Notice
5.7. The Fast Syndrome-Based (FSB) Hash Function
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
In the last session of thisweek, we will have a look at the FSB Hash Function whichis built using the one-way function we saw inthe previous session. What are the requirements fora cryptographic hash function? So, it is a function whichtakes an input of arbitrary size and outputs a fixed size. From a security point ofview, it should be hard to solve any of the three followingproblems: first, find an input with a given hash which iswhat we call preimage attacks; find an input with the samehash as a given input which is what we call secondpreimage attack; or find two inputs with the same hash whichis what we call collision attack. In addition, hash function havesome implementation constraints. It should be fast inboth software and hardware implementations, it shouldbe fast for both small inputs and large inputs and itshould have a compact description. Building a function ofarbitrary length is something which is not that obvious.Usually, you simply iterate a function with a fixed inputsize on blocks of the input. There are severalconstructions to achieve this, the oldest one is theMerkle-Damgård Construction. This function iterates acompression function f which takes at each round apart of the message m0, m1 or something like this andstarts with an IV or the chaining value which is the output ofthe previous compression function. It is easy to understand andit has a simple security proof. So, it is something that is usedpretty commonly in cryptography. Another constructionwhich is commonly used in cryptography is theDavies-Meyer Construction. For the compression function, thisconstruction uses a block cipher E. The message is used as thekey of the block cipher and the input is the chaining value. An interesting element ofthis construction is that it reuses the samehardware as the block cipher. So, if you have animplementation which already includes a block cipher, you don'tneed any more implementations. A much more recentconstruction is the Sponge construction. This construction uses a functionwith the same input and output size. The message is XORed to a partof an internal state fed to the function which issome kind of permutation, then, another part of themessage is exhorted and so on. This is the absorb phase. Once you have finishedabsorbing all the message in the padding, you have a squeezeout phase where you take out - bits of the message from the internalstate, iterating the function f again. The interesting aspect of thisconstruction is its versatility. It can be used as both thehash function where the input is larger than the outputor a pseudo-random generator where the input is smalland the output is large.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Dans la même collection
-
5.1. Code-Based Digital Signatures
