Notice
2.2. Security-Reduction Proof
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
Welcome to the second session. We will talk about thesecurity-reduction proof. The security of a given cryptographic algorithm is reduced to the securityof a known hard problem. To prove that acryptosystem is secure, we select a problem which we know ishard to solve, and we reduce the problem to thesecurity of the cryptosystem. Since the problem is hard to solve,the cryptosystem is hard to break. A security reduction is aproof that an adversary able to attack the scheme is ableto solve some presumably hard computational problem,with a similar effort. For the given parameters n,k, let G be the public-keyspace, K be the apparentpublic-key space. In theoriginal McEliece scheme Gis the set of all generator matrices of a family of binary Goppacodes of length n and dimension k. K is the set of binarymatrices of a size (k x n). A distinguisher is a mappingthat takes as input a binary matrix of size (k x n), andreturns true if the matrixis distinguishable. We define the followingsample space, the set of all matrices of size(k x n) uniformly distributed,and we define the event: theset of binary matrices such that the distinguisherreturns true, that is the matrices which are distinguishable.
The advantage of adistinguisher for the subset D, measures how such adistinguisher could be used as a characterization for G;formally, the probability that the event will occur,minus the probability that the event happensrestricted to the subset G.In other words, it is theprobability that the distinguisher detects a matrix from G, from arandomly picked up binary matrix. We will denote the running time ofa distinguisher by this formula.An algorithm is a (T, ε)-distinguisher for G against K, ifit runs in time at most T, and theadvantage for G is greater than ε. So, for givenparameters n, k and t, we definethis, the message space,this, the apparent public key space, and W the error vector space.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Dans la même collection
-
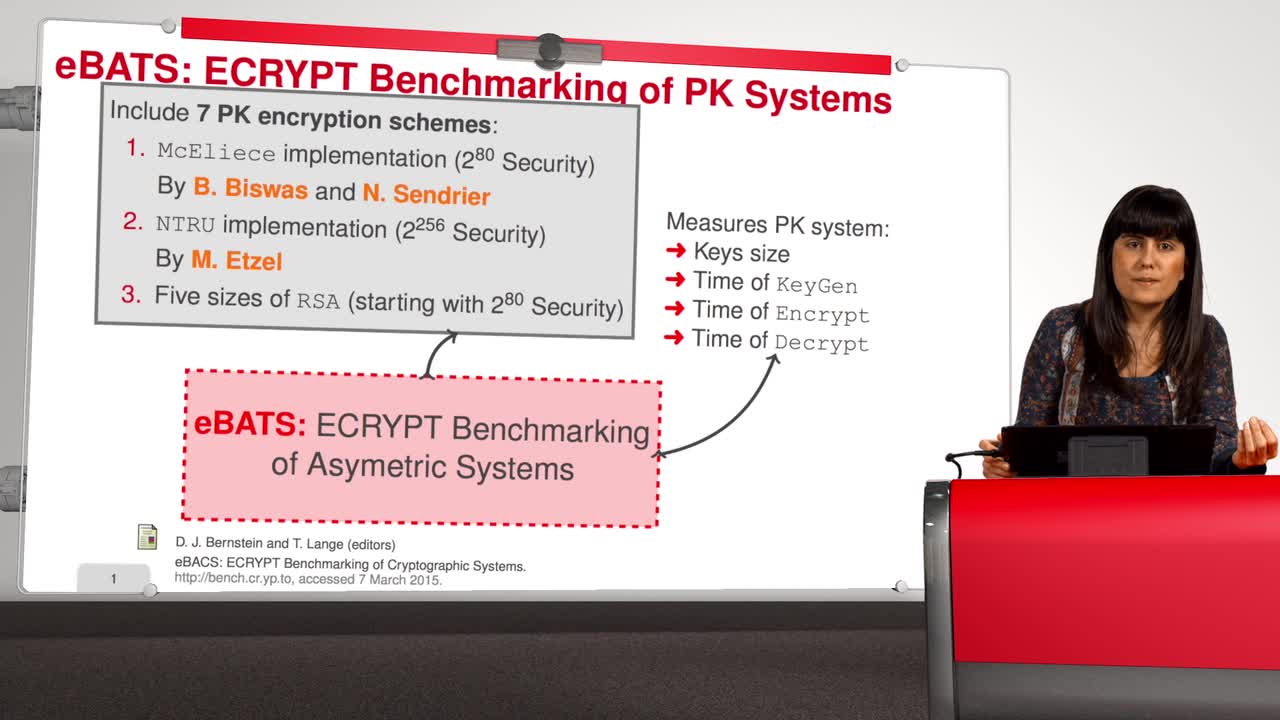
2.7. Reducing the Key Size - LDPC codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuLDPC codes have an interesting feature: they are free of algebraic structure. We will study in detail this proposal for the McEliece cryptosystem in this session. LDPC codes were originally
-
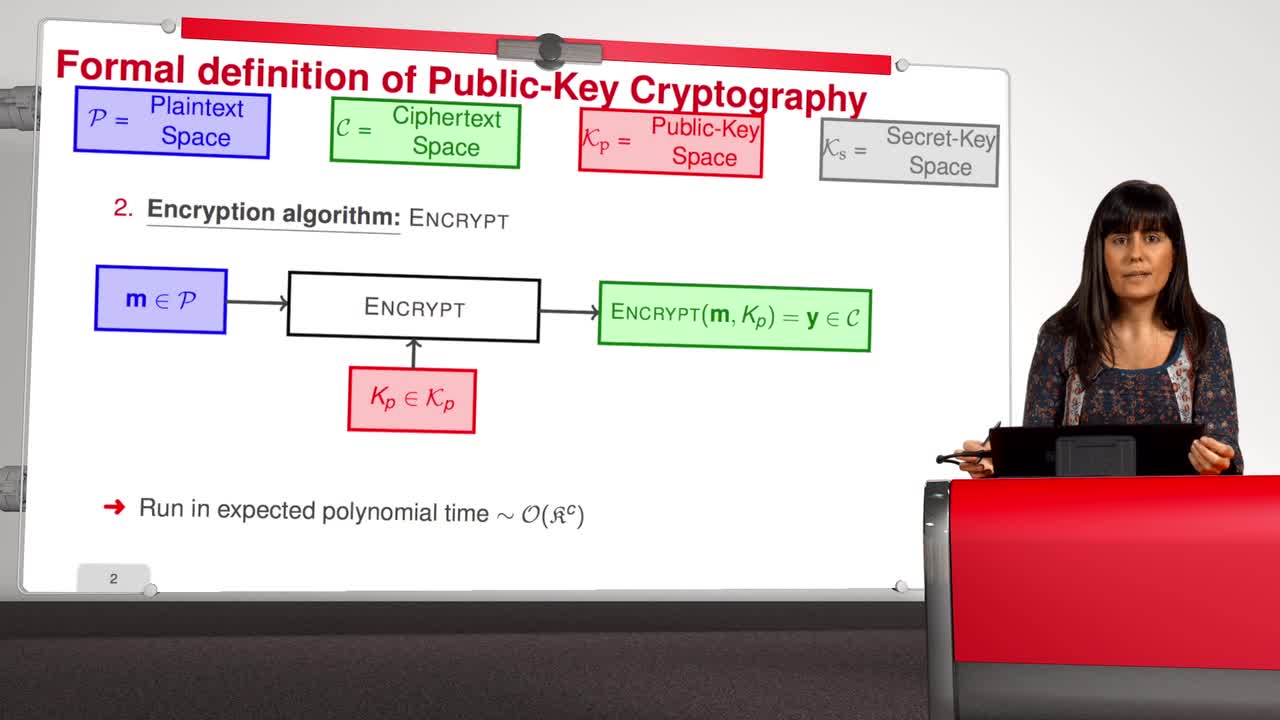
2.1. Formal Definition
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuWelcome to the second week of this MOOC entitled Code-Based Cryptography. This week, we will talk in detail about the McEliece cryptosystem. First, in this session, we will describe formally the
-
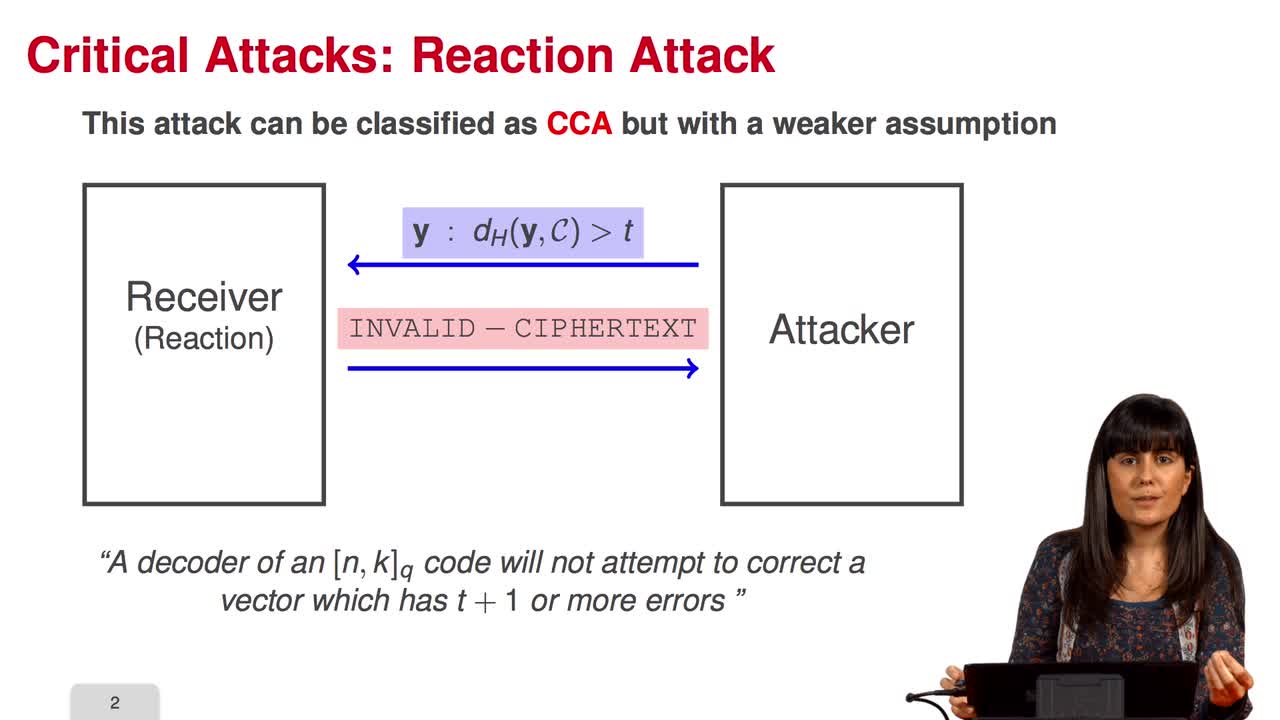
2.5. Critical Attacks - Semantic Secure Conversions
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will study critical attacks against the public-key cryptosystem. The partial knowledge on the plaintext reduces drastically the computational cost of the attack to the McEliece
