Notice
4.8. Attack against Algebraic Geometry codes
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
In this session, we will present anattack against Algebraic Geometry codes (AG codes). Algebraic Geometry codesis determined by a triple. First of all, analgebraic curve of genus g, then a n-tuple of rational pointsand then a divisor which has disjoint support from the n-tuple P. Then, the AlgebraicGeometry code is obtained by evaluating at P allfunctions that belong to the vector space associated to the divisor E. Some properties of thesecodes are nearly optimal codes, that is, their designed minimumdistance is nearly the optimal one. Moreover, the dual of anAG-code is again an AG-code. What about using AlgebraicGeometry codes in code-based cryptography? Janwa andMoreno suggest to use Algebraic Geometry codes for theMcEliece cryptosystem. This is a suitable proposalsince these codes are nearly optimal and haveefficient decoding algorithms. If we talk about codes overcurves of genus zero then we are talking aboutgeneralized Reed-Solomon codes, as we will see in the next slides.So, for a curve of genus 0, this proposal is broken. If we talk about codes overcurves of genus 1 and 2, then this proposal isbroken by Faure and Minder. However, this attack hasseveral drawbacks which makes it impossible to extend to ahigher genera. But there is an attack for the general case. We will explain here thisgeneral attack. First over generalized Reed-Solomoncodes and then we will give an idea on how it worksfor the general case. Recall that thegeneralized Reed-Solomon codes are Algebraic Geometry codesover curves of genus 0. Indeed, if we consider theprojective line, this curve has genus 0 and itspoints are of the form (x:y) Now, we will consider P the n-tuple of points formed by thesepoints and we take E to be K-1 times the point at the infinity. A basis of thevector space associated to this divisor is the following one. And if we evaluate thisbasis at the points P, we get a generator matrix of thisAG code, which is also a generator matrix of ageneralized Reed-Solomon code of dimension k associated to thepair (a,1), the all-ones vector.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Dans la même collection
-
4.4. Attack against subcodes of GRS codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will talk about using subcodes of a Generalized Reed–Solomon code for the McEliece Cryptosystem. Recall that to avoid the attack of Sidelnikov and Shestakov, Berger and
-
4.7. Attack against Reed-Muller codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will introduce an attack against binary Reed-Muller codes. Reed-Muller codes were introduced by Muller in 1954 and, later, Reed provided the first efficient decoding algorithm
-
4.5. Error-Correcting Pairs