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuWelcome to the last week of this MOOC on code-based cryptography. This week, we will be discussing other cryptographic constructions relying on coding theory. We have seen how to do public key
-
5.4. Parallel-CFS
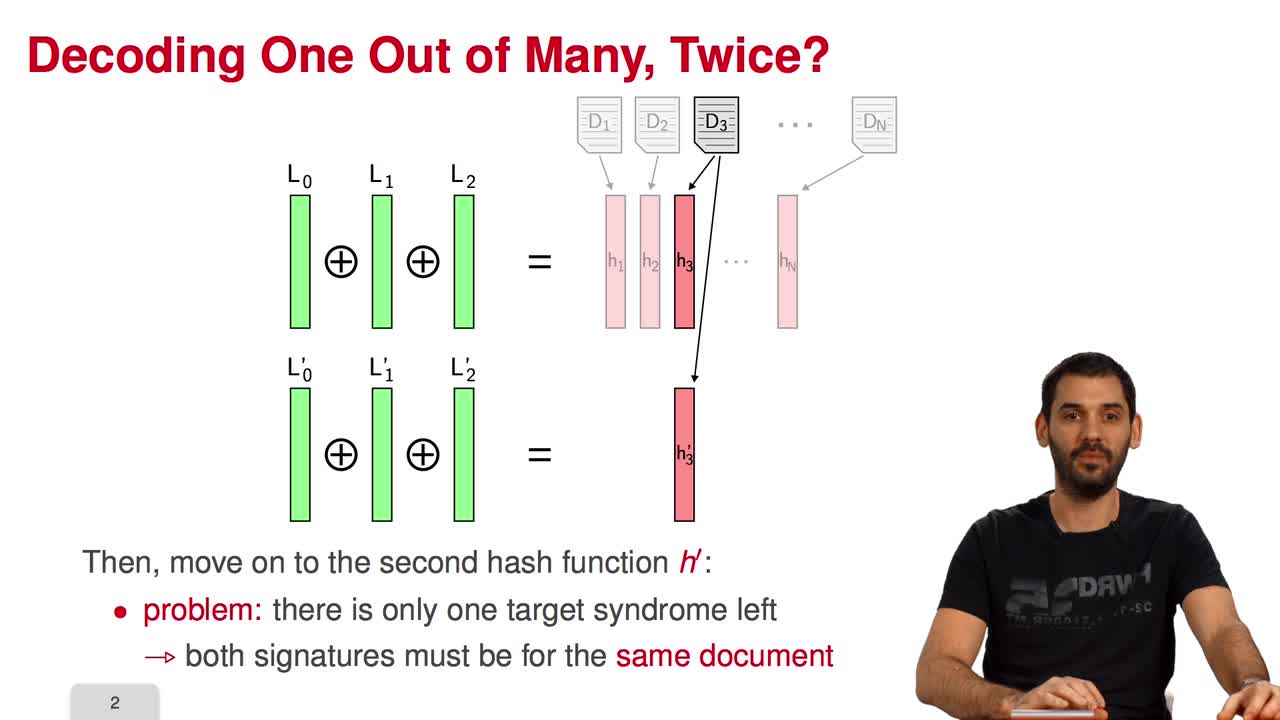
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, I will present a variant of the CFS signature scheme called parallel-CFS. We start from a simple question: what happens if you try to use two different hash functions and compute
-
5.2. The Courtois-Finiasz-Sendrier (CFS) Construction
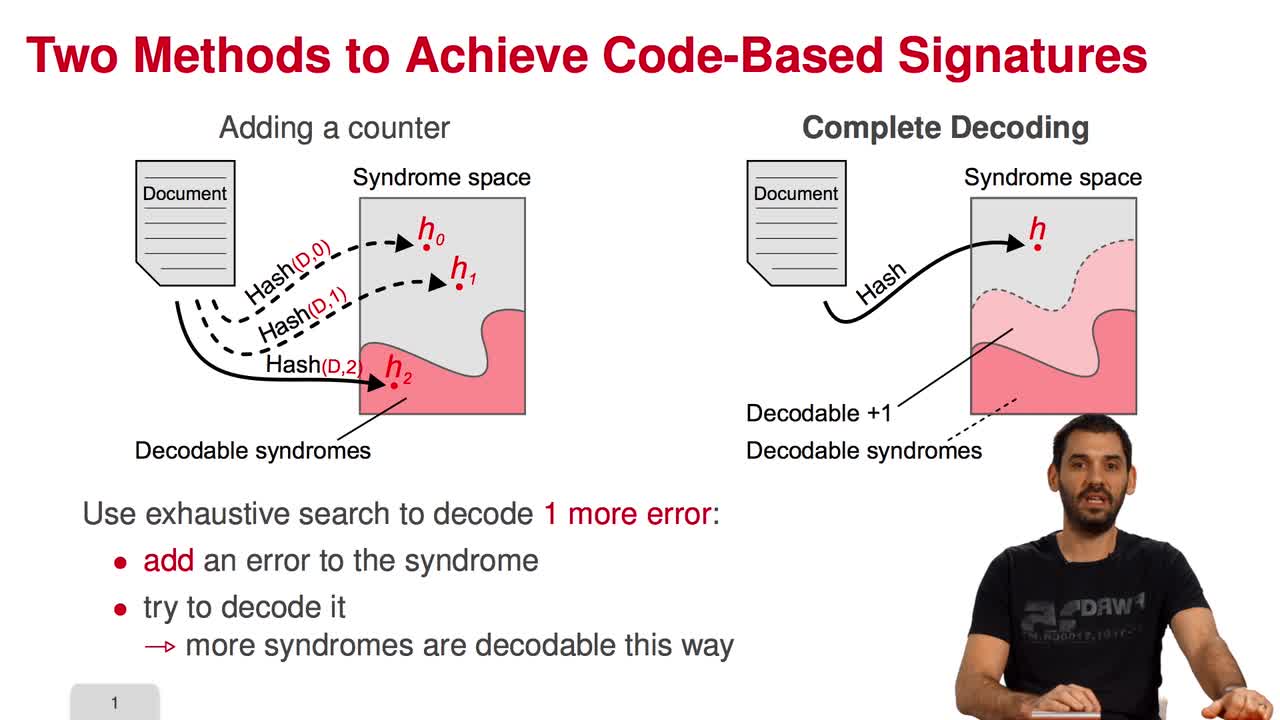
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, I am going to present the Courtois-Finiasz-Sendrier Construction of a code-based digital signature. In the previous session, we have seen that it is impossible to hash a document
-
5.5. Stern’s Zero-Knowledge Identification Scheme
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we are going to have a look at Stern’s Zero-Knowledge Identification Scheme. So, what is a Zero-Knowledge Identification Scheme? An identification scheme allows a prover to prove
-
5.3. Attacks against the CFS Scheme
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will have a look at the attacks against the CFS signature scheme. As for public-key encryption, there are two kinds of attacks against signature schemes. First kind of attack is
-
5.6. An Efficient Provably Secure One-Way Function
