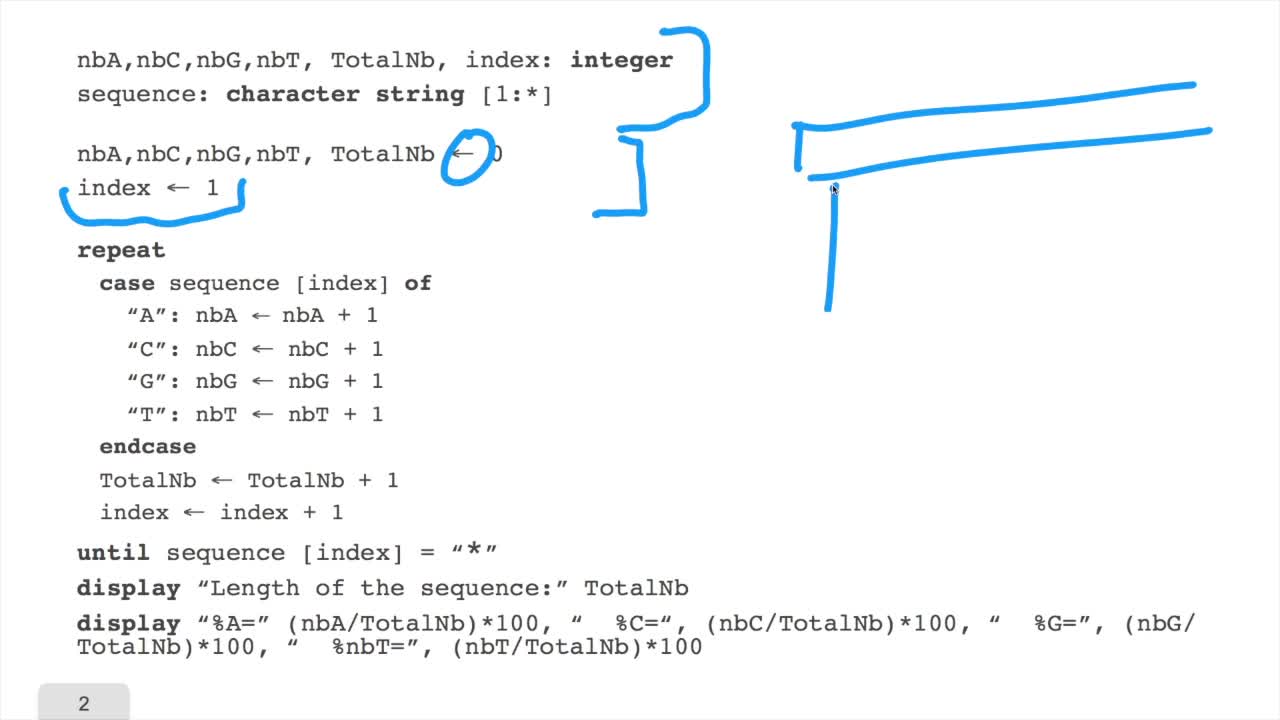
1.6. GC and AT contents of DNA sequence
RechenmannFrançoisWe have designed our first algorithmfor counting nucleotides. Remember, what we have writtenin pseudo code is first declaration of variables. We have several integer variables that are variables which
-
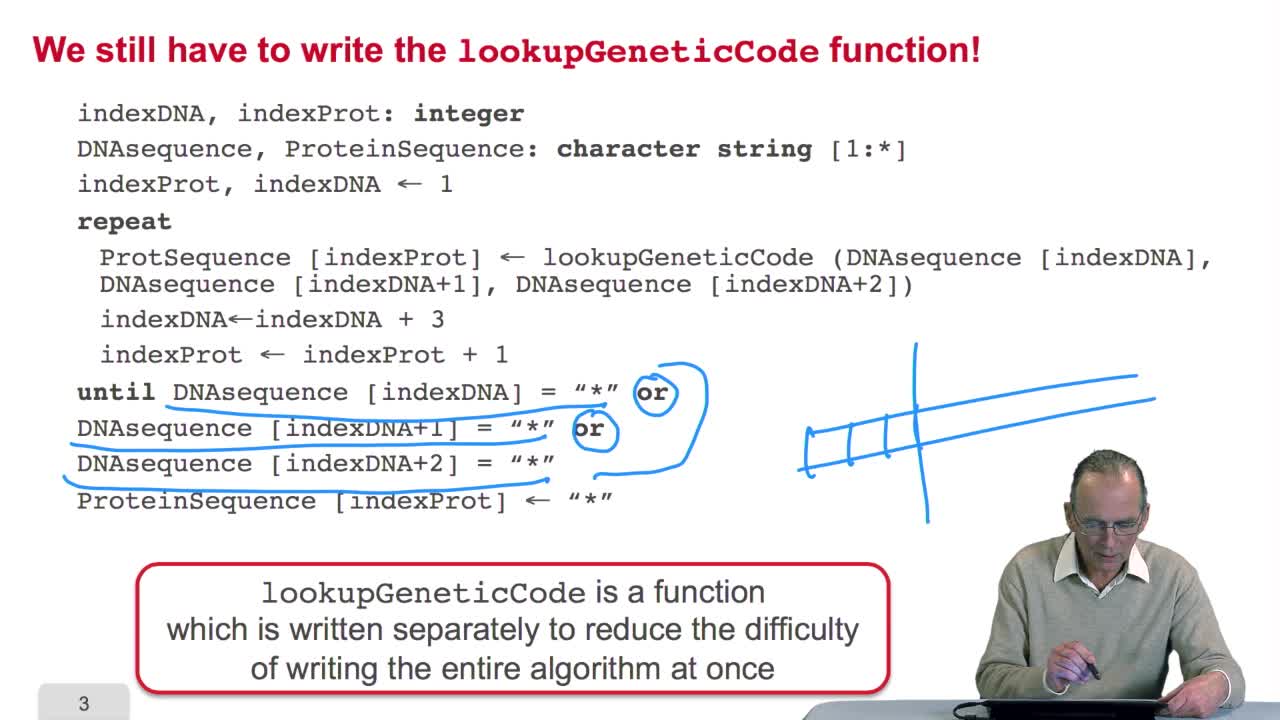
2.5. Implementing the genetic code
RechenmannFrançoisRemember we were designing our translation algorithm and since we are a bit lazy, we decided to make the hypothesis that there was the adequate function forimplementing the genetic code. It's now time
-
3.2. A simple algorithm for gene prediction
RechenmannFrançoisBased on the principle we statedin the last session, we will now write in pseudo code a firstalgorithm for locating genes on a bacterial genome. Remember first how this algorithm should work, we first
-
3.10. Gene prediction in eukaryotic genomes
RechenmannFrançoisIf it is possible to have verygood predictions for bacterial genes, it's certainly not the caseyet for eukaryotic genomes. Eukaryotic cells have manydifferences in comparison to prokaryotic cells. You
-
4.10. How efficient is this algorithm?
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen the principle of an iterative algorithm in two paths for aligning and comparing two sequences of characters, here DNA sequences. And we understoodwhy the iterative version is much more
-
5.7. The application domains in microbiology
RechenmannFrançoisBioinformatics relies on many domains of mathematics and computer science. Of course, algorithms themselves on character strings are important in bioinformatics, we have seen them. Algorithms and