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuWe present in this session a general decoding method for linear codes. And we will see it in an example. Let C be a generalized Reed-Solomon code of dimension k associated to the pair (c, d). Then,
-
4.9. Goppa codes still resist
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuAll the results that we have seen this week doesn't mean that code based cryptography is broken. So in this session we will see that Goppa code still resists to all these attacks. So recall that
-
4.6. Attack against GRS codes
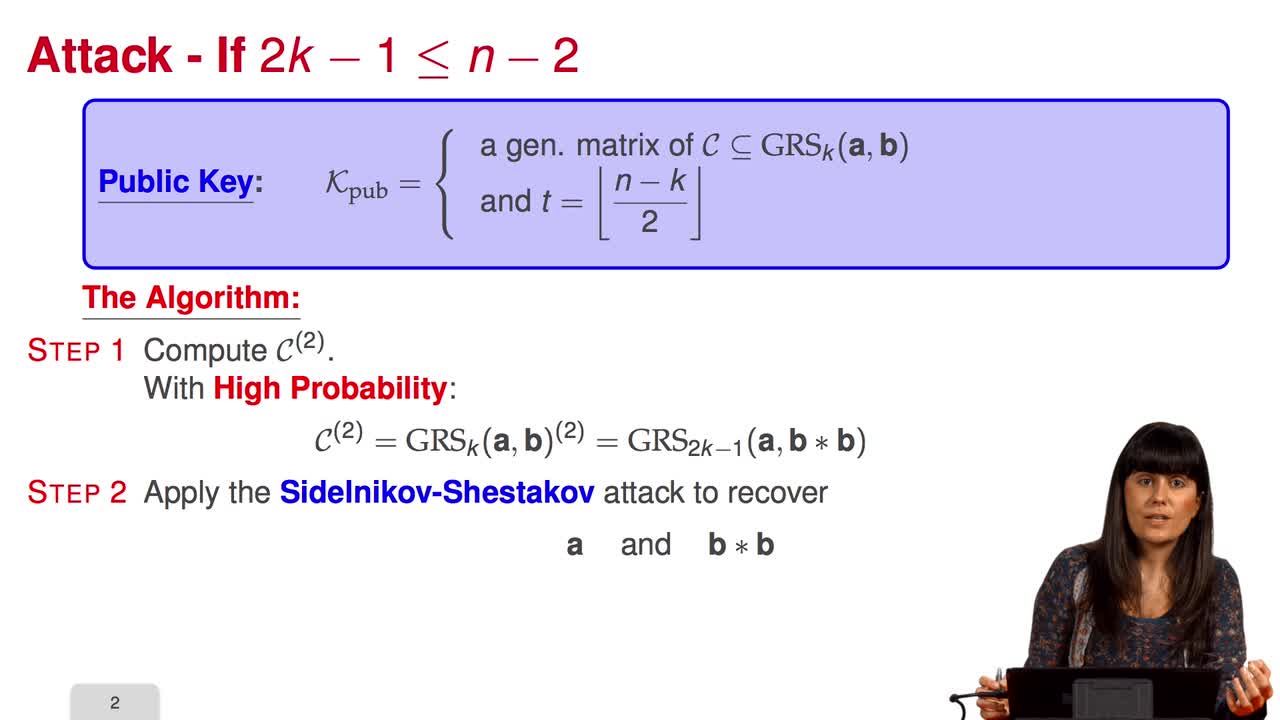
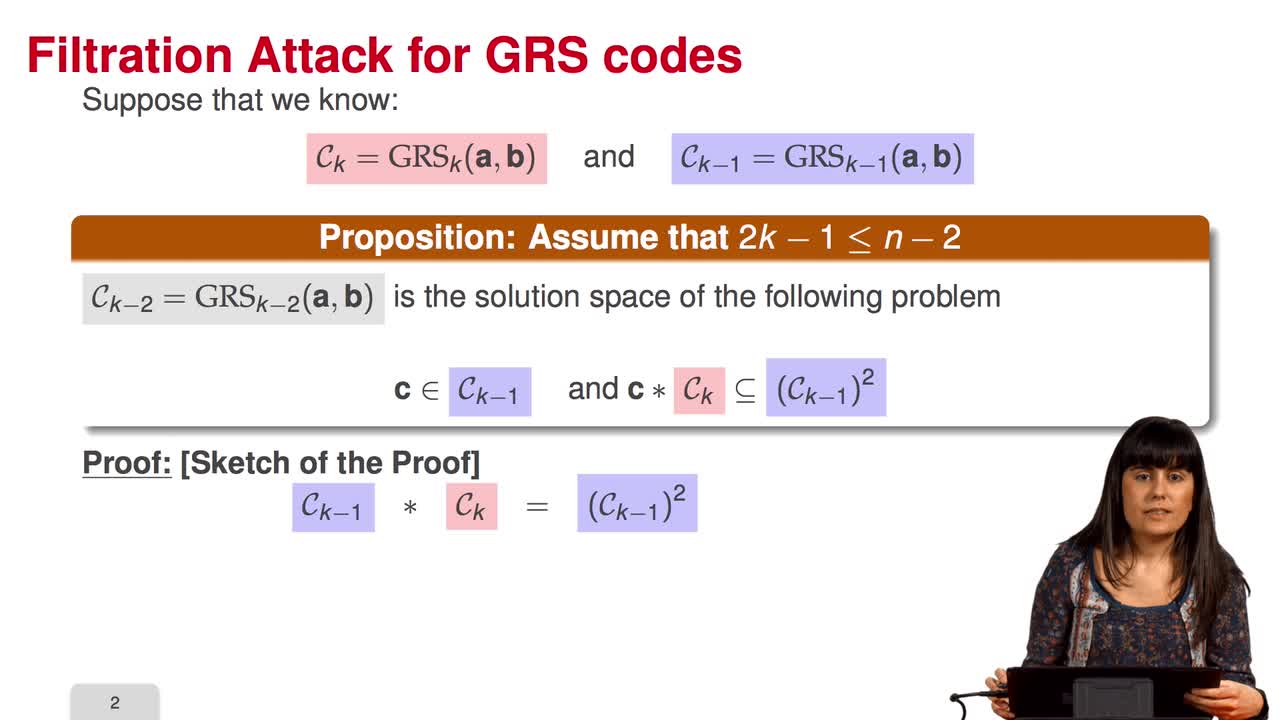
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session we will discuss the proposal of using generalized Reed-Solomon codes for the McEliece cryptosystem. As we have already said, generalized Reed-Solomon codes were proposed in 1986 by
-
4.2. Support Splitting Algorithm
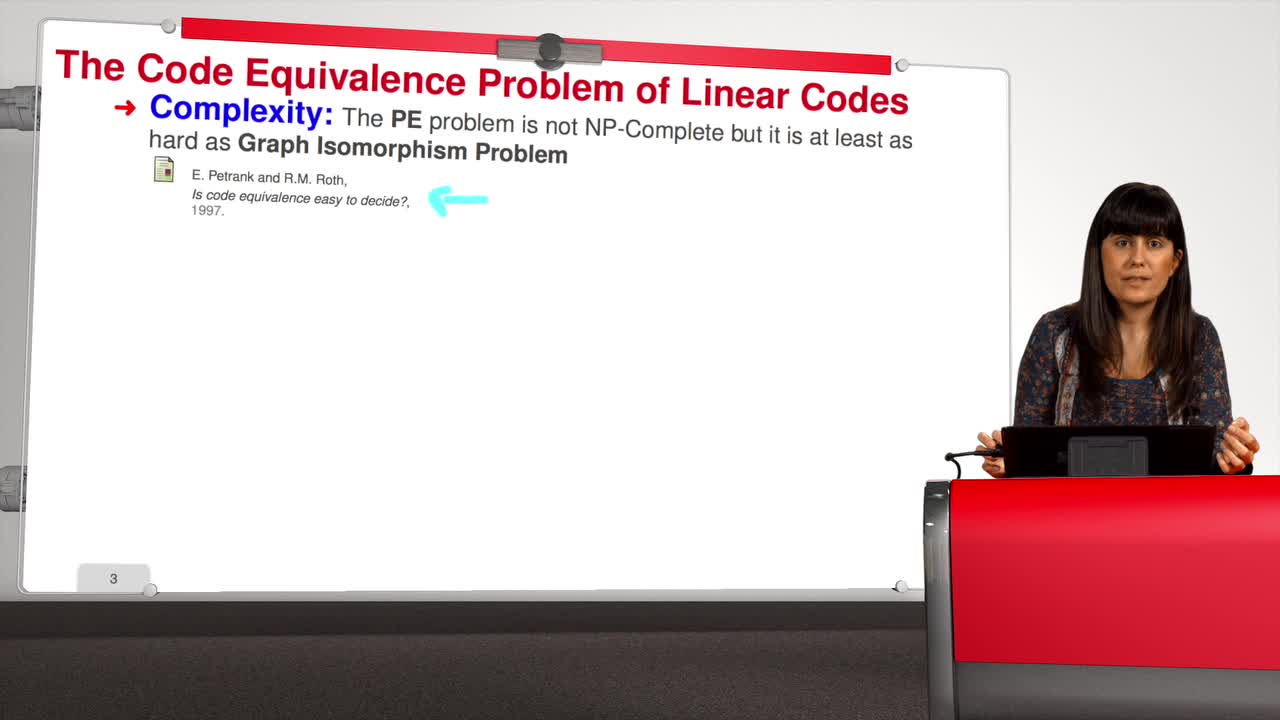
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuThis session will be about the support splitting algorithm. For the q-ary case, there are three different notions of equivalence. The general one: two codes of length n are semi-linear equivalent
-
4.3. Distinguisher for GRS codes
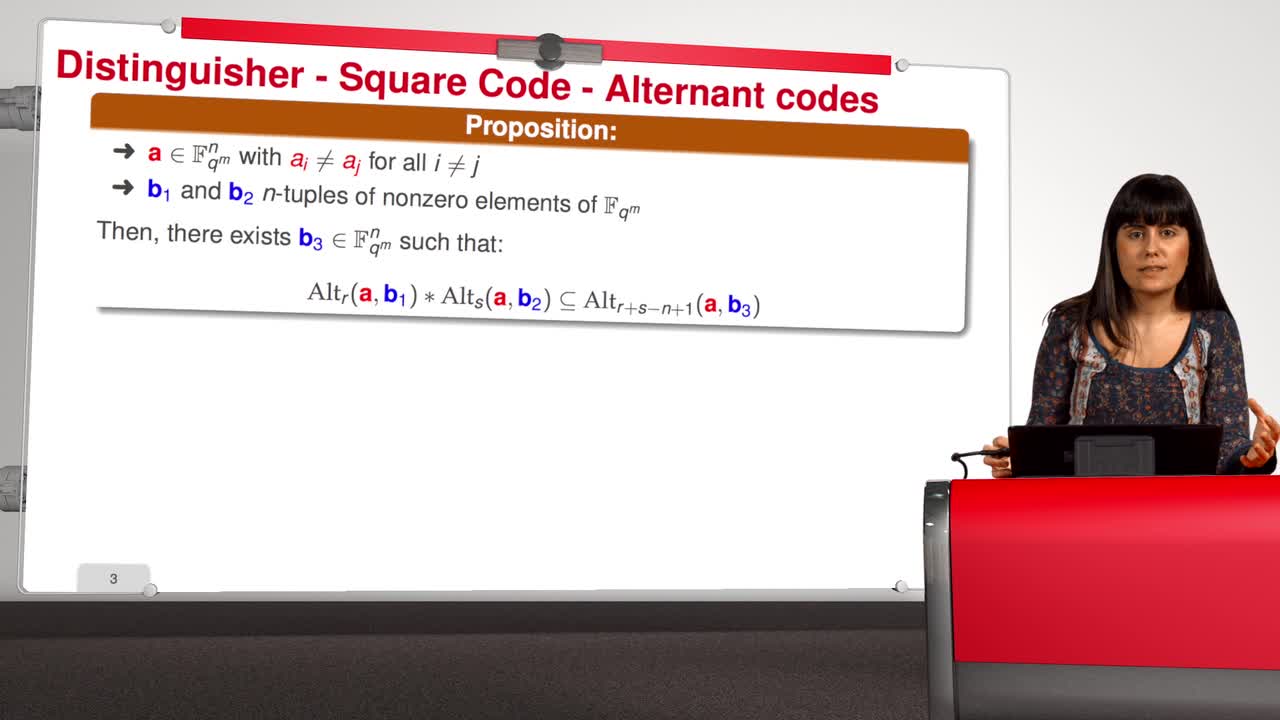
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session we will see that generalized Reed-Solomon codes behave differently than random codes with respect to the star operation. Thus we can define a distinguisher for Generalized Reed