-
2.8. Reducing the Key Size - MDPC codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuThis is the last session where we will talk about reducing the key size. Here we will introduce the MDPC codes. In 2012, the MDPC codes were proposed for the McEliece schemes. An MDPC code is a
-
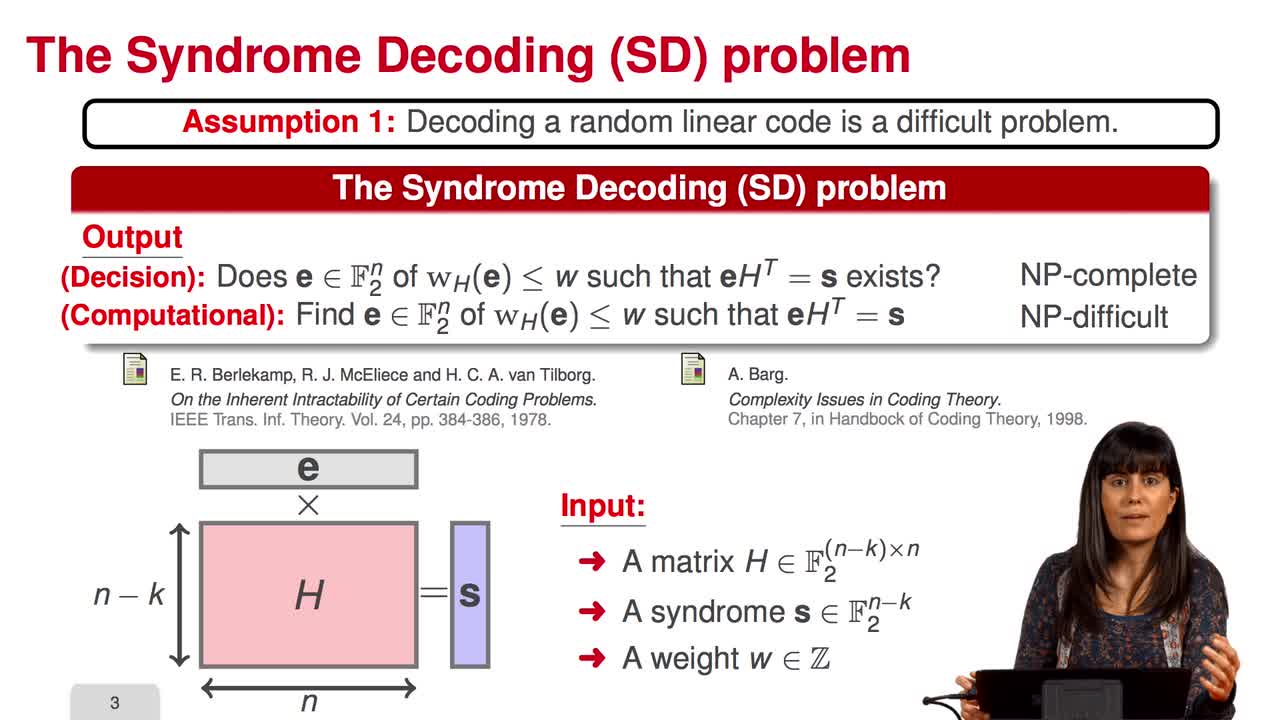
2.3. McEliece Assumptions
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will talk about McEliece assumptions. The security of the McEliece scheme is based on two assumptions as we have already seen: the hardness of decoding a random linear code and
-
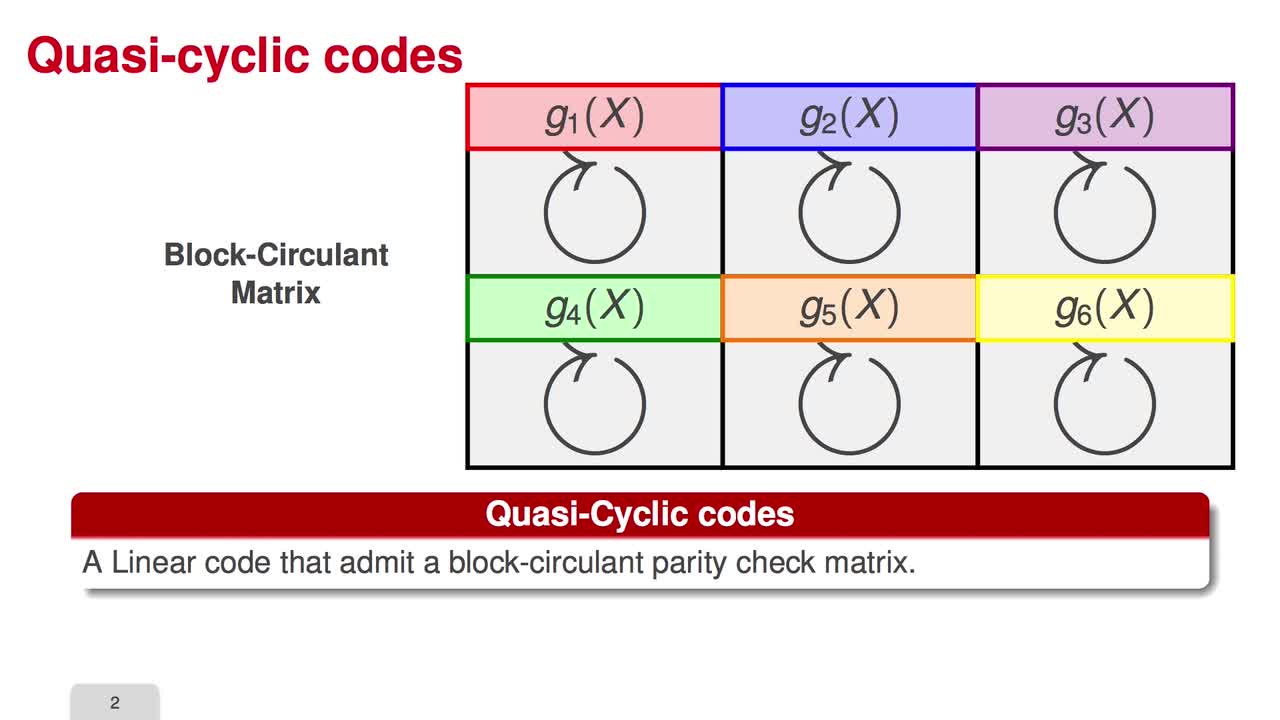
2.6. Reducing the Key Size
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn the next three sessions, I will explain how to reduce the key size of code-based cryptosystem. Circulant matrices are the central point in many attempts to reduce the key size of code-based
-
2.9. Implementation
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuThis is the last session of the second week. The cryptography community has different options for using public key cryptosystems, among others, they have RSA or DSA. But … McEliece has the same
-
2.4. Notions of Security
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will study the notion of security of public-key scheme. A public-key scheme is one-way if the probability of success of any adversary running in polynomial time is negligible.