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we are going to see how to build an efficient provably secure one-way function from coding theory. As you know, a one-way function is a function which is simple to evaluate and
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
4.5. Error-Correcting Pairs
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuWe present in this session a general decoding method for linear codes. And we will see it in an example. Let C be a generalized Reed-Solomon code of dimension k associated to the pair (c, d). Then,
-
5.4. Parallel-CFS
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, I will present a variant of the CFS signature scheme called parallel-CFS. We start from a simple question: what happens if you try to use two different hash functions and compute
-
4.8. Attack against Algebraic Geometry codes
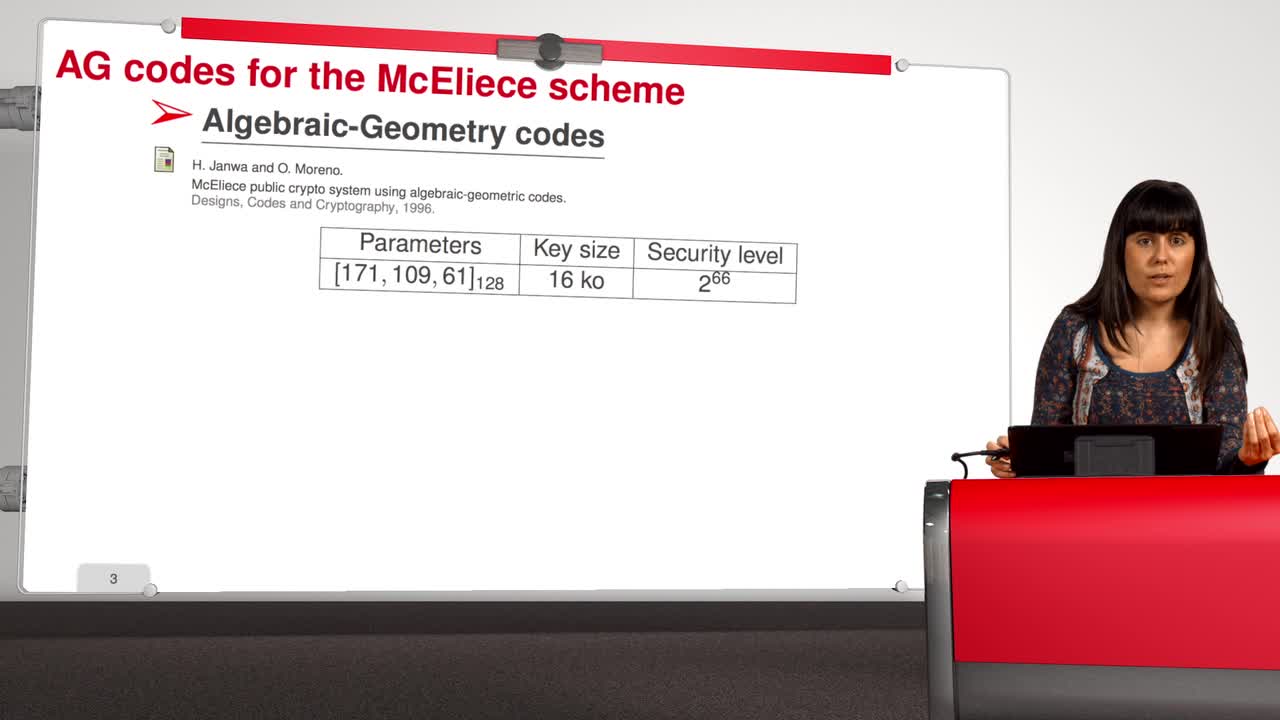
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will present an attack against Algebraic Geometry codes (AG codes). Algebraic Geometry codes is determined by a triple. First of all, an algebraic curve of genus g, then a n
-
5.2. The Courtois-Finiasz-Sendrier (CFS) Construction
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, I am going to present the Courtois-Finiasz-Sendrier Construction of a code-based digital signature. In the previous session, we have seen that it is impossible to hash a document
