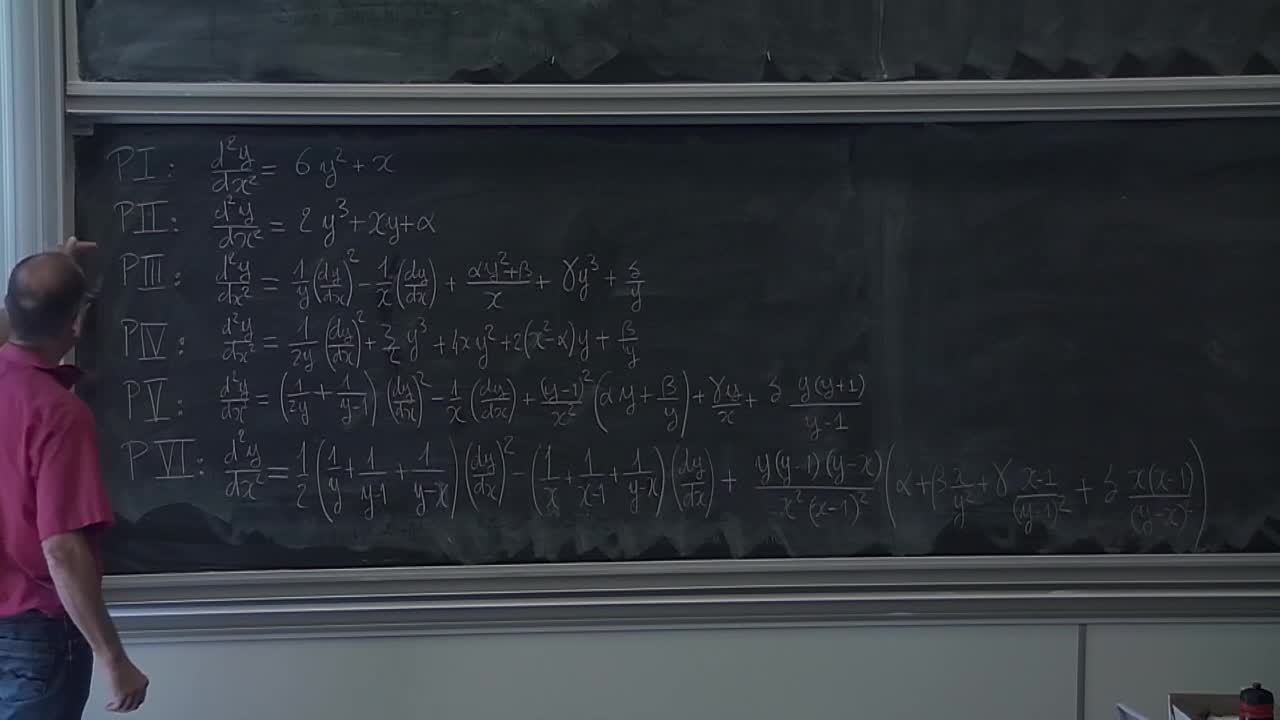Notice
F. Loray - Painlevé equations and isomonodromic deformations II (Part 3)
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
In these lectures, we use the material of V. Heu and H. Reis' lectures to introduce and study Painlevé equations from the isomonodromic point of view. The main objects are rank 2 systems of linear differential equations on the Riemann sphere, or more generally, rank 2 connections. We will mainly focus on the case they have 4 simple poles, corresponding to the Painlevé VI equation, while other Painlevé equations correspond to confluence of these poles.First, we settle the Riemann-Hilbert correspondance which establish, roughly speaking, a one-to-one correspondance between connections and their monodromy data, once the poles are fixed. This correspondance is analytic, but not algebraic, very transcendental. Then isomonodromic deformations arise when we deform poles and connection without deforming the monodromy representation. Although the deformation is also transcendental in general, the coefficients satisfy a non linear polynomial differential equation, namely the Painlevé VI equation. By constructing an universal isomonodromic deformation, we explain how Malgrange proved the Painlevé property for isomonodromic deformation equations: solutions admit analytic continuation (with poles) outside of a fixed singular set. At the end, we can describe the Okamoto space of initial conditions for Painlevé VI equation, as well as its non linear monodromy. This can be used to prove the irreductibility of Painlevé VI equation, i.e. the absence of special first integrals, and therefore the transcendance of the general solution.
Thème
Documentation
Dans la même collection
-
H. Guenancia - A decomposition theorem for singular spaces with trivial canonical class (Part 2)
GUENANCIA Henri
The Beauville-Bogomolov decomposition theorem asserts that any compact Kähler manifold with numerically trivial canonical bundle admits an étale cover that decomposes into a product of a torus, an
-
F. Touzet - About the analytic classification of two dimensional neighborhoods of elliptic curves
TOUZET Frédéric
I will investigate the analytic classification of two dimensional neighborhoods of an elliptic curve C with trivial normal bundle and discuss the existence of foliations having C as a leaf. Joint work
-
A. Höring - A decomposition theorem for singular spaces with trivial canonical class (Part 3)
HöRING Andreas
The Beauville-Bogomolov decomposition theorem asserts that any compact Kähler manifold with numerically trivial canonical bundle admits an étale cover that decomposes into a product of a torus, an
-
C. Spicer - Minimal models of foliations
SPICER Calum
We will discuss some recent work on the minimal model program (MMP) for foliations and explain some applications of the MMP to the study of foliation singularities and to the study of some
-
S. Druel - A decomposition theorem for singular spaces with trivial canonical class (Part 5)
DRUEL Stéphane
The Beauville-Bogomolov decomposition theorem asserts that any compact Kähler manifold with numerically trivial canonical bundle admits an étale cover that decomposes into a product of a torus, an
-
D. Novikov - Wilkie's conjecture for restricted elementary functions
NOVIKOV Dmitriĭ Aleksandrovich
We consider the structure $\mathbb{R}^{RE}$ obtained from $(\mathbb{R},
-
B. Deroin - The Jouanolou foliation
DEROIN Bertrand
I will discuss dynamical properties of the Jouanolou foliation of the complex projective plane in degree two. Joint work with Aurélien Alvarez.
