Notice
Bio-informatique et applications
- document 1 document 2 document 3
- niveau 1 niveau 2 niveau 3
Descriptif
La séquence de caractères est un des objets que lesinformaticiens connaissent bien et pour lequel ils ont développé de trèsnombreux algorithmes. C’est donc très naturellement que l’informatique et lessciences du vivant se sont rencontrées autour de la problématique de l’analysedes séquences génomiques.
Intervention / Responsable scientifique
Thème
Avec les mêmes intervenants et intervenantes
-
1.1. The cell, atom of the living world
RechenmannFrançoisWelcome to this introduction to bioinformatics. We will speak of genomes and algorithms. More specifically, we will see how genetic information can be analysed by algorithms. In these five weeks to
-
1.9. Predicting the origin of DNA replication?
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen a nice algorithm to draw, let's say, a DNA sequence. We will see that first, we have to correct a little bit this algorithm. And then we will see how such as imple algorithm can provide
-
2.8. DNA sequencing
RechenmannFrançoisDuring the last session, I explained several times how it was important to increase the efficiency of sequences processing algorithm because sequences arevery long and there are large volumes of
-
3.5. Making the predictions more reliable
RechenmannFrançoisWe have got a bacterial gene predictor but the way this predictor works is rather crude and if we want to have more reliable results, we have to inject into this algorithmmore biological knowledge. We
-
4.6. A path is optimal if all its sub-paths are optimal
RechenmannFrançoisA sequence alignment between two sequences is a path in a grid. So that, an optimal sequence alignmentis an optimal path in the same grid. We'll see now that a property of this optimal path provides
-
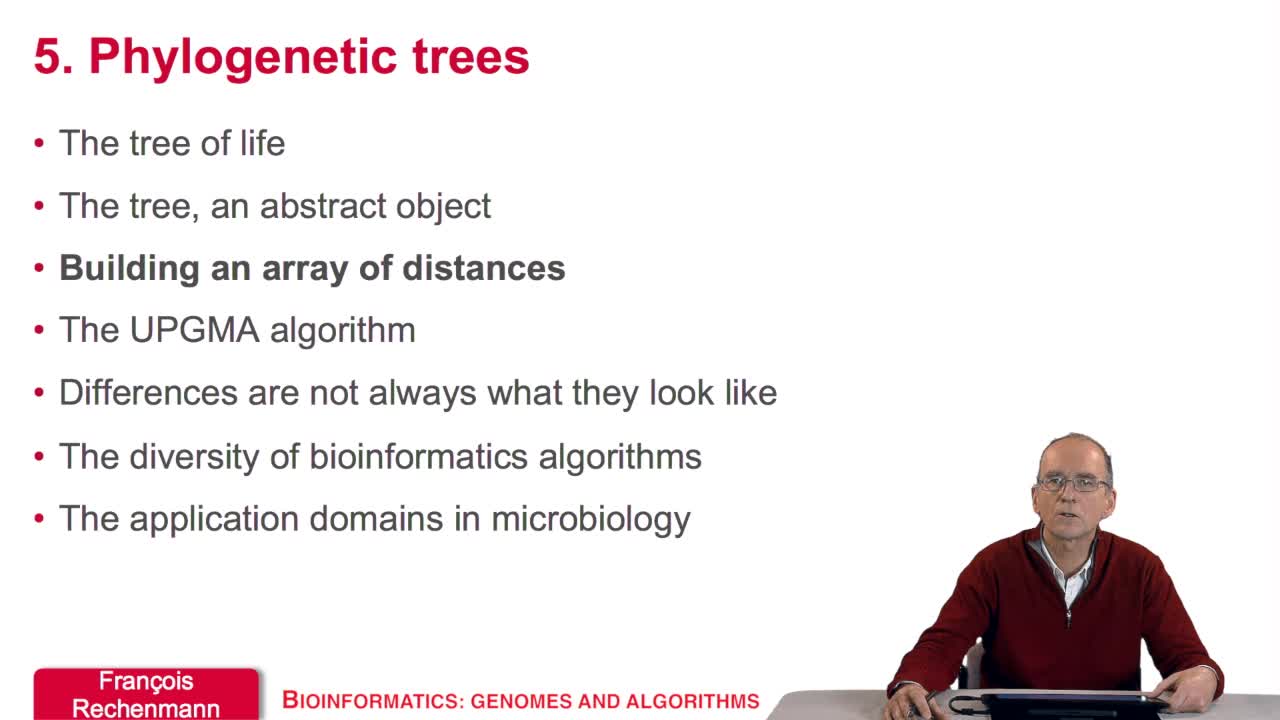
5.1. The tree of life
RechenmannFrançoisWelcome to this fifth and last week of our course on genomes and algorithms that is the computer analysis of genetic information. During this week, we will firstsee what phylogenetic trees are and how