-
4.1. Introduction
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuWelcome to the fourth week of the MOOC Code-based Cryptography. Recall that we have mainly two ways of cryptanalyzing in the McEliece cryptosystem. We have Message Attacks, which address the problem
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
4.9. Goppa codes still resist
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuAll the results that we have seen this week doesn't mean that code based cryptography is broken. So in this session we will see that Goppa code still resists to all these attacks. So recall that
-
5.3. Attacks against the CFS Scheme
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will have a look at the attacks against the CFS signature scheme. As for public-key encryption, there are two kinds of attacks against signature schemes. First kind of attack is
-
4.6. Attack against GRS codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session we will discuss the proposal of using generalized Reed-Solomon codes for the McEliece cryptosystem. As we have already said, generalized Reed-Solomon codes were proposed in 1986 by
-
5.6. An Efficient Provably Secure One-Way Function
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we are going to see how to build an efficient provably secure one-way function from coding theory. As you know, a one-way function is a function which is simple to evaluate and
-
5.1. Code-Based Digital Signatures
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuWelcome to the last week of this MOOC on code-based cryptography. This week, we will be discussing other cryptographic constructions relying on coding theory. We have seen how to do public key
-
4.4. Attack against subcodes of GRS codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will talk about using subcodes of a Generalized Reed–Solomon code for the McEliece Cryptosystem. Recall that to avoid the attack of Sidelnikov and Shestakov, Berger and
-
5.4. Parallel-CFS
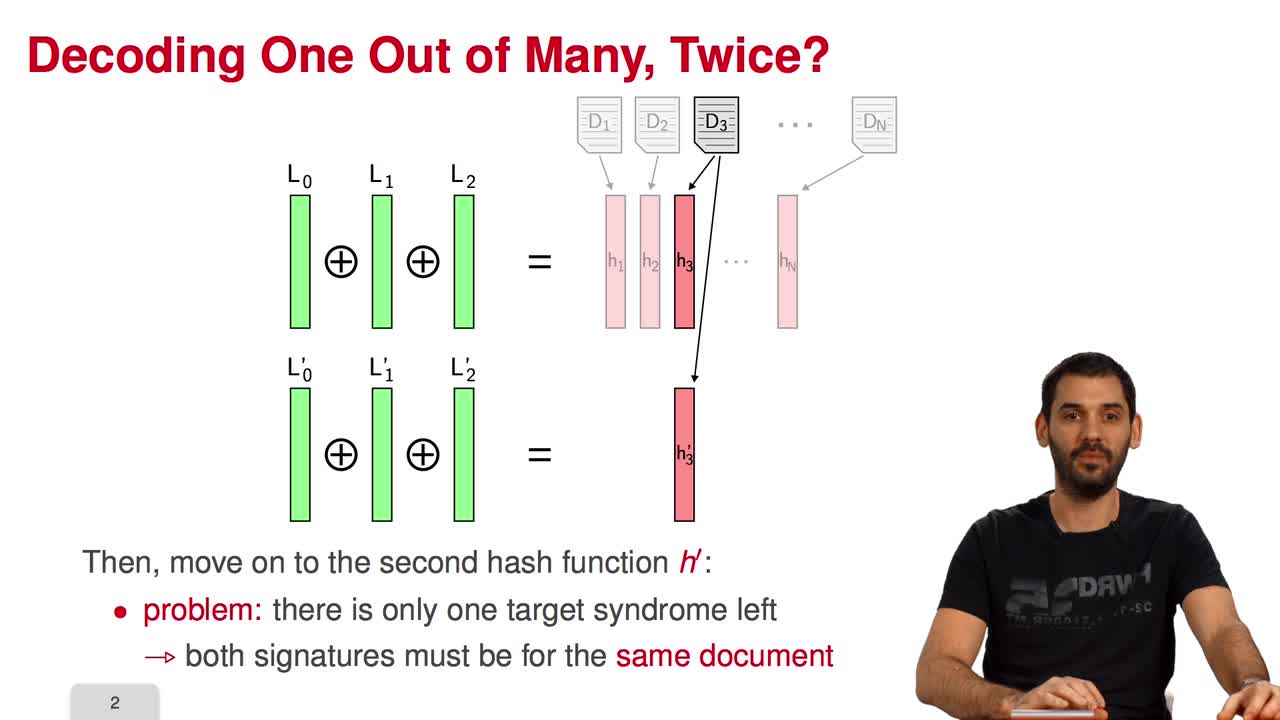
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, I will present a variant of the CFS signature scheme called parallel-CFS. We start from a simple question: what happens if you try to use two different hash functions and compute
-
4.7. Attack against Reed-Muller codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will introduce an attack against binary Reed-Muller codes. Reed-Muller codes were introduced by Muller in 1954 and, later, Reed provided the first efficient decoding algorithm
-
5.7. The Fast Syndrome-Based (FSB) Hash Function
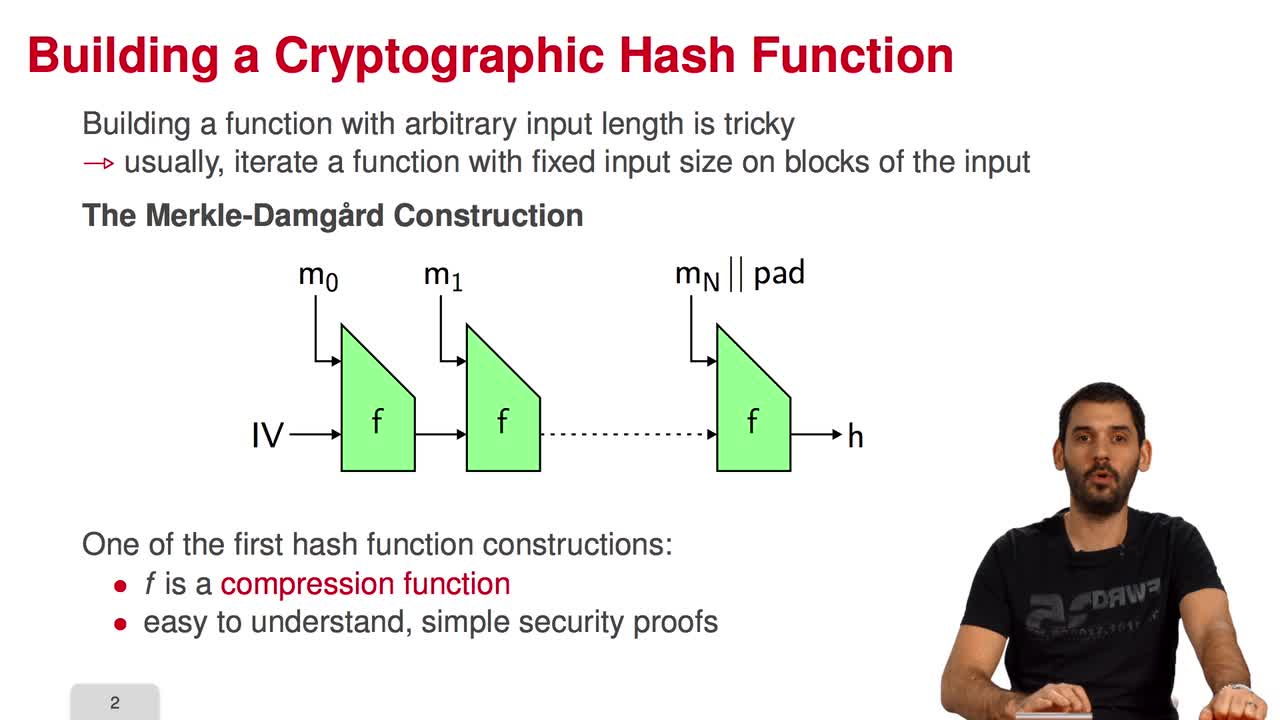
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn the last session of this week, we will have a look at the FSB Hash Function which is built using the one-way function we saw in the previous session. What are the requirements for a
-