-
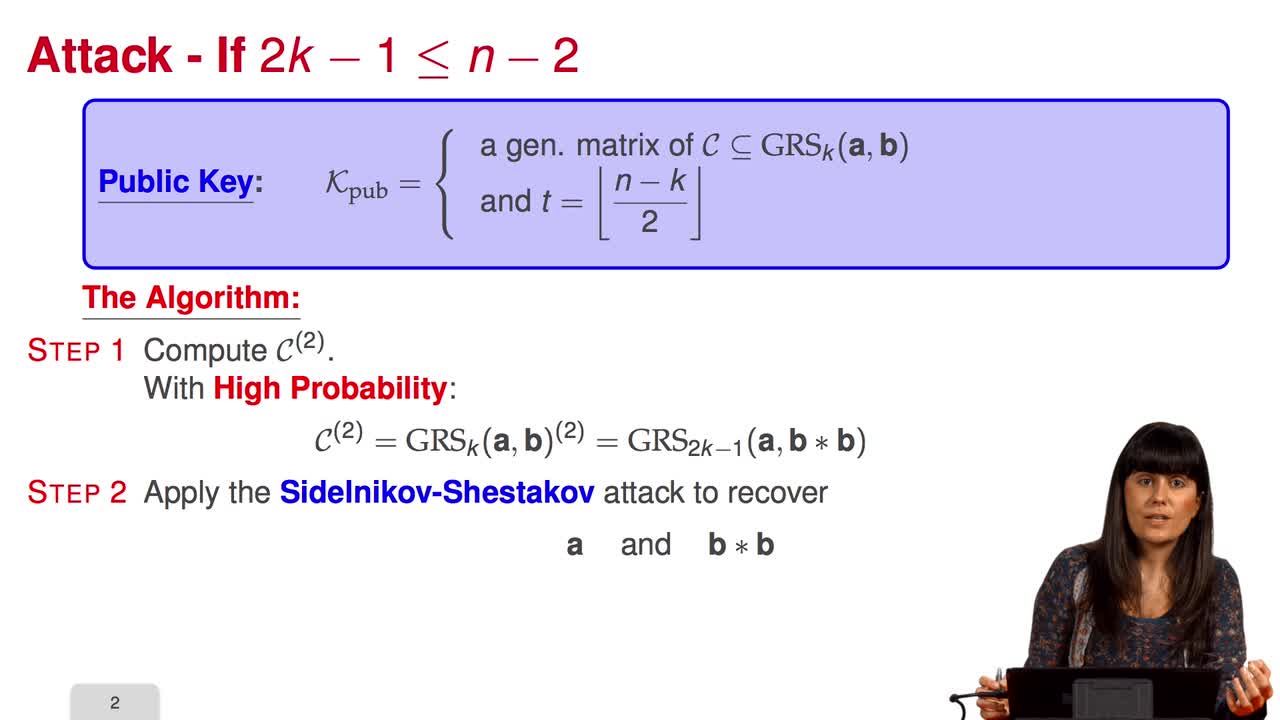
4.6. Attack against GRS codes
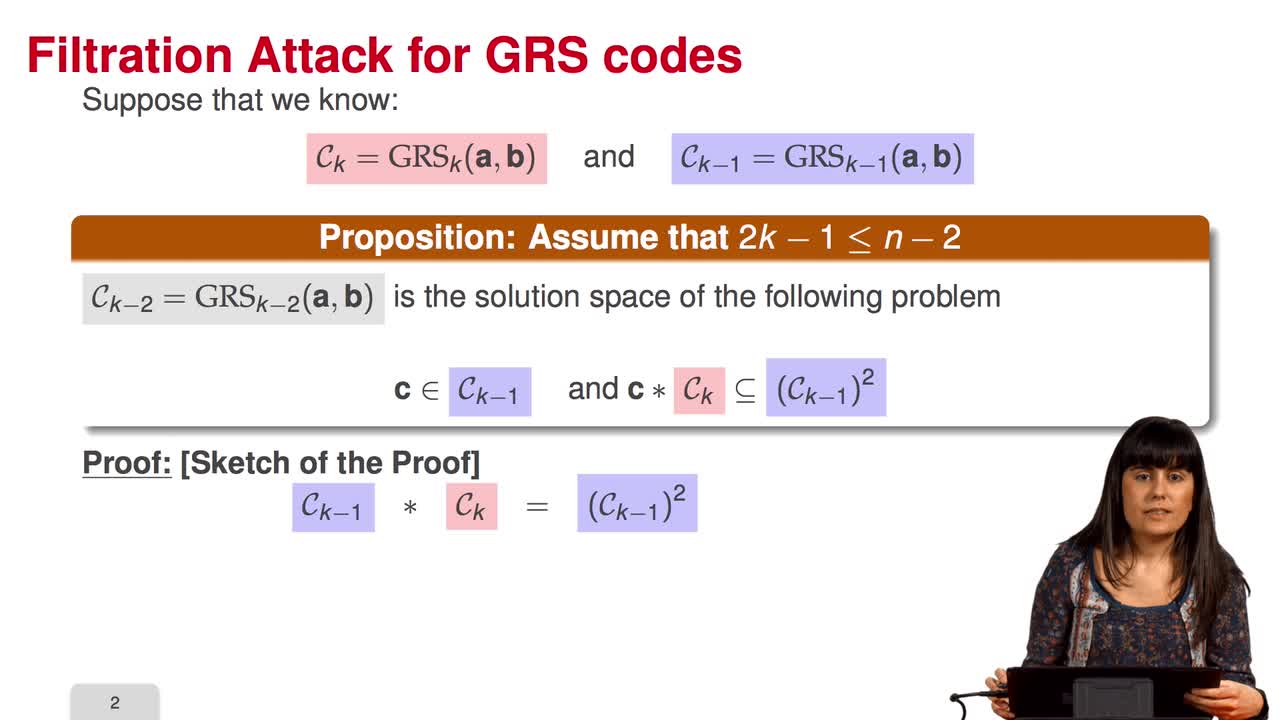
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session we will discuss the proposal of using generalized Reed-Solomon codes for the McEliece cryptosystem. As we have already said, generalized Reed-Solomon codes were proposed in 1986 by
-
5.5. Stern’s Zero-Knowledge Identification Scheme
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we are going to have a look at Stern’s Zero-Knowledge Identification Scheme. So, what is a Zero-Knowledge Identification Scheme? An identification scheme allows a prover to prove
-
4.9. Goppa codes still resist
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuAll the results that we have seen this week doesn't mean that code based cryptography is broken. So in this session we will see that Goppa code still resists to all these attacks. So recall that
-
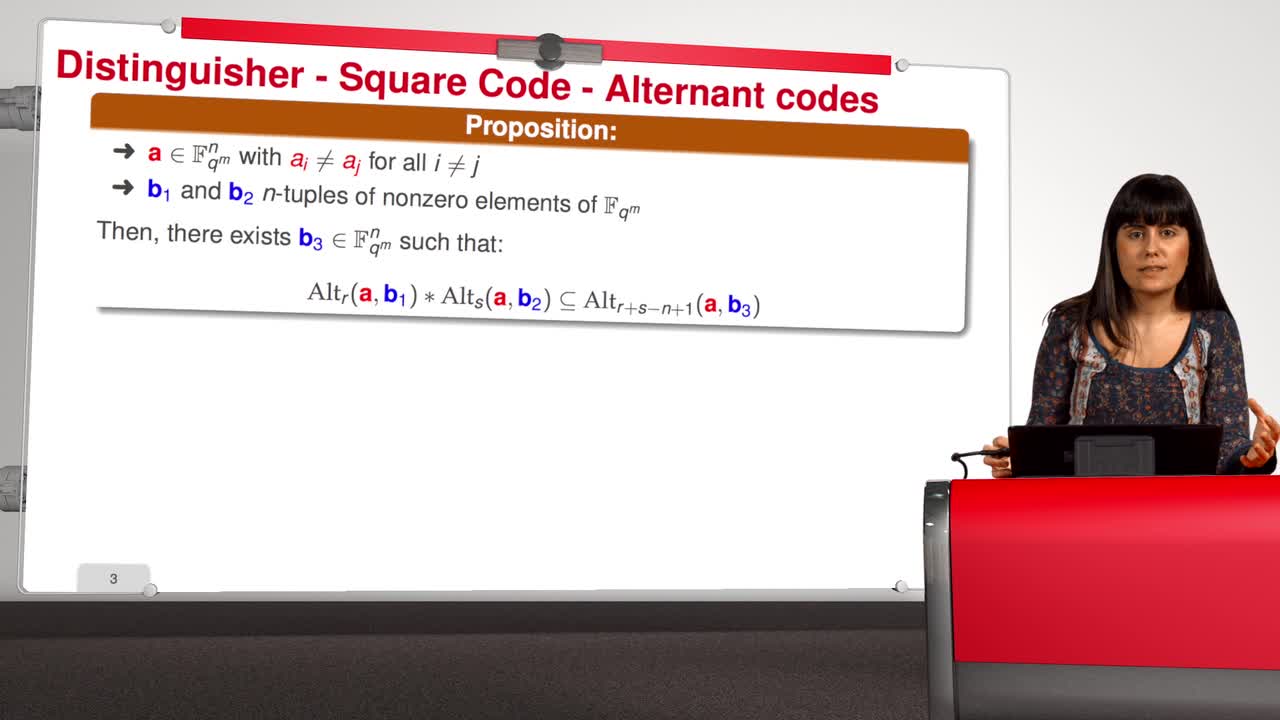
4.4. Attack against subcodes of GRS codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will talk about using subcodes of a Generalized Reed–Solomon code for the McEliece Cryptosystem. Recall that to avoid the attack of Sidelnikov and Shestakov, Berger and
-
5.3. Attacks against the CFS Scheme
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will have a look at the attacks against the CFS signature scheme. As for public-key encryption, there are two kinds of attacks against signature schemes. First kind of attack is
-
4.7. Attack against Reed-Muller codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will introduce an attack against binary Reed-Muller codes. Reed-Muller codes were introduced by Muller in 1954 and, later, Reed provided the first efficient decoding algorithm
-
5.6. An Efficient Provably Secure One-Way Function
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we are going to see how to build an efficient provably secure one-way function from coding theory. As you know, a one-way function is a function which is simple to evaluate and
-
5.1. Code-Based Digital Signatures
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuWelcome to the last week of this MOOC on code-based cryptography. This week, we will be discussing other cryptographic constructions relying on coding theory. We have seen how to do public key
Sur le même thème
-
La voix, une donnée identifiante à protéger
VincentEmmanuelEmmanuel Vincent, chercheur au Centre Inria de l'Université de Lorraine et au Loria (Laboratoire lorrain de recherche en informatique et ses applications), présente sa recherche sur l'anonymisation de
-
Podcast 1/4 d'heure avec : Emmanuel Vincent, chercheur au Centre Inria de l'Université de Lorraine …
VincentEmmanuelRencontre avec Emmanuel Vincent - chercheur au Centre Inria de l'Université de Lorraine et Loria (Laboratoire lorrain de recherche en informatique et ses applications).