-
1.4. What is an algorithm?
RechenmannFrançoisWe have seen that a genomic textcan be indeed a very long sequence of characters. And to interpret this sequence of characters, we will need to use computers. Using computers means writing program.
-
2.2. Genes: from Mendel to molecular biology
RechenmannFrançoisThe notion of gene emerged withthe works of Gregor Mendel. Mendel studied the inheritance on some traits like the shape of pea plant seeds,through generations. He stated the famous laws of inheritance
-
2.10. How to find genes?
RechenmannFrançoisGetting the sequence of the genome is only the beginning, as I explained, once you have the sequence what you want to do is to locate the gene, to predict the function of the gene and maybe study the
-
3.8. Probabilistic methods
RechenmannFrançoisUp to now, to predict our gene,we only rely on the process of searching certain strings or patterns. In order to further improve our gene predictor, the idea is to use, to rely onprobabilistic methods
-
4.3. Measuring sequence similarity
RechenmannFrançoisSo we understand why gene orprotein sequences may be similar. It's because they evolve togetherwith the species and they evolve in time, there aremodifications in the sequence and that the sequence
-
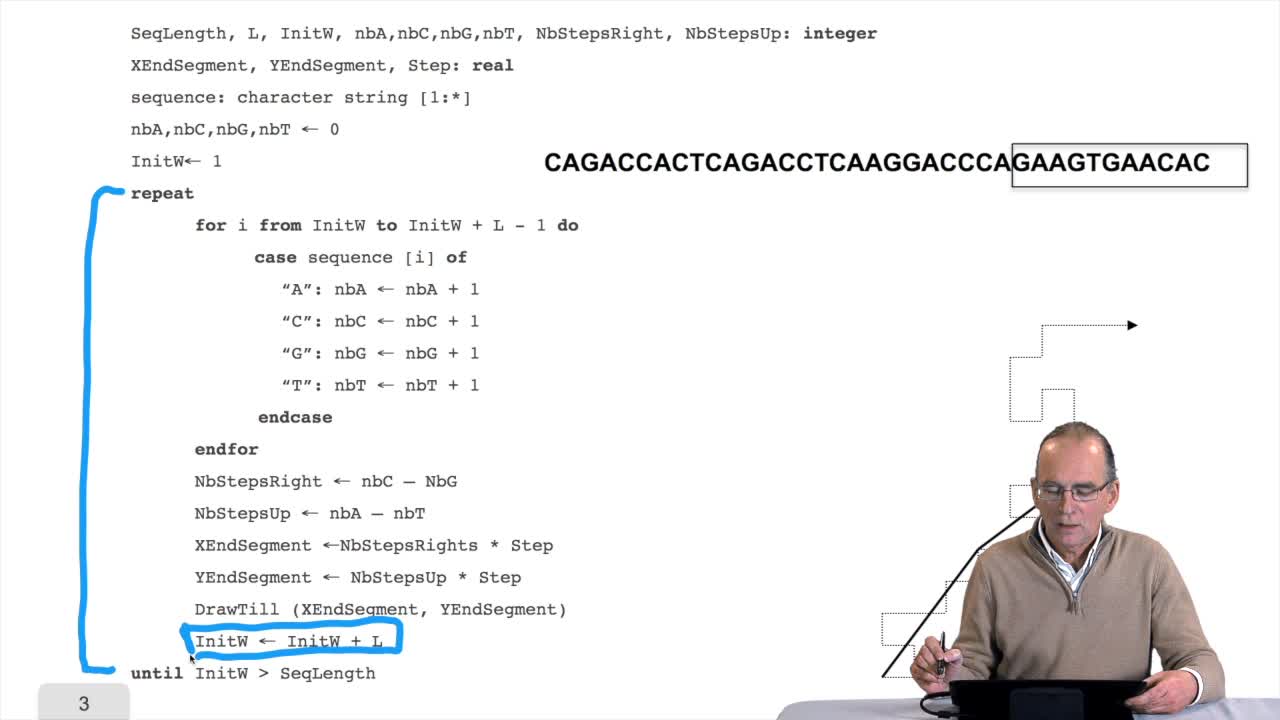
5.3. Building an array of distances
RechenmannFrançoisSo using the sequences of homologous gene between several species, our aim is to reconstruct phylogenetic tree of the corresponding species. For this, we have to comparesequences and compute distances
Sur le même thème
-
Stockage de données numériques sur ADN synthétique : Introduction au domaine
AntoniniMarcDuprazElsaLavenierDominiquePrésentation globale des différentes étapes du stockage de données sur des molécules d'ADN synthétique
-
Stockage de données numériques sur ADN synthétique : Production des données: synthèse, séquençage
LavenierDominiqueBarbryPascalDescription des opérations d'écriture et de lecture des molécules d'ADN : synthèse et séquençage.
-
Stockage de données numériques sur ADN synthétique : Reconstruction des données
LavenierDominiqueTraitement des données après séquençage