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
4.4. Attack against subcodes of GRS codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will talk about using subcodes of a Generalized Reed–Solomon code for the McEliece Cryptosystem. Recall that to avoid the attack of Sidelnikov and Shestakov, Berger and
-
5.3. Attacks against the CFS Scheme
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will have a look at the attacks against the CFS signature scheme. As for public-key encryption, there are two kinds of attacks against signature schemes. First kind of attack is
-
4.7. Attack against Reed-Muller codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will introduce an attack against binary Reed-Muller codes. Reed-Muller codes were introduced by Muller in 1954 and, later, Reed provided the first efficient decoding algorithm
-
5.6. An Efficient Provably Secure One-Way Function
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we are going to see how to build an efficient provably secure one-way function from coding theory. As you know, a one-way function is a function which is simple to evaluate and
-
5.1. Code-Based Digital Signatures
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuWelcome to the last week of this MOOC on code-based cryptography. This week, we will be discussing other cryptographic constructions relying on coding theory. We have seen how to do public key
-
4.5. Error-Correcting Pairs
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuWe present in this session a general decoding method for linear codes. And we will see it in an example. Let C be a generalized Reed-Solomon code of dimension k associated to the pair (c, d). Then,
-
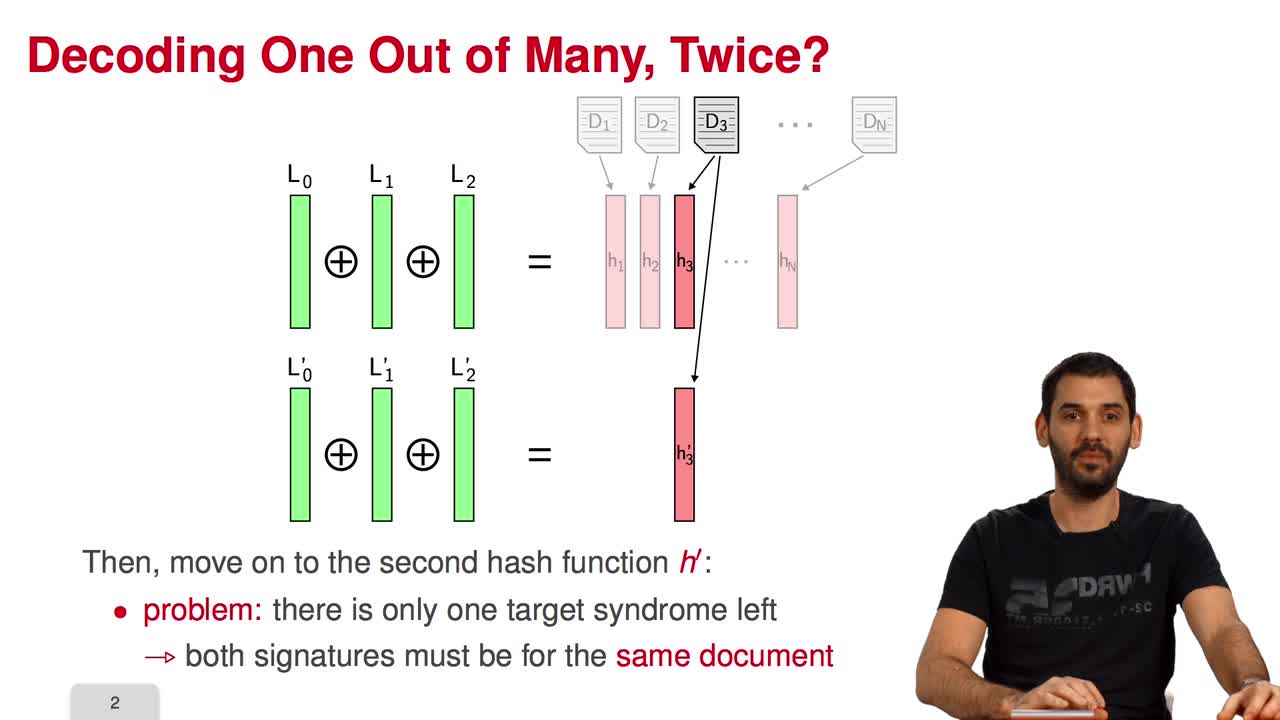
5.4. Parallel-CFS
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, I will present a variant of the CFS signature scheme called parallel-CFS. We start from a simple question: what happens if you try to use two different hash functions and compute
-
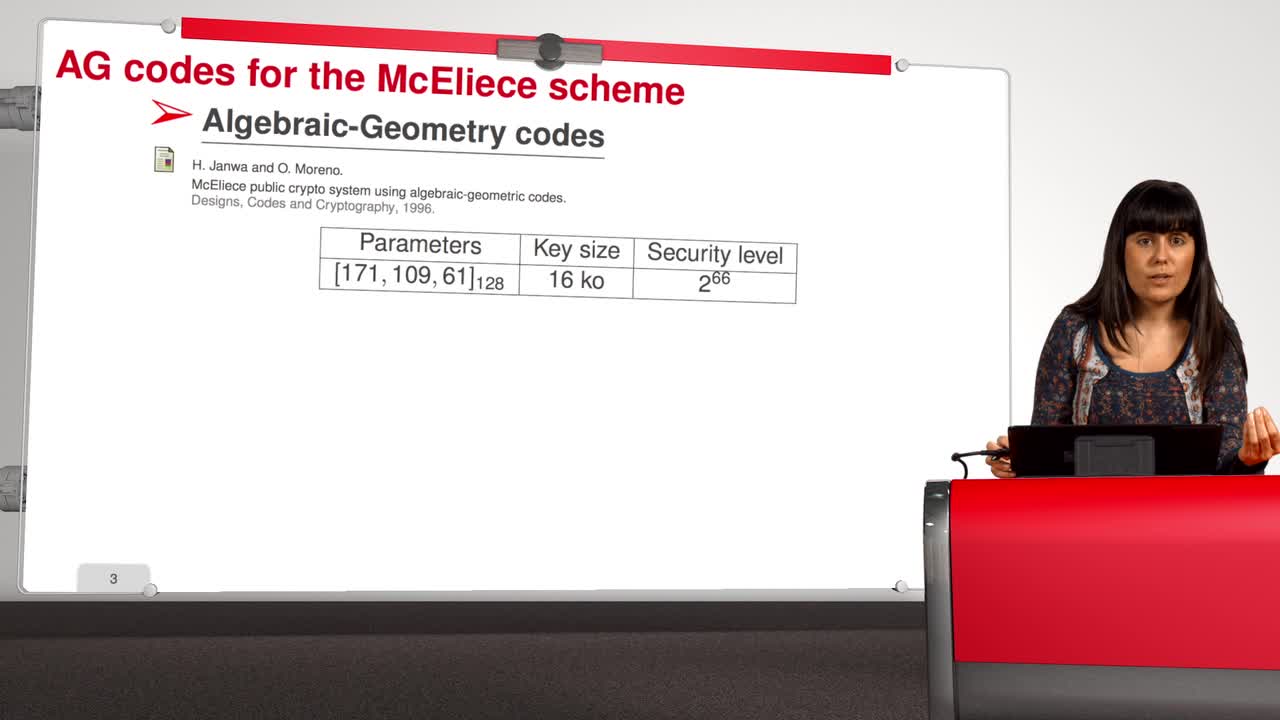
4.8. Attack against Algebraic Geometry codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we will present an attack against Algebraic Geometry codes (AG codes). Algebraic Geometry codes is determined by a triple. First of all, an algebraic curve of genus g, then a n
-
5.7. The Fast Syndrome-Based (FSB) Hash Function
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn the last session of this week, we will have a look at the FSB Hash Function which is built using the one-way function we saw in the previous session. What are the requirements for a