-
Tuan Ta Pesao : écritures de sable et de ficelle à l'Ile d'Ambrym
VandendriesscheEricCe film se déroule au Nord de l’île d’Ambrym, dans l’archipel de Vanuatu, en Mélanésie...
-
Machines algorithmiques, mythes et réalités
MazenodVincentVincent Mazenod, informaticien, partage le fruit de ses réflexions sur l'évolution des outils numériques, en lien avec les problématiques de souveraineté, de sécurité et de vie privée...
-
Désassemblons le numérique - #Episode11 : Les algorithmes façonnent-ils notre société ?
SchwartzArnaudLima PillaLaércioEstériePierreSalletFrédéricFerbosAudeRoumanosRayyaChraibi KadoudIkramUn an après le tout premier hackathon sur les méthodologies d'enquêtes journalistiques sur les algorithmes, ce nouvel épisode part à la rencontre de différents points de vue sur les algorithmes.
-
Les machines à enseigner. Du livre à l'IA...
BruillardÉricQue peut-on, que doit-on déléguer à des machines ? C'est l'une des questions explorées par Éric Bruillard qui, du livre aux IA génératives, expose l'évolution des machines à enseigner...
-
Quel est le prix à payer pour la sécurité de nos données ?
MinaudBriceÀ l'ère du tout connecté, la question de la sécurité de nos données personnelles est devenue primordiale. Comment faire pour garder le contrôle de nos données ? Comment déjouer les pièges de plus en
-
Désassemblons le numérique - #Episode9 : Bientôt des supercalculateurs dans nos piscines ?
BeaumontOlivierBouzelRémiDes supercalculateurs feraient-ils bientôt leur apparition dans les piscines municipales pour les chauffer ? Réponses d'Olivier Beaumont, responsable de l'équipe-projet Topal, et Rémi Bouzel,
-
Des systèmes de numération pour le calcul modulaire
BajardJean-ClaudeLe calcul modulaire est utilisé dans de nombreuses applications des mathématiques...
-
Projection methods for community detection in complex networks
LitvakNellyCommunity detection is one of most prominent tasks in the analysis of complex networks such as social networks, biological networks, and the world wide web. A community is loosely defined as a group
-
Lara Croft. doing fieldwork under surveillance
Dall'AgnolaJasminLara Croft. Doing Fieldwork Under Surveillance Intervention de Jasmin Dall'Agnola (The George Washington University), dans le cadre du Colloque coorganisé par Anders Albrechtslund, professeur en
-
Containing predictive tokens in the EU
CzarnockiJanContaining Predictive Tokens in the EU – Mapping the Laws Against Digital Surveillance, intervention de Jan Czarnocki (KU Leuven), dans le cadre du Colloque coorganisé par Anders Albrechtslund,