5.2. The Courtois-Finiasz-Sendrier (CFS) Construction
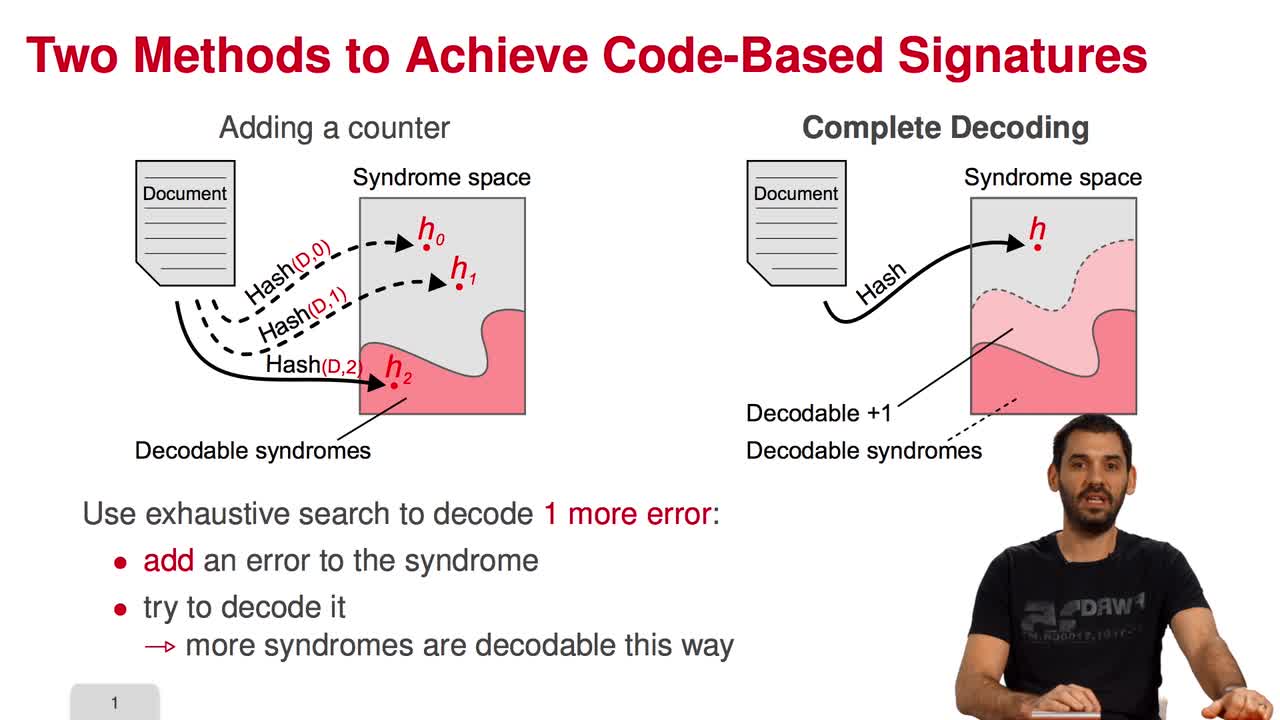
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, I am going to present the Courtois-Finiasz-Sendrier Construction of a code-based digital signature. In the previous session, we have seen that it is impossible to hash a document
-
4.5. Error-Correcting Pairs
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuWe present in this session a general decoding method for linear codes. And we will see it in an example. Let C be a generalized Reed-Solomon code of dimension k associated to the pair (c, d). Then,
-
5.5. Stern’s Zero-Knowledge Identification Scheme
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we are going to have a look at Stern’s Zero-Knowledge Identification Scheme. So, what is a Zero-Knowledge Identification Scheme? An identification scheme allows a prover to prove
Sur le même thème
-
La voix, une donnée identifiante à protéger
VincentEmmanuelEmmanuel Vincent, chercheur au Centre Inria de l'Université de Lorraine et au Loria (Laboratoire lorrain de recherche en informatique et ses applications), présente sa recherche sur l'anonymisation de
-
Podcast 1/4 d'heure avec : Emmanuel Vincent, chercheur au Centre Inria de l'Université de Lorraine …
VincentEmmanuelRencontre avec Emmanuel Vincent - chercheur au Centre Inria de l'Université de Lorraine et Loria (Laboratoire lorrain de recherche en informatique et ses applications).