-
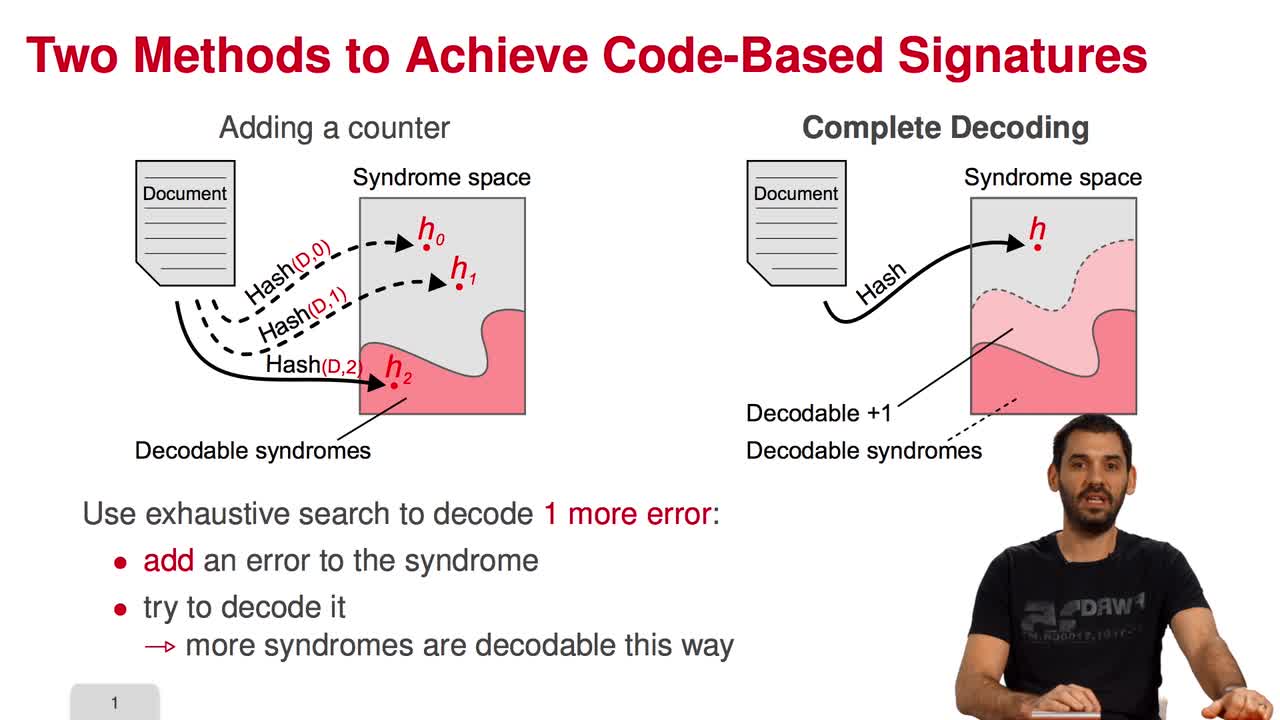
5.2. The Courtois-Finiasz-Sendrier (CFS) Construction
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, I am going to present the Courtois-Finiasz-Sendrier Construction of a code-based digital signature. In the previous session, we have seen that it is impossible to hash a document
-
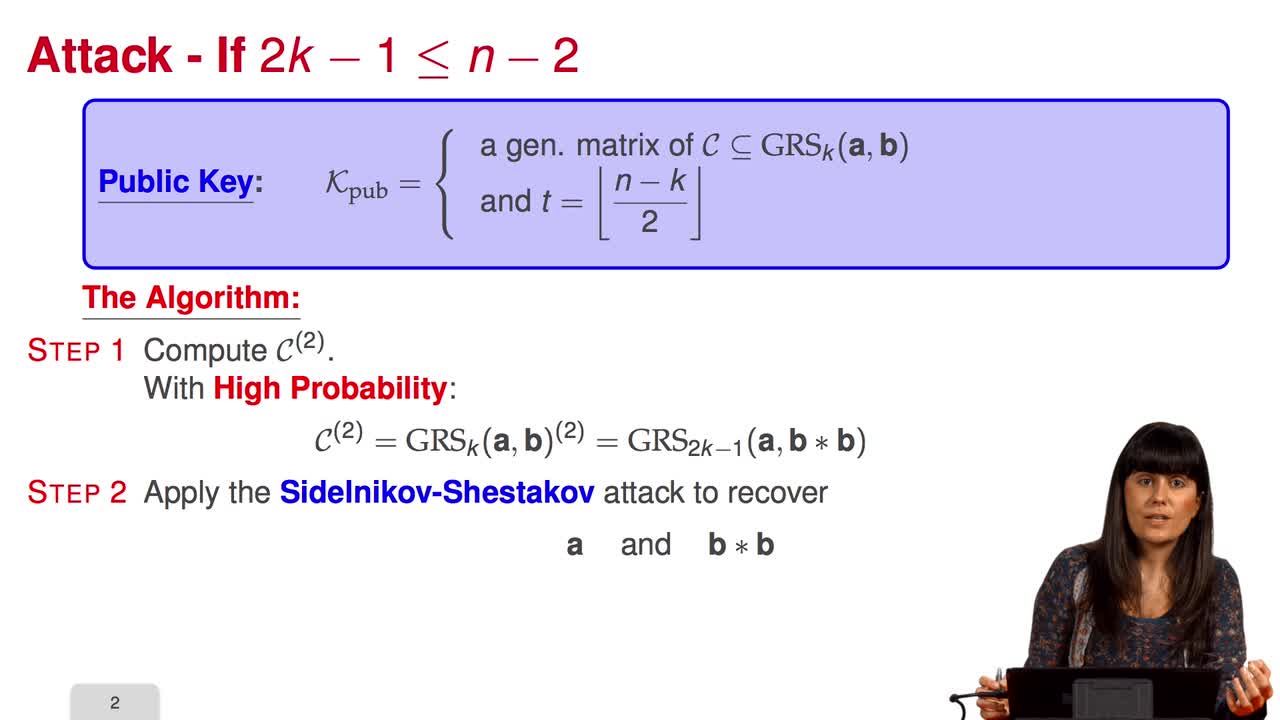
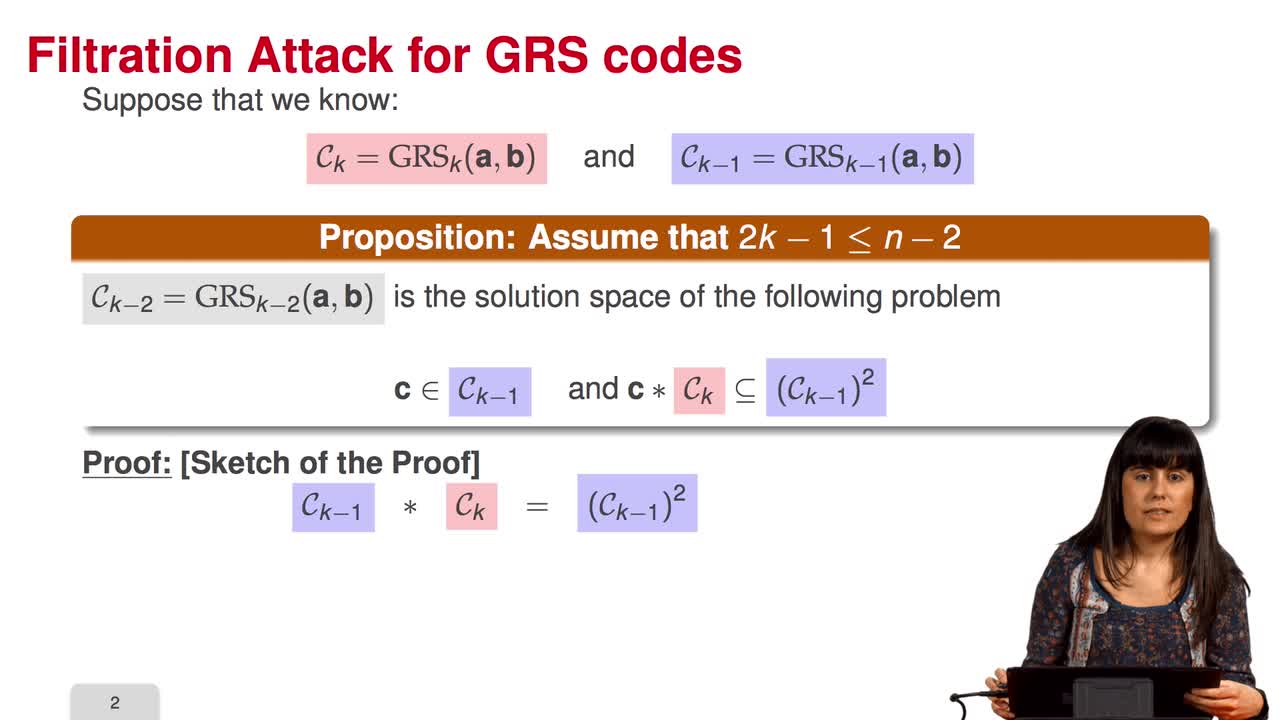
4.6. Attack against GRS codes
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session we will discuss the proposal of using generalized Reed-Solomon codes for the McEliece cryptosystem. As we have already said, generalized Reed-Solomon codes were proposed in 1986 by
-
5.5. Stern’s Zero-Knowledge Identification Scheme
Marquez-CorbellaIreneSendrierNicolasFiniaszMatthieuIn this session, we are going to have a look at Stern’s Zero-Knowledge Identification Scheme. So, what is a Zero-Knowledge Identification Scheme? An identification scheme allows a prover to prove
Sur le même thème
-
Tuan Ta Pesao : écritures de sable et de ficelle à l'Ile d'Ambrym
VandendriesscheEricCe film se déroule au Nord de l’île d’Ambrym, dans l’archipel de Vanuatu, en Mélanésie...