-
A. Belotto da Silva - Singular foliations in sub-Riemannian geometry and the Strong Sard Conjecture
BELOTTO DA SILVA André Ricardo
Given a totally nonholonomic distribution of rank two $\Delta$ on a three-dimensional manifold $M$, it is natural to investigate the size of the set of points $\mathcal{X}^x$ that can be reached
-
L. Meersseman - Kuranishi and Teichmüller
MEERSSEMAN Laurent
Let X be a compact complex manifold. The Kuranishi space of X is an analytic space which encodes every small deformation of X. The Teichmüller space is a topological space formed by the classes
-
J. Demailly - Existence of logarithmic and orbifold jet differentials
DEMAILLY Jean-Pierre
Given a projective algebraic orbifold, one can define associated logarithmic and orbifold jet bundles. These bundles describe the algebraic differential operators that act on germs of curves
-
E. Amerik - On the characteristic foliation
AMERIK Ekaterina
Let X be a holomorphic symplectic manifold and D a smooth hypersurface in X. Then the restriction of the symplectic form on D has one-dimensional kernel at each point. This distribution is
-
S. Ghazouani - Isoholonomic foliations of moduli spaces of Riemann surfaces
GHAZOUANI Selim
In this talk, I will introduce families of foliations on the moduli space of Riemann surfaces M_{g,n} which we call Veech foliations. These foliations are defined by identifying M_{g,n} to
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
F. Loray - Painlevé equations and isomonodromic deformations II (Part 1)
LORAY Frank
In these lectures, we use the material of V. Heu and H. Reis' lectures to introduce and study Painlevé equations from the isomonodromic point of view. The main objects are rank 2 systems of
-
F. Loray - Painlevé equations and isomonodromic deformations II (Part 2)
LORAY Frank
In these lectures, we use the material of V. Heu and H. Reis' lectures to introduce and study Painlevé equations from the isomonodromic point of view. The main objects are rank 2 systems of
-
F. Loray - Painlevé equations and isomonodromic deformations II (Part 4)
LORAY Frank
In these lectures, we use the material of V. Heu and H. Reis' lectures to introduce and study Painlevé equations from the isomonodromic point of view. The main objects are rank 2 systems of
Sur le même thème
-
"Le mathématicien Petre (Pierre) Sergescu, historien des sciences, personnalité du XXe siècle"
HERLéA Alexandre
Alexandre HERLEA est membre de la section « Sciences, histoire des sciences et des techniques et archéologie industrielle » du CTHS. Professeur émérite des universités, membre effectif de l'Académie
-
Webinaire sur la rédaction des PGD
LOUVET Violaine
Rédaction des Plans de Gestion de Données (PGD) sous l’angle des besoins de la communauté mathématique.
-
Alexandre Booms : « Usage de matériel pédagogique adapté en géométrie : une transposition à interro…
« Usage de matériel pédagogique adapté en géométrie : une transposition à interroger ». Alexandre Booms, doctorant (Université de Reims Champagne-Ardenne - Cérep UR 4692)
-
A. Mondino - Time-like Ricci curvature bounds via optimal transport
MONDINO Andrea
The goal of the talk is to present a recent work in collaboration with Cavalletti (SISSA) on optimal transport in Lorentzian synthetic spaces. The aim is to set up a “Lorentzian analog” of the
-
M. Lesourd - Positive Scalar Curvature on Noncompact Manifolds and the Positive Mass Theorem
LESOURD Martin
The study of positive scalar curvature on noncompact manifolds has seen significant progress in the last few years. A major role has been played by Gromov's results and conjectures, and in
-
R. Perales - Recent Intrinsic Flat Convergence Theorems
PERALES Raquel
Théorèmes récents de convergence plane intrinsèque
-
J. Fine - Knots, minimal surfaces and J-holomorphic curves
FINE Joël
I will describe work in progress, parts of which are joint with Marcelo Alves. Let L be a knot or link in the 3-sphere. I will explain how one can count minimal surfaces in hyperbolic 4-space
-
J. Wang - Topological rigidity and positive scalar curvature
WANG Jian
In this talk, we shall describe some topological rigidity and its relationship with positive scalar curvature. Precisely, we will present a proof that a complete contractible 3-manifold with
-
D. Semola - Boundary regularity and stability under lower Ricci bounds
SEMOLA Daniele
The theory of non smooth spaces with lower Ricci Curvature bounds has undergone huge developments in the last thirty years. On the one hand the impetus came from Gromov’s precompactness theorem
-
D. Stern - Harmonic map methods in spectral geometry
STERN Daniel
Over the last fifty years, the problem of finding sharp upper bounds for area-normalized Laplacian eigenvalues on closed surfaces has attracted the attention of many geometers, due in part to
-
R. Bamler - Compactness and partial regularity theory of Ricci flows in higher dimensions
BAMLER Richard H.
We present a new compactness theory of Ricci flows. This theory states that any sequence of Ricci flows that is pointed in an appropriate sense, subsequentially converges to a synthetic flow.
-
P. Burkhardt - Pointwise lower scalar curvature bounds for C0 metrics via regularizing Ricci flow
BURKHARDT-GUIM Paula
We propose a class of local definitions of weak lower scalar curvature bounds that is well defined for C0 metrics. We show the following: that our definitions are stable under greater-than-second