-
Tuan Ta Pesao : écritures de sable et de ficelle à l'Ile d'Ambrym
VandendriesscheEricCe film se déroule au Nord de l’île d’Ambrym, dans l’archipel de Vanuatu, en Mélanésie...
-
Machines algorithmiques, mythes et réalités
MazenodVincentVincent Mazenod, informaticien, partage le fruit de ses réflexions sur l'évolution des outils numériques, en lien avec les problématiques de souveraineté, de sécurité et de vie privée...
-
Désassemblons le numérique - #Episode11 : Les algorithmes façonnent-ils notre société ?
SchwartzArnaudLima PillaLaércioEstériePierreSalletFrédéricFerbosAudeRoumanosRayyaChraibi KadoudIkramUn an après le tout premier hackathon sur les méthodologies d'enquêtes journalistiques sur les algorithmes, ce nouvel épisode part à la rencontre de différents points de vue sur les algorithmes.
-
Les machines à enseigner. Du livre à l'IA...
BruillardÉricQue peut-on, que doit-on déléguer à des machines ? C'est l'une des questions explorées par Éric Bruillard qui, du livre aux IA génératives, expose l'évolution des machines à enseigner...
-
Quel est le prix à payer pour la sécurité de nos données ?
MinaudBriceÀ l'ère du tout connecté, la question de la sécurité de nos données personnelles est devenue primordiale. Comment faire pour garder le contrôle de nos données ? Comment déjouer les pièges de plus en
-
Désassemblons le numérique - #Episode9 : Bientôt des supercalculateurs dans nos piscines ?