-
Quel est le prix à payer pour la sécurité de nos données ?
MinaudBriceÀ l'ère du tout connecté, la question de la sécurité de nos données personnelles est devenue primordiale. Comment faire pour garder le contrôle de nos données ? Comment déjouer les pièges de plus en
-
Des systèmes de numération pour le calcul modulaire
BajardJean-ClaudeLe calcul modulaire est utilisé dans de nombreuses applications des mathématiques...
-
Inauguration de l'exposition - Vanessa Vitse : Nombres de Sophie Germain et codes secrets
VitseVanessaExposé de Vanessa Vitse (Institut Fourier) : Nombres de Sophie Germain et codes secrets
-
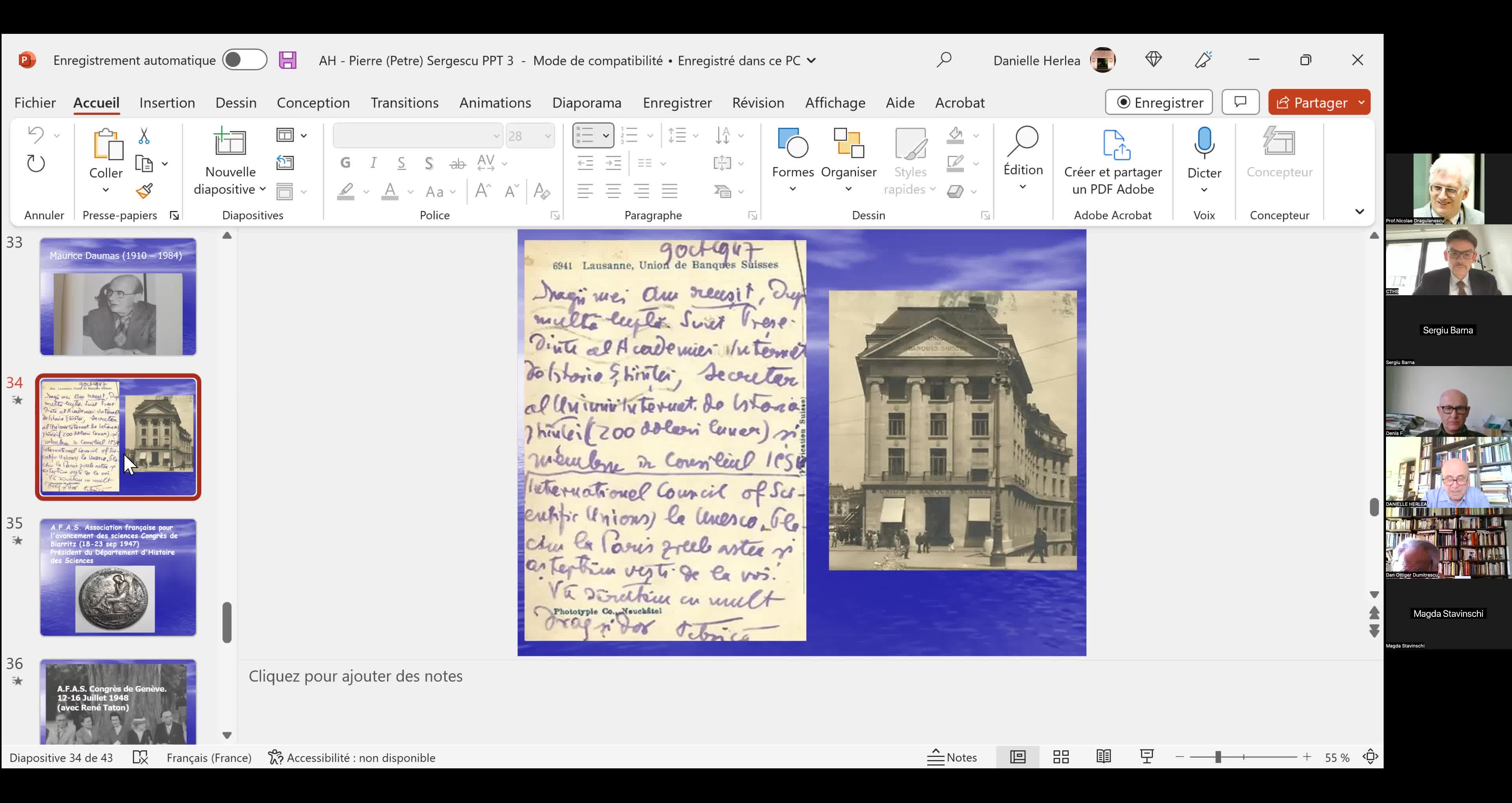
"Le mathématicien Petre (Pierre) Sergescu, historien des sciences, personnalité du XXe siècle"
HerléaAlexandreAlexandre HERLEA est membre de la section « Sciences, histoire des sciences et des techniques et archéologie industrielle » du CTHS. Professeur émérite des universités, membre effectif de l'Académie
-
Retour d'expérience sur l'utilisation croisée de plusieurs archives de fouilles
TufféryChristopheDans le cadre d'une thèse de doctorat engagée depuis 2019, une étude historiographique et épistémologique des effets des dispositifs numériques sur l'archéologie et sur les archéologues au cours des
-
Information Structures for Privacy and Fairness
PalamidessiCatusciaInformation Structures for Privacy and Fairness