-
Stockage de données numériques sur ADN synthétique : Codage Canal
DuprazElsaTechniques de codage pour le stockage de données sur ADN
-
Stockage de données numériques sur ADN synthétique : Codage Source
AntoniniMarcCodage source pour le stockage de données sur ADN synthétique
-
Stockage de données numériques sur ADN synthétique : Théorie de l'information
Kas HannaSergeQuelle quantité d'information peut-on stocker et récupérer de manière fiable dans l'ADN ?
-
Le projet dnarXiv : Stockage de données sur des molécules d'ADN
LavenierDominiqueDuprazElsaLeblancJulienCoatrieuxGouenouDominique Lavenier, Elsa Dupraz, Julien Leblanc et Gouenou Coatrieux nous présentent le projet dnarXiv, un projet porté par le LabEx CominLabs qui explore le stockage de données sur des molécules d
-
21 Molecular Algorithms Using Reprogrammable DNA Self-Assembly
WoodsDamienThe history of computing tells us that computers can be made of almost anything: silicon, gears and levers, neurons, flowing water, interacting particles or even light. Although lithographically
-
Des métiers de la bio-informatique
Courtes vidéos pour sensibiliser le jeune public aux débouchés/métiers de la filière numérique et pour promouvoir les sciences du numérique, plus globalement les carrières scientifiques.L'objectif est
-
Reasoning over large-scale biological systems with heterogeneous and incomplete data
SiegelAnneData produced by the domain of life sciences in the next decade are expected to be highly challenging. In addition to scalability issues which are shared with other applications domains, data produced
-
Biological Networks Entropies: examples in neural, genetic and social networks
DemongeotJacquesThe networks used in biological applications at different scales (molecular, cellular and populational) are of different types, genetic, neuronal, and social, but they share the same dynamical
-
Génomique et informatique
RislerJean-LoupLa presse généraliste, et bien entendu la presse spécialisée, se font régulièrement l'écho du séquençage complet d'un nouveau génome. Il est cependant impossible pour le grand public de se rendre