BeaumontOlivierBouzelRémiDes supercalculateurs feraient-ils bientôt leur apparition dans les piscines municipales pour les chauffer ? Réponses d'Olivier Beaumont, responsable de l'équipe-projet Topal, et Rémi Bouzel,
-
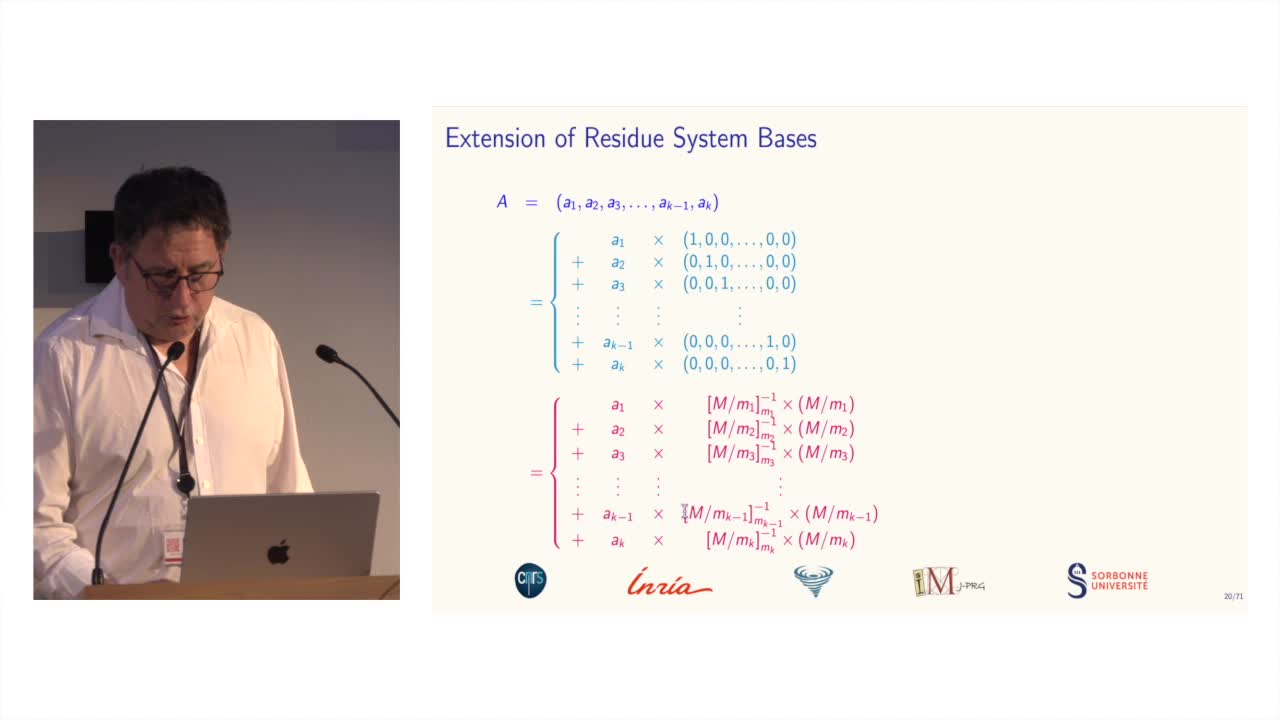
Des systèmes de numération pour le calcul modulaire
BajardJean-ClaudeLe calcul modulaire est utilisé dans de nombreuses applications des mathématiques...
-
Projection methods for community detection in complex networks
LitvakNellyCommunity detection is one of most prominent tasks in the analysis of complex networks such as social networks, biological networks, and the world wide web. A community is loosely defined as a group
-
Lara Croft. doing fieldwork under surveillance
Dall'AgnolaJasminLara Croft. Doing Fieldwork Under Surveillance Intervention de Jasmin Dall'Agnola (The George Washington University), dans le cadre du Colloque coorganisé par Anders Albrechtslund, professeur en
-
Containing predictive tokens in the EU
CzarnockiJanContaining Predictive Tokens in the EU – Mapping the Laws Against Digital Surveillance, intervention de Jan Czarnocki (KU Leuven), dans le cadre du Colloque coorganisé par Anders Albrechtslund,