-
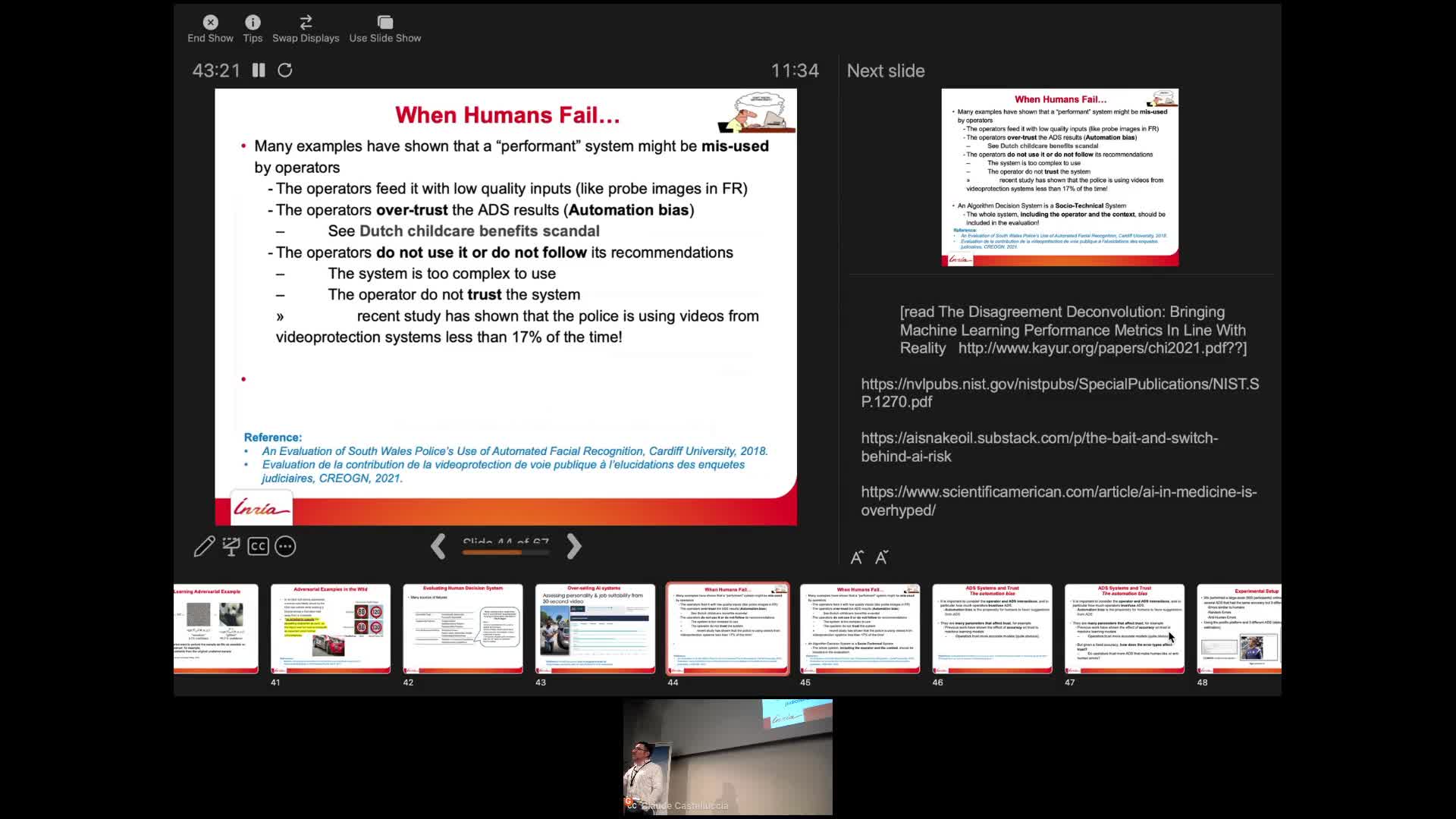
AI and Human Decision-Making: An Interdisciplinary Perspective
CastellucciaClaudeThis seminar will talk about some of the privacy risks of these systems and will describe some recent attacks. It will also discuss why they sometimes fail to deliver. Finally, we will also show that
-
Webinaire sur la rédaction des PGD
LouvetViolaineRédaction des Plans de Gestion de Données (PGD) sous l’angle des besoins de la communauté mathématique.
-
Alexandre Booms : « Usage de matériel pédagogique adapté en géométrie : une transposition à interro…
« Usage de matériel pédagogique adapté en géométrie : une transposition à interroger ». Alexandre Booms, doctorant (Université de Reims Champagne-Ardenne - Cérep UR 4692)
-
Présentation de la rencontre. A l’heure du numérique « Quelles mesures pour la mesure ? ». Le relev…
BadieAlainTardyDominiqueMalmaryJean-JacquesZugmeyerStéphanieRencontre-Atelier de l'ANR Ornementation Architecturale des Gaules. À l’heure du numérique, « Quelles mesures pour la mesure ? ». Le relevé des blocs d’architecture décorés et l’apport des outils
-
Photogrammétrie : Performances et limitations
EgelsYvesRencontre-Atelier de l'ANR Ornementation Architecturale des Gaules. À l’heure du numérique, « Quelles mesures pour la mesure ? ». Le relevé des blocs d’architecture décorés et l’apport des outils